I have an application that uses secure websockets that I am having trouble with.
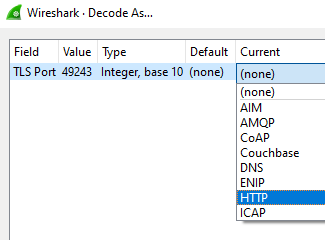
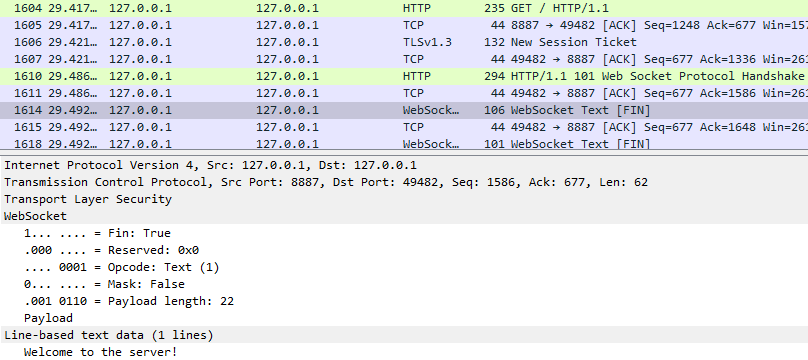
I would like to use wireshark to debug the problem, however I can not figure out the correct parameters to put into wireshark to monitor and display a secure web socket connection using HTTPS.
Does anyone know of a wireshark filter that would accomplish what I need and if I need to do anything else to monitor secure websockets using wireshark?