I am working on a marketplace, and was wondering what is the best way of handling website settings such as title, url, if its https, contact email, version, etc.
I am trying to structure the table so it is easy to update, and able to have more and more settings added to it to fetch.
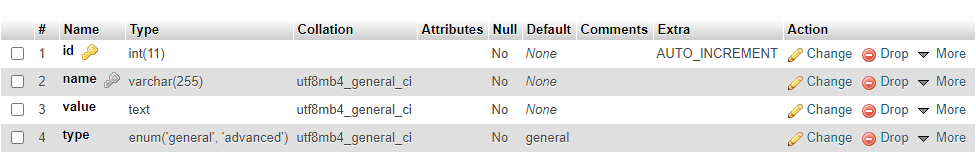
I developed 2 structures, either keep it in one row, with column names as the setting name, and the row column value as the setting value. and just echoing the first row value column name with a mysql_fetch_assoc.

I was also thinking about having a new auto-increment row for every setting. And turning it into an array to fetch from the database to assign a column name for the column im fetching of the setting name.

What would be your way of handling this efficiently. thank you.