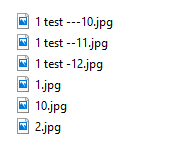
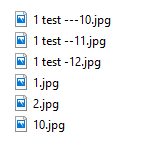
I am trying to use code suggested by Sander Pham on another question. I need my java ArrayList of string names to be sorted like Windows Explorer does. His code worked for everything but for one issue. I would have liked to comment onto that question, but I need more reputation points to comment. Anyways... He suggested to use a custom comparator implemented class and use that to compare the string names. Here is the code of that class:
class IntuitiveStringComparator implements Comparator<String>
{
private String str1, str2;
private int pos1, pos2, len1, len2;
public int compare(String s1, String s2)
{
str1 = s1;
str2 = s2;
len1 = str1.length();
len2 = str2.length();
pos1 = pos2 = 0;
int result = 0;
while (result == 0 && pos1 < len1 && pos2 < len2)
{
char ch1 = str1.charAt(pos1);
char ch2 = str2.charAt(pos2);
if (Character.isDigit(ch1))
{
result = Character.isDigit(ch2) ? compareNumbers() : -1;
}
else if (Character.isLetter(ch1))
{
result = Character.isLetter(ch2) ? compareOther(true) : 1;
}
else
{
result = Character.isDigit(ch2) ? 1
: Character.isLetter(ch2) ? -1
: compareOther(false);
}
pos1++;
pos2++;
}
return result == 0 ? len1 - len2 : result;
}
private int compareNumbers()
{
// Find out where the digit sequence ends, save its length for
// later use, then skip past any leading zeroes.
int end1 = pos1 + 1;
while (end1 < len1 && Character.isDigit(str1.charAt(end1)))
{
end1++;
}
int fullLen1 = end1 - pos1;
while (pos1 < end1 && str1.charAt(pos1) == '0')
{
pos1++;
}
// Do the same for the second digit sequence.
int end2 = pos2 + 1;
while (end2 < len2 && Character.isDigit(str2.charAt(end2)))
{
end2++;
}
int fullLen2 = end2 - pos2;
while (pos2 < end2 && str2.charAt(pos2) == '0')
{
pos2++;
}
// If the remaining subsequences have different lengths,
// they can't be numerically equal.
int delta = (end1 - pos1) - (end2 - pos2);
if (delta != 0)
{
return delta;
}
// We're looking at two equal-length digit runs; a sequential
// character comparison will yield correct results.
while (pos1 < end1 && pos2 < end2)
{
delta = str1.charAt(pos1++) - str2.charAt(pos2++);
if (delta != 0)
{
return delta;
}
}
pos1--;
pos2--;
// They're numerically equal, but they may have different
// numbers of leading zeroes. A final length check will tell.
return fullLen2 - fullLen1;
}
private int compareOther(boolean isLetters)
{
char ch1 = str1.charAt(pos1);
char ch2 = str2.charAt(pos2);
if (ch1 == ch2)
{
return 0;
}
if (isLetters)
{
ch1 = Character.toUpperCase(ch1);
ch2 = Character.toUpperCase(ch2);
if (ch1 != ch2)
{
ch1 = Character.toLowerCase(ch1);
ch2 = Character.toLowerCase(ch2);
}
}
return ch1 - ch2;
}
}
In using this, it works great except for if the string name does not have a number after it. If it does not have a number, it is put at the end of the list, which is wrong. If it doesn't have a number, it should be at the beginning.
i.e.
filename.jpg
filename2.jpg
filename03.jpg
filename3.jpg
Currently it sorts that...
filename2.jpg
filename03.jpg
filename3.jpg
filename.jpg
What do I need to change in the code to correct this behavior?
Thanks