I am going through their sample app tutorial here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/GettingStarted.html and even though I am able to get a working app from Step 1, I consistently get warning messages about being unable to assume the Service Role I set up for this app and being unable to find permissions to check for managed updates. I already set up a service role with all the permissions listed here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/iam-servicerole.html, and my understanding is that I should be able to get managed updates with this app.
I have attached the error I am seeing on my environment page.
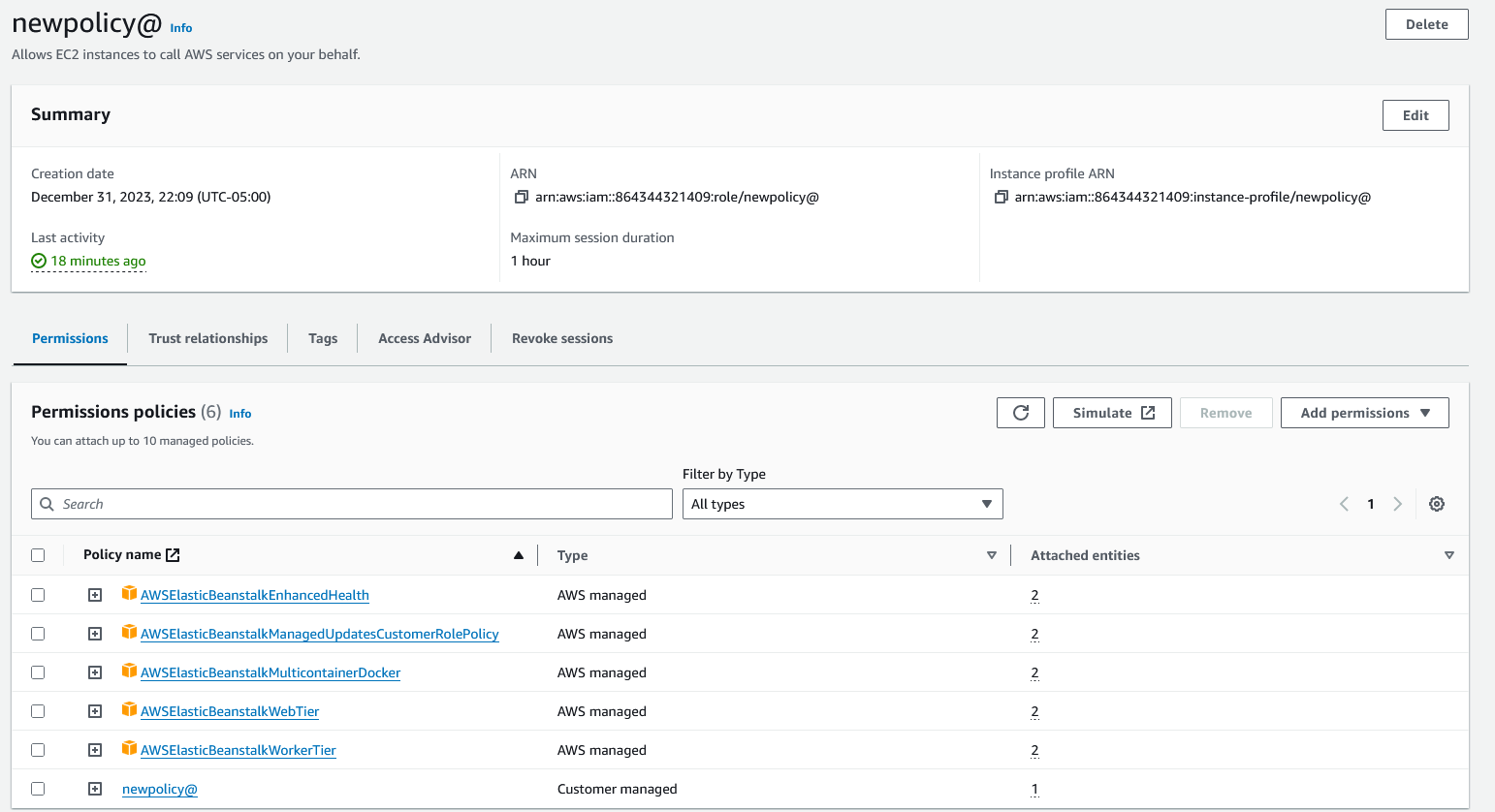
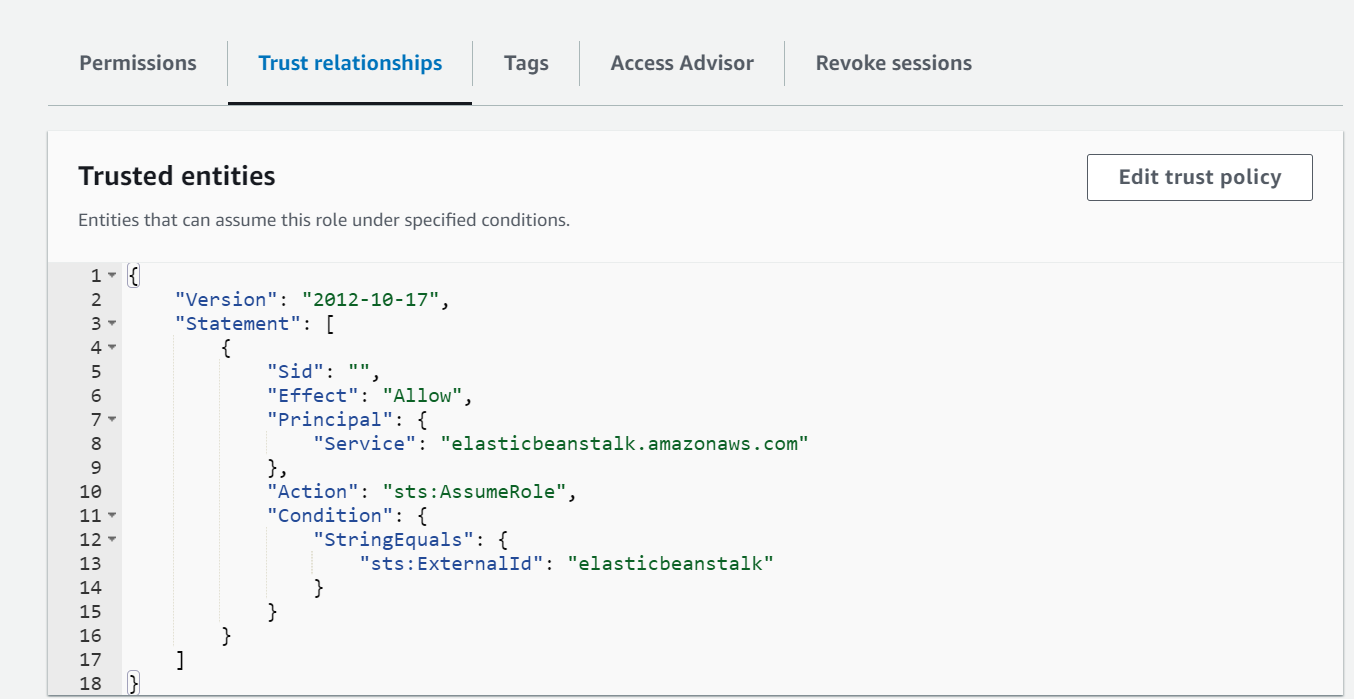
Also attaching the screenshot of what I see on my role I named newpolicy@.
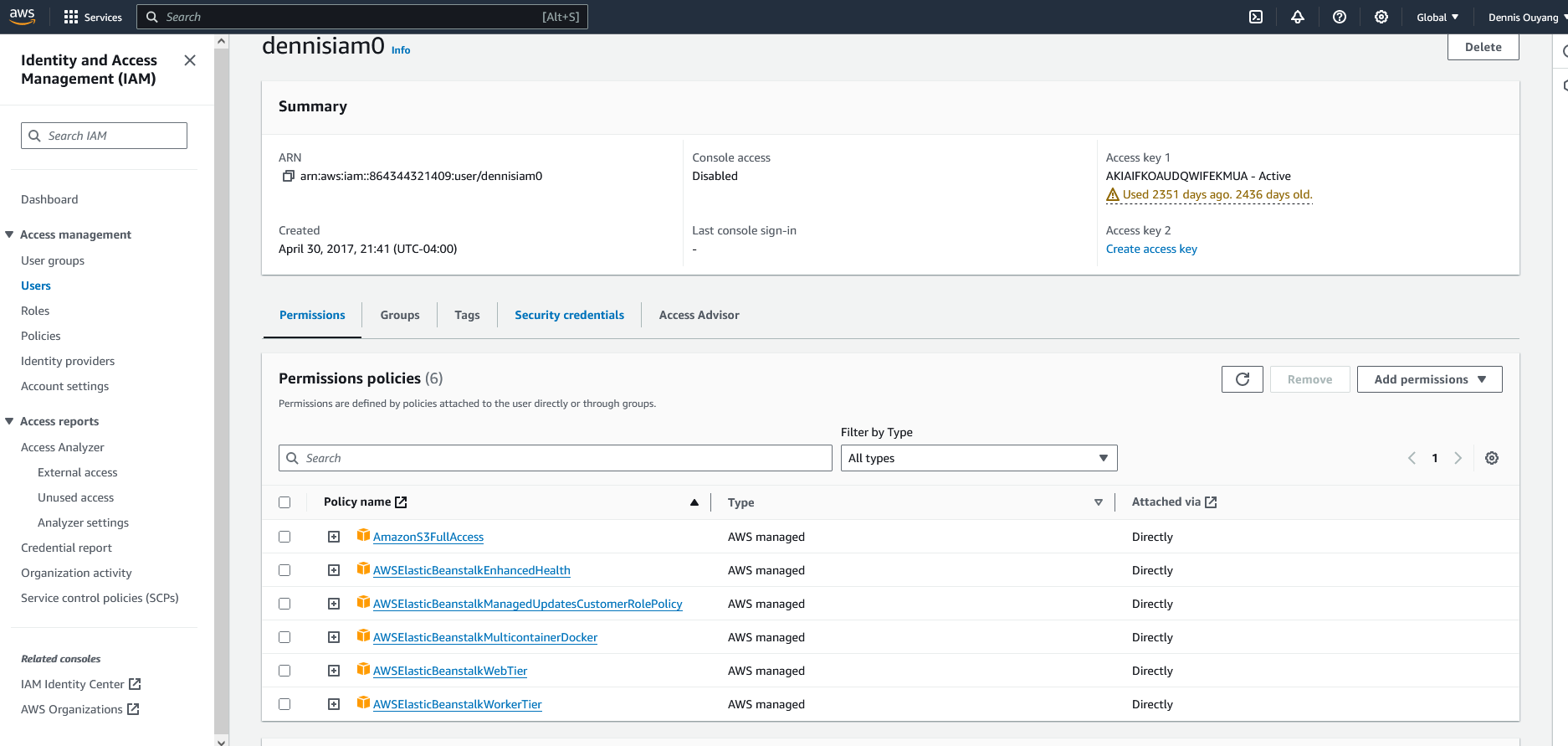
I even tried attaching the necessary policies directly to my user, which is the root user of the account.
I have deleted the app, environment, and role, and rebuilt them using the Amazon tutorials from scratch, multiple times, all with the same problem.
Tried creating a new app, with a new environment, and created a new role with added permissions including AWSElasticBeanstalkEnhancedHealth and AWSElasticBeanstalkManagedUpdatesCustomerRolePolicy along with the standard AWSElasticBeanstalkWebTier, AWSElasticBeanstalkWorkerTier, AWSElasticBeanstalkMulticontainerDocker recommended by the tutorial.
I expected to see a new app with no issues, but instead, I am getting warning events:
Unable to assume role "arn:aws:iam::xxxxxx:role/newpolicy@". Verify that the role exists and is configured correctly.
Service role "arn:aws:iam::xxxxxx:role/newpolicy@" is missing permissions required to check for managed updates. Verify the role's policies.
I can still view the sample app when I click the provided url, however.
In response to Arpit Jain's question: here are my trust relationships for newpolicy@:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
In response to Arpit Jain's answer below, here is the profile info for my new environment: 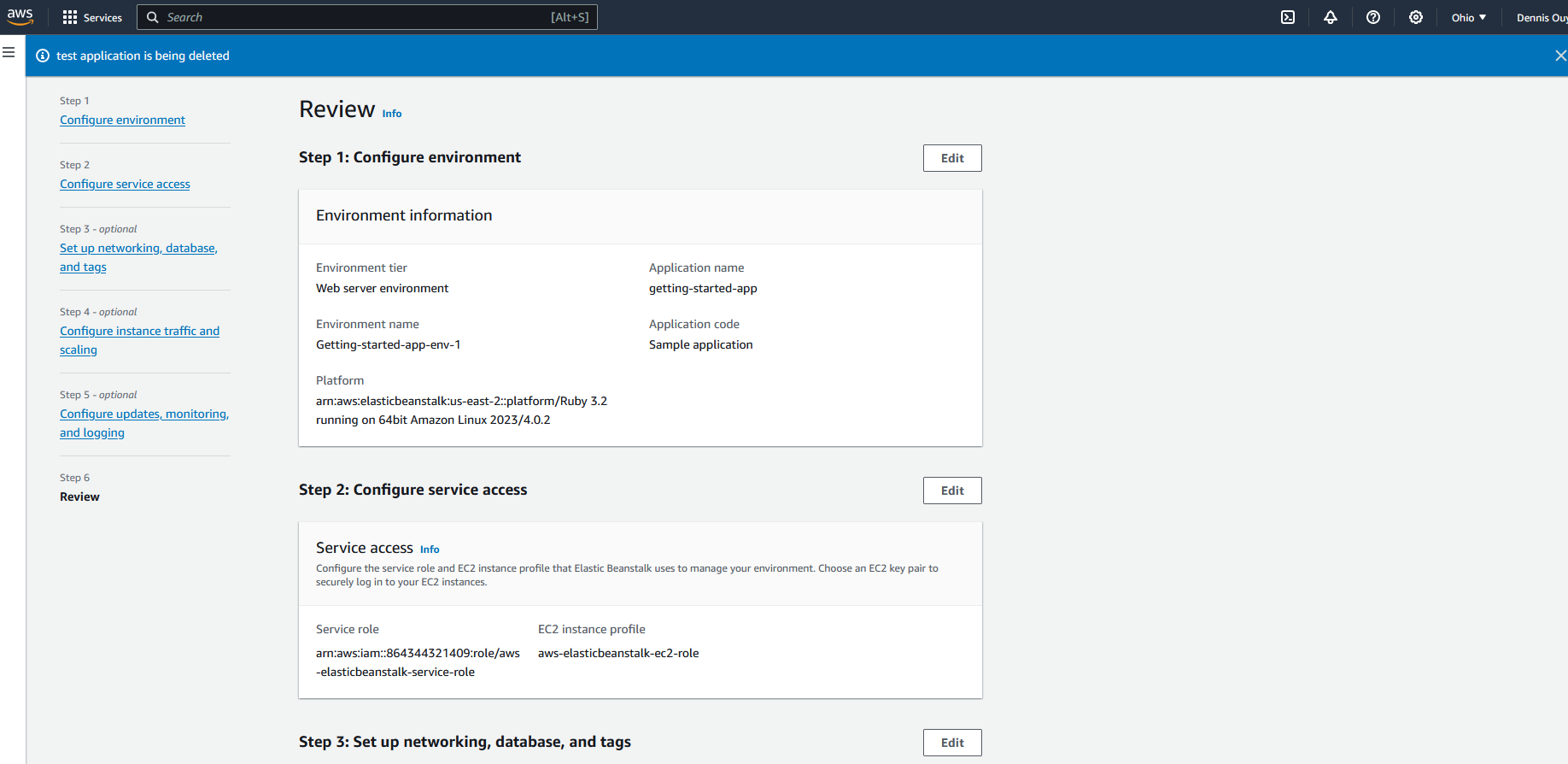


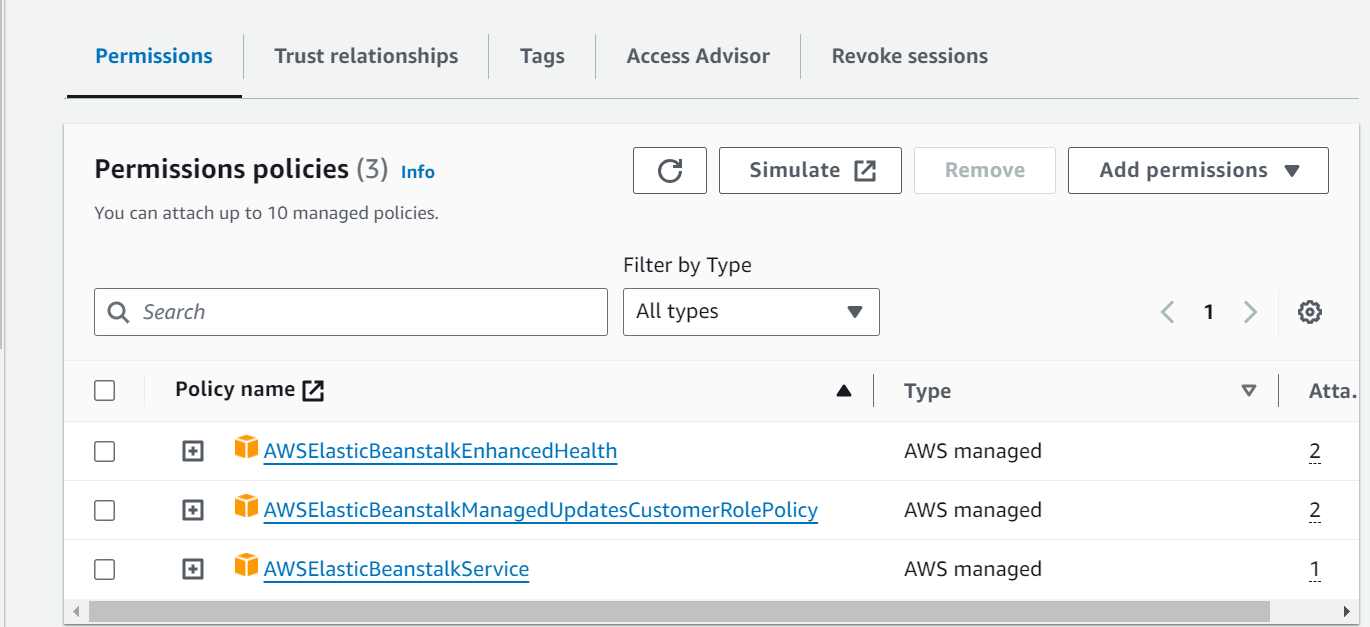
newpolicy@to allow the Elastic Beanstalk to assume the role? – Toleration