I'm going through this tutorial
Whenever my mouse hovers over the cube created with this code (my version below), the Atmosphere and Stars disappear.
This is how it looks normally:
This is how it looks when I hover over the cube (Look at the atmosphere):
I'm not sure what is going on here.
/*
* Copyright (C) 2012 United States Government as represented by the Administrator of the
* National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
* All Rights Reserved.
*/
package gov.nasa.worldwindx.examples.tutorial;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.Configuration;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.avlist.AVKey;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.geom.*;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.layers.RenderableLayer;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.pick.PickSupport;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.render.*;
import gov.nasa.worldwind.util.OGLUtil;
import gov.nasa.worldwindx.examples.ApplicationTemplate;
import javax.media.opengl.*;
import java.awt.*;
/**
* Example of a custom {@link Renderable} that draws a cube at a geographic position. This class shows the simplest
* possible example of a custom Renderable, while still following World Wind best practices. See
* http://goworldwind.org/developers-guide/how-to-build-a-custom-renderable/ for a complete description of this
* example.
*
* @author pabercrombie
* @version $Id: Cube.java 691 2012-07-12 19:17:17Z pabercrombie $
*/
public class Cube extends ApplicationTemplate implements Renderable
{
/** Geographic position of the cube. */
protected Position position;
/** Length of each face, in meters. */
protected double size;
/** Support object to help with pick resolution. */
protected PickSupport pickSupport = new PickSupport();
// Determined each frame
protected long frameTimestamp = -1L;
protected OrderedCube currentFramesOrderedCube;
/**
* This class holds the Cube's Cartesian coordinates. An instance of it is added to the scene controller's ordered
* renderable queue during picking and rendering.
*/
protected class OrderedCube implements OrderedRenderable
{
/** Cartesian position of the cube, computed from
* {@link gov.nasa.worldwindx.examples.tutorial.Cube#position}. */
protected Vec4 placePoint;
/** Distance from the eye point to the cube. */
protected double eyeDistance;
/**
* The cube's Cartesian bounding extent.
*/
protected Extent extent;
public double getDistanceFromEye()
{
return this.eyeDistance;
}
public void pick(DrawContext dc, Point pickPoint)
{
// Use same code for rendering and picking.
this.render(dc);
}
public void render(DrawContext dc)
{
Cube.this.drawOrderedRenderable(dc, Cube.this.pickSupport);
}
}
public Cube(Position position, double sizeInMeters)
{
this.position = position;
this.size = sizeInMeters;
}
public void render(DrawContext dc)
{
// Render is called twice, once for picking and once for rendering. In both cases an OrderedCube is added to
// the ordered renderable queue.
OrderedCube orderedCube = this.makeOrderedRenderable(dc);
if (orderedCube.extent != null)
{
if (!this.intersectsFrustum(dc, orderedCube))
return;
// If the shape is less that a pixel in size, don't render it.
if (dc.isSmall(orderedCube.extent, 1))
return;
}
// Add the cube to the ordered renderable queue. The SceneController sorts the ordered renderables by eye
// distance, and then renders them back to front.
dc.addOrderedRenderable(orderedCube);
}
/**
* Determines whether the cube intersects the view frustum.
*
* @param dc the current draw context.
*
* @return true if this cube intersects the frustum, otherwise false.
*/
protected boolean intersectsFrustum(DrawContext dc, OrderedCube orderedCube)
{
if (dc.isPickingMode())
return dc.getPickFrustums().intersectsAny(orderedCube.extent);
return dc.getView().getFrustumInModelCoordinates().intersects(orderedCube.extent);
}
/**
* Compute per-frame attributes, and add the ordered renderable to the ordered renderable list.
*
* @param dc Current draw context.
*/
protected OrderedCube makeOrderedRenderable(DrawContext dc)
{
// This method is called twice each frame: once during picking and once during rendering. We only need to
// compute the placePoint, eye distance and extent once per frame, so check the frame timestamp to see if
// this is a new frame. However, we can't use this optimization for 2D continuous globes because the
// Cartesian coordinates of the cube are different for each 2D globe drawn during the current frame.
if (dc.getFrameTimeStamp() != this.frameTimestamp || dc.isContinuous2DGlobe())
{
OrderedCube orderedCube = new OrderedCube();
// Convert the cube's geographic position to a position in Cartesian coordinates. If drawing to a 2D
// globe ignore the shape's altitude.
if (dc.is2DGlobe())
{
orderedCube.placePoint = dc.getGlobe().computePointFromPosition(this.position.getLatitude(),
this.position.getLongitude(), 0);
}
else
{
orderedCube.placePoint = dc.getGlobe().computePointFromPosition(this.position);
}
// Compute the distance from the eye to the cube's position.
orderedCube.eyeDistance = dc.getView().getEyePoint().distanceTo3(orderedCube.placePoint);
// Compute a sphere that encloses the cube. We'll use this sphere for intersection calculations to determine
// if the cube is actually visible.
orderedCube.extent = new Sphere(orderedCube.placePoint, Math.sqrt(3.0) * this.size / 2.0);
// Keep track of the timestamp we used to compute the ordered renderable.
this.frameTimestamp = dc.getFrameTimeStamp();
this.currentFramesOrderedCube = orderedCube;
return orderedCube;
}
else
{
return this.currentFramesOrderedCube;
}
}
/**
* Set up drawing state, and draw the cube. This method is called when the cube is rendered in ordered rendering
* mode.
*
* @param dc Current draw context.
*/
protected void drawOrderedRenderable(DrawContext dc, PickSupport pickCandidates)
{
this.beginDrawing(dc);
try
{
GL2 gl = dc.getGL().getGL2(); // GL initialization checks for GL2 compatibility.
if (dc.isPickingMode())
{
Color pickColor = dc.getUniquePickColor();
pickCandidates.addPickableObject(pickColor.getRGB(), this, this.position);
gl.glColor3ub((byte) pickColor.getRed(), (byte) pickColor.getGreen(), (byte) pickColor.getBlue());
}
// Render a unit cube and apply a scaling factor to scale the cube to the appropriate size.
gl.glScaled(this.size, this.size, this.size);
this.drawUnitCube(dc);
}
finally
{
this.endDrawing(dc);
}
}
/**
* Setup drawing state in preparation for drawing the cube. State changed by this method must be restored in
* endDrawing.
*
* @param dc Active draw context.
*/
protected void beginDrawing(DrawContext dc)
{
GL2 gl = dc.getGL().getGL2(); // GL initialization checks for GL2 compatibility.
int attrMask = GL2.GL_CURRENT_BIT | GL2.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT;
gl.glPushAttrib(attrMask);
if (!dc.isPickingMode())
{
dc.beginStandardLighting();
gl.glEnable(GL.GL_BLEND);
OGLUtil.applyBlending(gl, false);
// Were applying a scale transform on the modelview matrix, so the normal vectors must be re-normalized
// before lighting is computed.
gl.glEnable(GL2.GL_NORMALIZE);
}
// Multiply the modelview matrix by a surface orientation matrix to set up a local coordinate system with the
// origin at the cube's center position, the Y axis pointing North, the X axis pointing East, and the Z axis
// normal to the globe.
gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_MODELVIEW);
Matrix matrix = dc.getGlobe().computeSurfaceOrientationAtPosition(this.position);
matrix = dc.getView().getModelviewMatrix().multiply(matrix);
double[] matrixArray = new double[16];
matrix.toArray(matrixArray, 0, false);
gl.glLoadMatrixd(matrixArray, 0);
}
/**
* Restore drawing state changed in beginDrawing to the default.
*
* @param dc Active draw context.
*/
protected void endDrawing(DrawContext dc)
{
GL2 gl = dc.getGL().getGL2(); // GL initialization checks for GL2 compatibility.
if (!dc.isPickingMode())
dc.endStandardLighting();
gl.glPopAttrib();
}
/**
* Draw a unit cube, using the active modelview matrix to orient the shape.
*
* @param dc Current draw context.
*/
protected void drawUnitCube(DrawContext dc)
{
// Vertices of a unit cube, centered on the origin.
float[][] v = {{-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f}, {-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f}, {0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f}, {0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f},
{-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f}, {0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f}, {0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f}, {-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f}};
// Array to group vertices into faces
int[][] faces = {{0, 1, 2, 3}, {2, 5, 6, 3}, {1, 4, 5, 2}, {0, 7, 4, 1}, {0, 7, 6, 3}, {4, 7, 6, 5}};
// Normal vectors for each face
float[][] n = {{0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1}, {-1, 0, 0}, {0, 0, -1}, {0, -1, 0}};
// Note: draw the cube in OpenGL immediate mode for simplicity. Real applications should use vertex arrays
// or vertex buffer objects to achieve better performance.
GL2 gl = dc.getGL().getGL2(); // GL initialization checks for GL2 compatibility.
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_QUADS);
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < faces.length; i++)
{
gl.glNormal3f(n[i][0], n[i][1], n[i][2]);
for (int j = 0; j < faces[0].length; j++)
{
gl.glVertex3f(v[faces[i][j]][0], v[faces[i][j]][1], v[faces[i][j]][2]);
}
}
}
finally
{
gl.glEnd();
}
}
protected static class AppFrame extends ApplicationTemplate.AppFrame
{
public AppFrame()
{
super(true, true, false);
RenderableLayer layer = new RenderableLayer();
Cube cube = new Cube(Position.fromDegrees(35.0, -120.0, 3000), 100000);
layer.addRenderable(cube);
getWwd().getModel().getLayers().add(layer);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Configuration.setValue(AVKey.INITIAL_LATITUDE, 35.0);
Configuration.setValue(AVKey.INITIAL_LONGITUDE, -120.0);
Configuration.setValue(AVKey.INITIAL_ALTITUDE, 2550000);
Configuration.setValue(AVKey.INITIAL_PITCH, 45);
Configuration.setValue(AVKey.INITIAL_HEADING, 45);
ApplicationTemplate.start("World Wind Custom Renderable Tutorial", AppFrame.class);
}
}

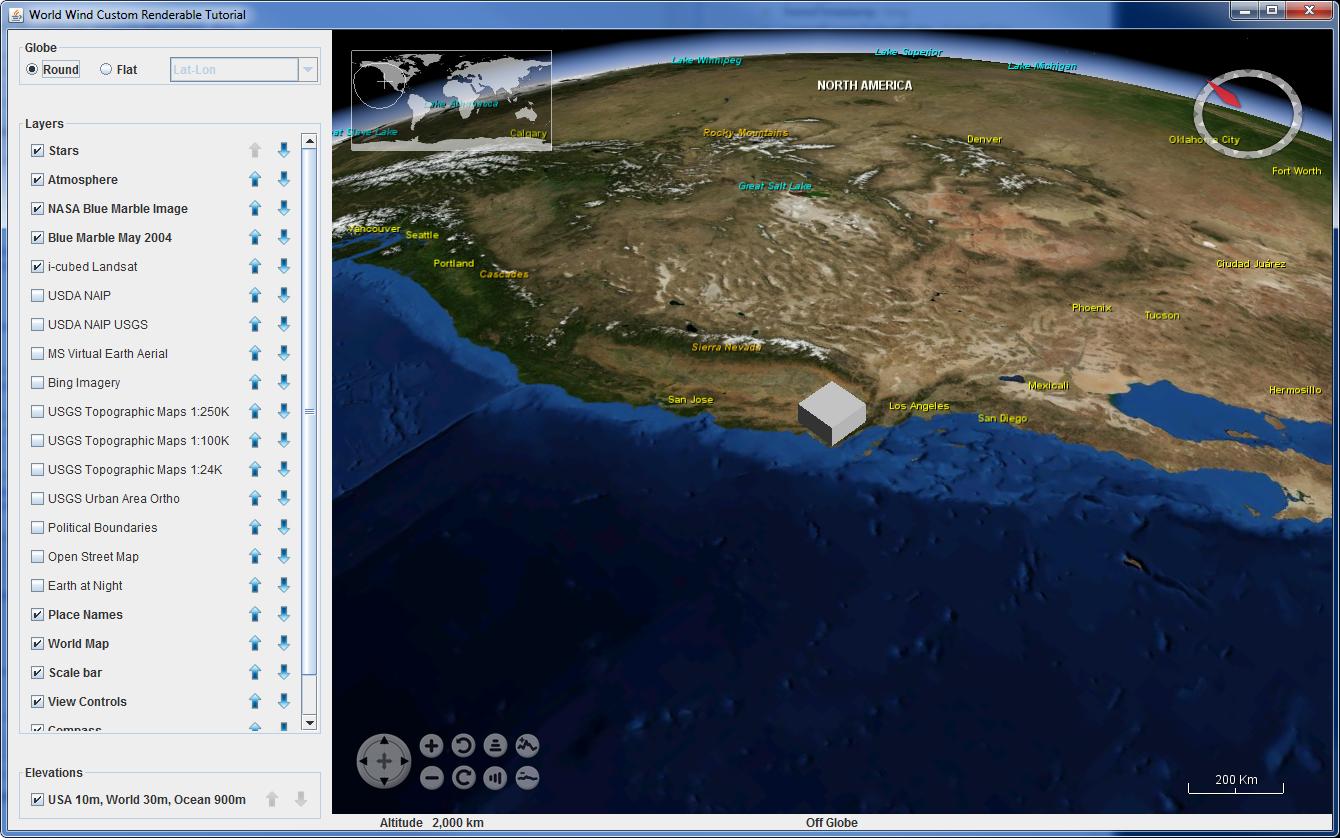
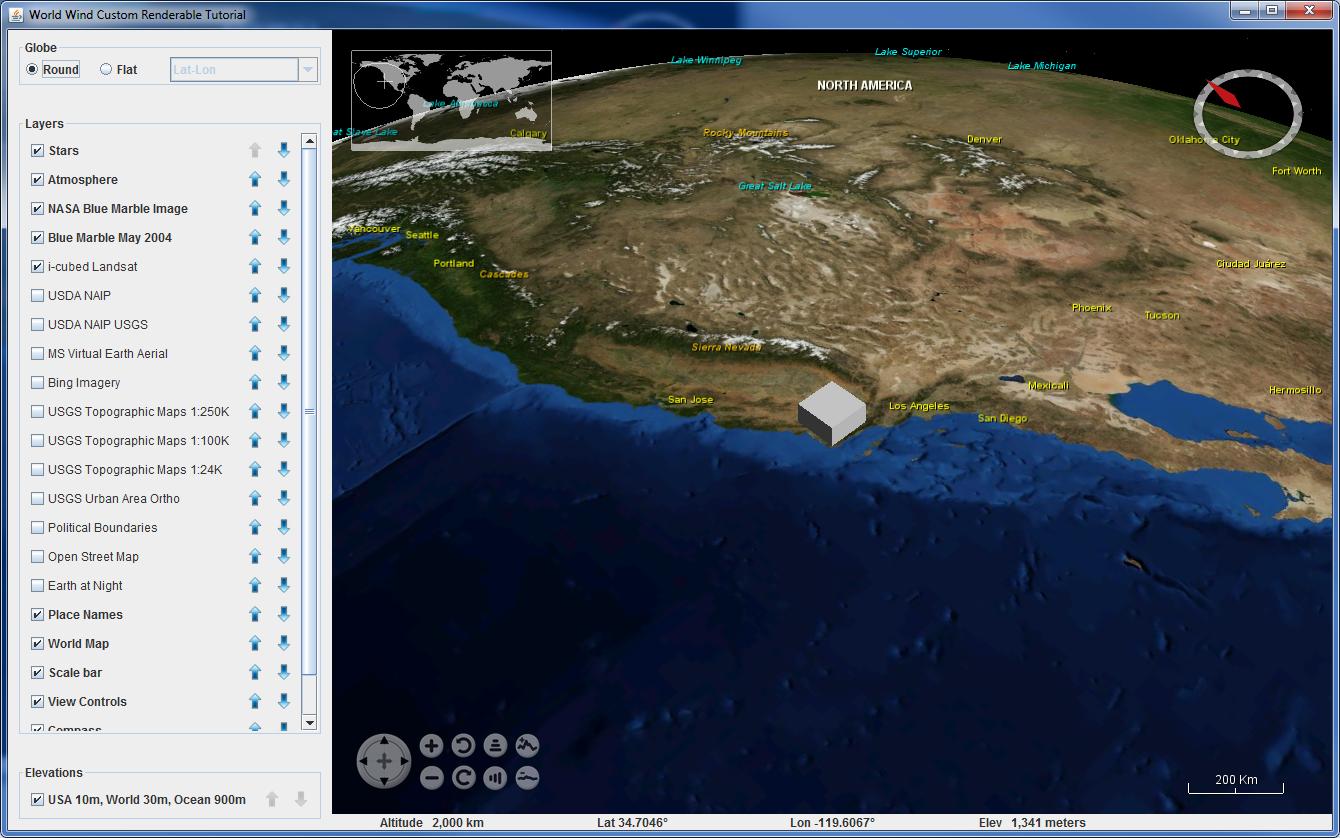
dc.isPickingModeis true). I guess that somehow affects theSkyGradientLayerrendering. Maybe that can help you debug, meanwhile - I can reproduce the issue. I'll try to figure it out when I have some time. – VaccaroCubeclass bundled in theworldwindx.jartoo. It's a bit hard to repro, as their cube is much smaller in scale than yours, but if you set the right viewing angle (inclination?) you can do it. I'm still digging into why it occurs. – Vaccaro