You're on the right track. You can change a pixel's property using Numpy splicing
img[x,y] = [B,G,R]
So for example, to change a pixel at (50,50) to red, you can do
img[50,50] = [0,0,255]
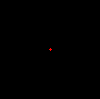
Here we change a single pixel to red (it's pretty tiny)
![enter image description here]()
import cv2
import numpy as np
width = 100
height = 100
# Make empty black image of size (100,100)
img = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
red = [0,0,255]
# Change pixel (50,50) to red
img[50,50] = red
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
An alternative method is to use cv2.circle() to draw your point inplace.
The function header is
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), radius, (B,G,R), thickness)
Using this, we obtain the same result
cv2.circle(img, (50,50), 1, red, -1)
![enter image description here]()





imgis 3 dimensional, so you are setting a list as a value (img[ 0.,-26.10911452,0. ]) in your 3-d array. Although I don't see why that would cause your error. Also probably unrelated, why are you using floats to index your array? – Arbe