Many applications have text and in this text are web hyperlinks in rounded rect. When I click them UIWebView opens. What puzzles me is that they often have custom links, for example if words starts with # it is also clickable and the application responds by opening another view. How can I do that? Is it possible with UILabel or do I need UITextView or something else?
In general, if we want to have a clickable link in text displayed by UILabel, we would need to resolve two independent tasks:
- Changing the appearance of a portion of the text to look like a link
- Detecting and handling touches on the link (opening an URL is a particular case)
The first one is easy. Starting from iOS 6 UILabel supports display of attributed strings. All you need to do is to create and configure an instance of NSMutableAttributedString:
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedString = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"String with a link" attributes:nil];
NSRange linkRange = NSMakeRange(14, 4); // for the word "link" in the string above
NSDictionary *linkAttributes = @{ NSForegroundColorAttributeName : [UIColor colorWithRed:0.05 green:0.4 blue:0.65 alpha:1.0],
NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName : @(NSUnderlineStyleSingle) };
[attributedString setAttributes:linkAttributes range:linkRange];
// Assign attributedText to UILabel
label.attributedText = attributedString;
That's it! The code above makes UILabel to display String with a link
Now we should detect touches on this link. The idea is to catch all taps within UILabel and figure out whether the location of the tap was close enough to the link. To catch touches we can add tap gesture recognizer to the label. Make sure to enable userInteraction for the label, it's turned off by default:
label.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
[label addGestureRecognizer:[[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(handleTapOnLabel:)]];
Now the most sophisticated stuff: finding out whether the tap was on where the link is displayed and not on any other portion of the label. If we had single-lined UILabel, this task could be solved relatively easy by hardcoding the area bounds where the link is displayed, but let's solve this problem more elegantly and for general case - multiline UILabel without preliminary knowledge about the link layout.
One of the approaches is to use capabilities of Text Kit API introduced in iOS 7:
// Create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
NSLayoutManager *layoutManager = [[NSLayoutManager alloc] init];
NSTextContainer *textContainer = [[NSTextContainer alloc] initWithSize:CGSizeZero];
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:attributedString];
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
[layoutManager addTextContainer:textContainer];
[textStorage addLayoutManager:layoutManager];
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0;
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode;
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines;
Save created and configured instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage in properties in your class (most likely UIViewController's descendant) - we'll need them in other methods.
Now, each time the label changes its frame, update textContainer's size:
- (void)viewDidLayoutSubviews
{
[super viewDidLayoutSubviews];
self.textContainer.size = self.label.bounds.size;
}
And finally, detect whether the tap was exactly on the link:
- (void)handleTapOnLabel:(UITapGestureRecognizer *)tapGesture
{
CGPoint locationOfTouchInLabel = [tapGesture locationInView:tapGesture.view];
CGSize labelSize = tapGesture.view.bounds.size;
CGRect textBoundingBox = [self.layoutManager usedRectForTextContainer:self.textContainer];
CGPoint textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
CGPoint locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake(locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x,
locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y);
NSInteger indexOfCharacter = [self.layoutManager characterIndexForPoint:locationOfTouchInTextContainer
inTextContainer:self.textContainer
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints:nil];
NSRange linkRange = NSMakeRange(14, 4); // it's better to save the range somewhere when it was originally used for marking link in attributed string
if (NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, linkRange)) {
// Open an URL, or handle the tap on the link in any other way
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"https://stackoverflow.com/"]];
}
}
cellForRowAtIndexPath? I'm creating and configuring instances within cellForRowAtIndexPath and hosting the handleTapOnLabel function in it too. But at cell.textLabel.addGestureRecognizer(UITapGestureRecognizer(target: cell, action: "handleTapOnLabel:")), I'm getting unrecognized selector. –
Ferrari textAlignment attribute is set to NSTextAlignmentCenter. If you are using non-centered text, you'll need to adjust the calculation of your textContainerOffset in the above code. –
Ivey textContainerOffset? –
Quickfreeze x value of textContainerOffset, the constant 0.5 is used. This will calculate the correct position for NSTextAlignmentCenter. To align left, natural or justified, use a value of 0.0. To align right, use 1.0. –
Ivey indexOfCharacter is always returning 0 and textBoundingBox.size is always 0, 0. I can't figure out what I'm doing wrong. –
Linesman self.textContainer.size = self.myLabel.bounds.size; is not updating the textContainer.size. It's continuing to return zero, even though my label's bounds size is not zero. –
Linesman NSParagraphStyleAttributeName and the text alignment property of your label. 2. Ensure the NSTextStorage has the font attribute set using NSFontAttributeName and the font property of your label. –
Erminiaerminie I am extending @NAlexN original detailed solution, with @zekel excellent extension of UITapGestureRecognizer, and providing in Swift.
Extending UITapGestureRecognizer
extension UITapGestureRecognizer {
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
// Create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: label.attributedText!)
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
let labelSize = label.bounds.size
textContainer.size = labelSize
// Find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.location(in: label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer)
let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(
x: (labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
y: (labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y
)
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(
x: locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x,
y: locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y
)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
return NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange)
}
}
Usage
Setup UIGestureRecognizer to send actions to tapLabel:, and you can detect if the target ranges is being tapped on in myLabel.
@IBAction func tapLabel(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
if gesture.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(myLabel, inRange: targetRange1) {
print("Tapped targetRange1")
} else if gesture.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(myLabel, inRange: targetRange2) {
print("Tapped targetRange2")
} else {
print("Tapped none")
}
}
IMPORTANT: The UILabel line break mode must be set to wrap by word/char. Somehow, NSTextContainer will assume that the text is single line only if the line break mode is otherwise.
targetRange1 and targetRange2. –
Broadnax NSMutableAttributedString(attributedString: text) where 'text' is an NSAttributedString –
Dulaney Old question but if anyone can use a UITextView instead of a UILabel, then it is easy. Standard URLs, phone numbers etc will be automatically detected (and be clickable).
However, if you need custom detection, that is, if you want to be able to call any custom method after a user clicks on a particular word, you need to use NSAttributedStrings with an NSLinkAttributeName attribute that will point to a custom URL scheme(as opposed to having the http url scheme by default). Ray Wenderlich has it covered here
Quoting the code from the aforementioned link:
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedString = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"This is an example by @marcelofabri_"];
[attributedString addAttribute:NSLinkAttributeName
value:@"username://marcelofabri_"
range:[[attributedString string] rangeOfString:@"@marcelofabri_"]];
NSDictionary *linkAttributes = @{NSForegroundColorAttributeName: [UIColor greenColor],
NSUnderlineColorAttributeName: [UIColor lightGrayColor],
NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName: @(NSUnderlinePatternSolid)};
// assume that textView is a UITextView previously created (either by code or Interface Builder)
textView.linkTextAttributes = linkAttributes; // customizes the appearance of links
textView.attributedText = attributedString;
textView.delegate = self;
To detect those link clicks, implement this:
- (BOOL)textView:(UITextView *)textView shouldInteractWithURL:(NSURL *)URL inRange:(NSRange)characterRange {
if ([[URL scheme] isEqualToString:@"username"]) {
NSString *username = [URL host];
// do something with this username
// ...
return NO;
}
return YES; // let the system open this URL
}
PS: Make sure your UITextView is selectable.
Make sure your UITextView is selectable : this saved my day –
Sayed (My answer builds on @NAlexN's excellent answer. I won't duplicate his detailed explanation of each step here.)
I found it most convenient and straightforward to add support for tap-able UILabel text as a category to UITapGestureRecognizer. (You don't have to use UITextView's data detectors, as some answers suggest.)
Add the following method to your UITapGestureRecognizer category:
/**
Returns YES if the tap gesture was within the specified range of the attributed text of the label.
*/
- (BOOL)didTapAttributedTextInLabel:(UILabel *)label inRange:(NSRange)targetRange {
NSParameterAssert(label != nil);
CGSize labelSize = label.bounds.size;
// create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
NSLayoutManager *layoutManager = [[NSLayoutManager alloc] init];
NSTextContainer *textContainer = [[NSTextContainer alloc] initWithSize:CGSizeZero];
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:label.attributedText];
// configure layoutManager and textStorage
[layoutManager addTextContainer:textContainer];
[textStorage addLayoutManager:layoutManager];
// configure textContainer for the label
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0;
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode;
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines;
textContainer.size = labelSize;
// find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
CGPoint locationOfTouchInLabel = [self locationInView:label];
CGRect textBoundingBox = [layoutManager usedRectForTextContainer:textContainer];
CGPoint textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
CGPoint locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake(locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x,
locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y);
NSInteger indexOfCharacter = [layoutManager characterIndexForPoint:locationOfTouchInTextContainer
inTextContainer:textContainer
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints:nil];
if (NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange)) {
return YES;
} else {
return NO;
}
}
Example Code
// (in your view controller)
// create your label, gesture recognizer, attributed text, and get the range of the "link" in your label
myLabel.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
[myLabel addGestureRecognizer:
[[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self
action:@selector(handleTapOnLabel:)]];
// create your attributed text and keep an ivar of your "link" text range
NSAttributedString *plainText;
NSAttributedString *linkText;
plainText = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"Add label links with UITapGestureRecognizer"
attributes:nil];
linkText = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@" Learn more..."
attributes:@{
NSForegroundColorAttributeName:[UIColor blueColor]
}];
NSMutableAttributedString *attrText = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] init];
[attrText appendAttributedString:plainText];
[attrText appendAttributedString:linkText];
// ivar -- keep track of the target range so you can compare in the callback
targetRange = NSMakeRange(plainText.length, linkText.length);
Gesture Callback
// handle the gesture recognizer callback and call the category method
- (void)handleTapOnLabel:(UITapGestureRecognizer *)tapGesture {
BOOL didTapLink = [tapGesture didTapAttributedTextInLabel:myLabel
inRange:targetRange];
NSLog(@"didTapLink: %d", didTapLink);
}
plainText.length. –
Gallion UITapGestureRecognizer. Here is some info on adding categories. –
Gallion extensions in Swift. Im implementing this using Swift now and have no prior experience with ObjC, so wasn't sure what this as about. –
Argeliaargent UILabel. We have solved this by applying the original string attributes from UILabel to NSTextStorage, so NSLayoutManager can render the exact location of the target text range. See: https://mcmap.net/q/99746/-create-tap-able-quot-links-quot-in-the-nsattributedstring-of-a-uilabel for the code snippet. –
Renege The UIButtonTypeCustom is a clickable label if you don't set any images for it.
Translating @samwize's Extension to Swift 4:
extension UITapGestureRecognizer {
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
guard let attrString = label.attributedText else {
return false
}
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: .zero)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: attrString)
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
let labelSize = label.bounds.size
textContainer.size = labelSize
let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.location(in: label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer)
let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(x: (labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x, y: (labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y)
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x, y: locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
return NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange)
}
}
To set up the recognizer (once you colored the text and stuff):
lblTermsOfUse.isUserInteractionEnabled = true
lblTermsOfUse.addGestureRecognizer(UITapGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(handleTapOnLabel(_:))))
...then the gesture recognizer:
@objc func handleTapOnLabel(_ recognizer: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
guard let text = lblAgreeToTerms.attributedText?.string else {
return
}
if let range = text.range(of: NSLocalizedString("_onboarding_terms", comment: "terms")),
recognizer.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: lblAgreeToTerms, inRange: NSRange(range, in: text)) {
goToTermsAndConditions()
} else if let range = text.range(of: NSLocalizedString("_onboarding_privacy", comment: "privacy")),
recognizer.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: lblAgreeToTerms, inRange: NSRange(range, in: text)) {
goToPrivacyPolicy()
}
}
didTapAttributedTextInLabel needs an NSRange as an argument but rangeTerms returns something different. Also the handleTapOnLabel function should be marked with @objc in Swift 4. –
Pilsen UITextView supports data-detectors in OS3.0, whereas UILabel doesn't.
If you enable the data-detectors on the UITextView and your text contains URLs, phone numbers, etc. they will appear as links.
hashtag:// or something, then use textView(_:shouldInteractWith:in:interaction:) to detect it. See the answer below: https://mcmap.net/q/99746/-create-tap-able-quot-links-quot-in-the-nsattributedstring-of-a-uilabel –
Seidler Most simple and reliable approach is to use UITextView as Kedar Paranjape recommended. Based on answer of Karl Nosworthy I finally came up with a simple UITextView subclass:
class LinkTextView: UITextView, UITextViewDelegate {
typealias Links = [String: String]
typealias OnLinkTap = (URL) -> Bool
var onLinkTap: OnLinkTap?
override init(frame: CGRect, textContainer: NSTextContainer?) {
super.init(frame: frame, textContainer: textContainer)
isEditable = false
isSelectable = true
isScrollEnabled = false //to have own size and behave like a label
delegate = self
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: coder)
}
func addLinks(_ links: Links) {
guard attributedText.length > 0 else {
return
}
let mText = NSMutableAttributedString(attributedString: attributedText)
for (linkText, urlString) in links {
if linkText.count > 0 {
let linkRange = mText.mutableString.range(of: linkText)
mText.addAttribute(.link, value: urlString, range: linkRange)
}
}
attributedText = mText
}
func textView(_ textView: UITextView, shouldInteractWith URL: URL, in characterRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
return onLinkTap?(URL) ?? true
}
// to disable text selection
func textViewDidChangeSelection(_ textView: UITextView) {
textView.selectedTextRange = nil
}
}
Usage is very simple:
let linkTextView = LinkTextView()
let tu = "Terms of Use"
let pp = "Privacy Policy"
linkTextView.text = "Please read the Some Company \(tu) and \(pp)"
linkTextView.addLinks([
tu: "https://some.com/tu",
pp: "https://some.com/pp"
])
linkTextView.onLinkTap = { url in
print("url: \(url)")
return true
}
Note that isScrollEnabled is false by default, as in most cases we need small label-like view with own size and without scrolling. Just set it to true if you want a scrollable text view.
Also note that the UITextView unlike UILabel has default text padding. To remove it and make layout same as in UILabel just add:
linkTextView.textContainerInset = .zero
linkTextView.textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0
Implementing onLinkTap closure is not necessary, without it URLs are automatically open by UIApplication.
Links appearance can be customized by setting linkTextAttributes property of the UITextView.
As Text selection is undesirable in most cases, but it can't be turned off it is dismissed in delegate method (Thanks to Carson Vo)
linkTextView.onLinkTap seems never to be hit. I prefer using a segue behind the code, so it's important to catch that. Do you know what could be wrong? –
Hoopes Some answers didn't work for me as expected. This is Swift solution that supports also textAlignment and multiline. No subclassing needed, just this UITapGestureRecognizer extension:
import UIKit
extension UITapGestureRecognizer {
func didTapAttributedString(_ string: String, in label: UILabel) -> Bool {
guard let text = label.text else {
return false
}
let range = (text as NSString).range(of: string)
return self.didTapAttributedText(label: label, inRange: range)
}
private func didTapAttributedText(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
guard let attributedText = label.attributedText else {
assertionFailure("attributedText must be set")
return false
}
let textContainer = createTextContainer(for: label)
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: attributedText)
if let font = label.font {
textStorage.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.font, value: font, range: NSMakeRange(0, attributedText.length))
}
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
let locationOfTouchInLabel = location(in: label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer)
let alignmentOffset = aligmentOffset(for: label)
let xOffset = ((label.bounds.size.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * alignmentOffset) - textBoundingBox.origin.x
let yOffset = ((label.bounds.size.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * alignmentOffset) - textBoundingBox.origin.y
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: locationOfTouchInLabel.x - xOffset, y: locationOfTouchInLabel.y - yOffset)
let characterTapped = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let lineTapped = Int(ceil(locationOfTouchInLabel.y / label.font.lineHeight)) - 1
let rightMostPointInLineTapped = CGPoint(x: label.bounds.size.width, y: label.font.lineHeight * CGFloat(lineTapped))
let charsInLineTapped = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: rightMostPointInLineTapped, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
return characterTapped < charsInLineTapped ? targetRange.contains(characterTapped) : false
}
private func createTextContainer(for label: UILabel) -> NSTextContainer {
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: label.bounds.size)
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
return textContainer
}
private func aligmentOffset(for label: UILabel) -> CGFloat {
switch label.textAlignment {
case .left, .natural, .justified:
return 0.0
case .center:
return 0.5
case .right:
return 1.0
@unknown default:
return 0.0
}
}
}
Usage:
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet var label : UILabel!
let selectableString1 = "consectetur"
let selectableString2 = "cupidatat"
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let text = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, \(selectableString1) adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat \(selectableString2) non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum."
label.attributedText = NSMutableAttributedString(attributedString: NSAttributedString(string: text))
let tapGesture = UITapGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(labelTapped))
label.addGestureRecognizer(tapGesture)
label.isUserInteractionEnabled = true
}
@objc func labelTapped(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
if gesture.didTapAttributedString(selectableString1, in: label) {
print("\(selectableString1) tapped")
} else if gesture.didTapAttributedString(selectableString2, in: label) {
print("\(selectableString2) tapped")
} else {
print("Text tapped")
}
}
}
As I mentioned in this post, here is a light-weighted library I created specially for links in UILabel FRHyperLabel.
To achieve an effect like this:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Pellentesque quis blandit eros, sit amet vehicula justo. Nam at urna neque. Maecenas ac sem eu sem porta dictum nec vel tellus.
use code:
//Step 1: Define a normal attributed string for non-link texts
NSString *string = @"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Pellentesque quis blandit eros, sit amet vehicula justo. Nam at urna neque. Maecenas ac sem eu sem porta dictum nec vel tellus.";
NSDictionary *attributes = @{NSFontAttributeName: [UIFont preferredFontForTextStyle:UIFontTextStyleHeadline]};
label.attributedText = [[NSAttributedString alloc]initWithString:string attributes:attributes];
//Step 2: Define a selection handler block
void(^handler)(FRHyperLabel *label, NSString *substring) = ^(FRHyperLabel *label, NSString *substring){
NSLog(@"Selected: %@", substring);
};
//Step 3: Add link substrings
[label setLinksForSubstrings:@[@"Lorem", @"Pellentesque", @"blandit", @"Maecenas"] withLinkHandler:handler];
Here is a swift version of NAlexN's answer.
class TapabbleLabel: UILabel {
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
var textStorage = NSTextStorage() {
didSet {
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
}
}
var onCharacterTapped: ((label: UILabel, characterIndex: Int) -> Void)?
let tapGesture = UITapGestureRecognizer()
override var attributedText: NSAttributedString? {
didSet {
if let attributedText = attributedText {
textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: attributedText)
} else {
textStorage = NSTextStorage()
}
}
}
override var lineBreakMode: NSLineBreakMode {
didSet {
textContainer.lineBreakMode = lineBreakMode
}
}
override var numberOfLines: Int {
didSet {
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = numberOfLines
}
}
/**
Creates a new view with the passed coder.
:param: aDecoder The a decoder
:returns: the created new view.
*/
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: aDecoder)
setUp()
}
/**
Creates a new view with the passed frame.
:param: frame The frame
:returns: the created new view.
*/
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
setUp()
}
/**
Sets up the view.
*/
func setUp() {
userInteractionEnabled = true
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = numberOfLines
tapGesture.addTarget(self, action: #selector(TapabbleLabel.labelTapped(_:)))
addGestureRecognizer(tapGesture)
}
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
textContainer.size = bounds.size
}
func labelTapped(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
guard gesture.state == .Ended else {
return
}
let locationOfTouch = gesture.locationInView(gesture.view)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRectForTextContainer(textContainer)
let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(x: (bounds.width - textBoundingBox.width) / 2 - textBoundingBox.minX,
y: (bounds.height - textBoundingBox.height) / 2 - textBoundingBox.minY)
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: locationOfTouch.x - textContainerOffset.x,
y: locationOfTouch.y - textContainerOffset.y)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndexForPoint(locationOfTouchInTextContainer,
inTextContainer: textContainer,
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
onCharacterTapped?(label: self, characterIndex: indexOfCharacter)
}
}
You can then create an instance of that class inside your viewDidLoad method like this:
let label = TapabbleLabel()
label.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(label)
view.addConstraints(NSLayoutConstraint.constraintsWithVisualFormat("V:|-[view]-|",
options: [], metrics: nil, views: ["view" : label]))
view.addConstraints(NSLayoutConstraint.constraintsWithVisualFormat("H:|-[view]-|",
options: [], metrics: nil, views: ["view" : label]))
let attributedString = NSMutableAttributedString(string: "String with a link", attributes: nil)
let linkRange = NSMakeRange(14, 4); // for the word "link" in the string above
let linkAttributes: [String : AnyObject] = [
NSForegroundColorAttributeName : UIColor.blueColor(), NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName : NSUnderlineStyle.StyleSingle.rawValue,
NSLinkAttributeName: "http://www.apple.com"]
attributedString.setAttributes(linkAttributes, range:linkRange)
label.attributedText = attributedString
label.onCharacterTapped = { label, characterIndex in
if let attribute = label.attributedText?.attribute(NSLinkAttributeName, atIndex: characterIndex, effectiveRange: nil) as? String,
let url = NSURL(string: attribute) {
UIApplication.sharedApplication().openURL(url)
}
}
It's better to have a custom attribute to use when a character is tapped. Now, it's the NSLinkAttributeName, but could be anything and you can use that value to do other things other than opening a url, you can do any custom action.
Worked in Swift 3, pasting the entire code here
//****Make sure the textview 'Selectable' = checked, and 'Editable = Unchecked'
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, UITextViewDelegate {
@IBOutlet var theNewTextView: UITextView!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
//****textview = Selectable = checked, and Editable = Unchecked
theNewTextView.delegate = self
let theString = NSMutableAttributedString(string: "Agree to Terms")
let theRange = theString.mutableString.range(of: "Terms")
theString.addAttribute(NSLinkAttributeName, value: "ContactUs://", range: theRange)
let theAttribute = [NSForegroundColorAttributeName: UIColor.blue, NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName: NSUnderlineStyle.styleSingle.rawValue] as [String : Any]
theNewTextView.linkTextAttributes = theAttribute
theNewTextView.attributedText = theString
theString.setAttributes(theAttribute, range: theRange)
}
func textView(_ textView: UITextView, shouldInteractWith URL: URL, in characterRange: NSRange, interaction: UITextItemInteraction) -> Bool {
if (URL.scheme?.hasPrefix("ContactUs://"))! {
return false //interaction not allowed
}
//*** Set storyboard id same as VC name
self.navigationController!.pushViewController((self.storyboard?.instantiateViewController(withIdentifier: "TheLastViewController"))! as UIViewController, animated: true)
return true
}
}
I created UILabel subclass named ResponsiveLabel which is based on textkit API introduced in iOS 7. It uses the same approach suggested by NAlexN. It provides flexibility to specify a pattern to search in the text. One can specify styles to be applied to those patterns as well as action to be performed on tapping the patterns.
//Detects email in text
NSString *emailRegexString = @"[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+\\.[A-Z]{2,4}";
NSError *error;
NSRegularExpression *regex = [[NSRegularExpression alloc]initWithPattern:emailRegexString options:0 error:&error];
PatternDescriptor *descriptor = [[PatternDescriptor alloc]initWithRegex:regex withSearchType:PatternSearchTypeAll withPatternAttributes:@{NSForegroundColorAttributeName:[UIColor redColor]}];
[self.customLabel enablePatternDetection:descriptor];
If you want to make a string clickable, you can do this way. This code applies attributes to each occurrence of the string "text".
PatternTapResponder tapResponder = ^(NSString *string) {
NSLog(@"tapped = %@",string);
};
[self.customLabel enableStringDetection:@"text" withAttributes:@{NSForegroundColorAttributeName:[UIColor redColor],
RLTapResponderAttributeName: tapResponder}];
Here is example code to hyperlink UILabel: Source:http://sickprogrammersarea.blogspot.in/2014/03/adding-links-to-uilabel.html
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "TTTAttributedLabel.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
{
UITextField *loc;
TTTAttributedLabel *data;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
UILabel *lbl = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(5, 20, 80, 25) ];
[lbl setText:@"Text:"];
[lbl setFont:[UIFont fontWithName:@"Verdana" size:16]];
[lbl setTextColor:[UIColor grayColor]];
loc=[[UITextField alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(4, 20, 300, 30)];
//loc.backgroundColor = [UIColor grayColor];
loc.borderStyle=UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect;
loc.clearButtonMode=UITextFieldViewModeWhileEditing;
//[loc setText:@"Enter Location"];
loc.clearsOnInsertion = YES;
loc.leftView=lbl;
loc.leftViewMode=UITextFieldViewModeAlways;
[loc setDelegate:self];
[self.view addSubview:loc];
[loc setRightViewMode:UITextFieldViewModeAlways];
CGRect frameimg = CGRectMake(110, 70, 70,30);
UIButton *srchButton = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeRoundedRect];
srchButton.frame=frameimg;
[srchButton setTitle:@"Go" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
[srchButton setTitleColor:[UIColor blackColor] forState:UIControlStateNormal];
srchButton.backgroundColor=[UIColor clearColor];
[srchButton addTarget:self action:@selector(go:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchDown];
[self.view addSubview:srchButton];
data = [[TTTAttributedLabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(5, 120,self.view.frame.size.width,200) ];
[data setFont:[UIFont fontWithName:@"Verdana" size:16]];
[data setTextColor:[UIColor blackColor]];
data.numberOfLines=0;
data.delegate = self;
data.enabledTextCheckingTypes=NSTextCheckingTypeLink|NSTextCheckingTypePhoneNumber;
[self.view addSubview:data];
}
- (void)attributedLabel:(TTTAttributedLabel *)label didSelectLinkWithURL:(NSURL *)url
{
NSString *val=[[NSString alloc]initWithFormat:@"%@",url];
if ([[url scheme] hasPrefix:@"mailto"]) {
NSLog(@" mail URL Selected : %@",url);
MFMailComposeViewController *comp=[[MFMailComposeViewController alloc]init];
[comp setMailComposeDelegate:self];
if([MFMailComposeViewController canSendMail])
{
NSString *recp=[[val substringToIndex:[val length]] substringFromIndex:7];
NSLog(@"Recept : %@",recp);
[comp setToRecipients:[NSArray arrayWithObjects:recp, nil]];
[comp setSubject:@"From my app"];
[comp setMessageBody:@"Hello bro" isHTML:NO];
[comp setModalTransitionStyle:UIModalTransitionStyleCrossDissolve];
[self presentViewController:comp animated:YES completion:nil];
}
}
else{
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:val]];
}
}
-(void)mailComposeController:(MFMailComposeViewController *)controller didFinishWithResult:(MFMailComposeResult)result error:(NSError *)error{
if(error)
{
UIAlertView *alrt=[[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:@"Erorr" message:@"Some error occureed" delegate:nil cancelButtonTitle:@"" otherButtonTitles:nil, nil];
[alrt show];
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
else{
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
}
- (void)attributedLabel:(TTTAttributedLabel *)label didSelectLinkWithPhoneNumber:(NSString *)phoneNumber
{
NSLog(@"Phone Number Selected : %@",phoneNumber);
UIDevice *device = [UIDevice currentDevice];
if ([[device model] isEqualToString:@"iPhone"] ) {
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"tel:%@",phoneNumber]]];
} else {
UIAlertView *Notpermitted=[[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"Alert" message:@"Your device doesn't support this feature." delegate:nil cancelButtonTitle:@"OK" otherButtonTitles:nil];
[Notpermitted show];
}
}
-(void)go:(id)sender
{
[data setText:loc.text];
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"Reached");
[loc resignFirstResponder];
}
Like there is reported in earlier answer the UITextView is able to handle touches on links. This can easily be extended by making other parts of the text work as links. The AttributedTextView library is a UITextView subclass that makes it very easy to handle these. For more info see: https://github.com/evermeer/AttributedTextView
You can make any part of the text interact like this (where textView1 is a UITextView IBOutlet):
textView1.attributer =
"1. ".red
.append("This is the first test. ").green
.append("Click on ").black
.append("evict.nl").makeInteract { _ in
UIApplication.shared.open(URL(string: "http://evict.nl")!, options: [:], completionHandler: { completed in })
}.underline
.append(" for testing links. ").black
.append("Next test").underline.makeInteract { _ in
print("NEXT")
}
.all.font(UIFont(name: "SourceSansPro-Regular", size: 16))
.setLinkColor(UIColor.purple)
And for handling hashtags and mentions you can use code like this:
textView1.attributer = "@test: What #hashtags do we have in @evermeer #AtributedTextView library"
.matchHashtags.underline
.matchMentions
.makeInteract { link in
UIApplication.shared.open(URL(string: "https://twitter.com\(link.replacingOccurrences(of: "@", with: ""))")!, options: [:], completionHandler: { completed in })
}
Here’s a Swift implementation that is about as minimal as possible that also includes touch feedback. Caveats:
- You must set fonts in your NSAttributedStrings
- You can only use NSAttributedStrings!
- You must ensure your links cannot wrap (use non breaking spaces:
"\u{a0}") - You cannot change the lineBreakMode or numberOfLines after setting the text
- You create links by adding attributes with
.linkkeys
.
public class LinkLabel: UILabel {
private var storage: NSTextStorage?
private let textContainer = NSTextContainer()
private let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
private var selectedBackgroundView = UIView()
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textContainer.layoutManager = layoutManager
isUserInteractionEnabled = true
selectedBackgroundView.isHidden = true
selectedBackgroundView.backgroundColor = UIColor(white: 0, alpha: 0.3333)
selectedBackgroundView.layer.cornerRadius = 4
addSubview(selectedBackgroundView)
}
public required convenience init(coder: NSCoder) {
self.init(frame: .zero)
}
public override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
textContainer.size = frame.size
}
public override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
super.touchesBegan(touches, with: event)
setLink(for: touches)
}
public override func touchesMoved(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
super.touchesMoved(touches, with: event)
setLink(for: touches)
}
private func setLink(for touches: Set<UITouch>) {
if let pt = touches.first?.location(in: self), let (characterRange, _) = link(at: pt) {
let glyphRange = layoutManager.glyphRange(forCharacterRange: characterRange, actualCharacterRange: nil)
selectedBackgroundView.frame = layoutManager.boundingRect(forGlyphRange: glyphRange, in: textContainer).insetBy(dx: -3, dy: -3)
selectedBackgroundView.isHidden = false
} else {
selectedBackgroundView.isHidden = true
}
}
public override func touchesCancelled(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
super.touchesCancelled(touches, with: event)
selectedBackgroundView.isHidden = true
}
public override func touchesEnded(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
super.touchesEnded(touches, with: event)
selectedBackgroundView.isHidden = true
if let pt = touches.first?.location(in: self), let (_, url) = link(at: pt) {
UIApplication.shared.open(url)
}
}
private func link(at point: CGPoint) -> (NSRange, URL)? {
let touchedGlyph = layoutManager.glyphIndex(for: point, in: textContainer)
let touchedChar = layoutManager.characterIndexForGlyph(at: touchedGlyph)
var range = NSRange()
let attrs = attributedText!.attributes(at: touchedChar, effectiveRange: &range)
if let urlstr = attrs[.link] as? String {
return (range, URL(string: urlstr)!)
} else {
return nil
}
}
public override var attributedText: NSAttributedString? {
didSet {
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = numberOfLines
textContainer.lineBreakMode = lineBreakMode
if let txt = attributedText {
storage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: txt)
storage!.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
layoutManager.textStorage = storage
textContainer.size = frame.size
}
}
}
}
mxcl, I give it a try, works great. If you want to style your link appearance, use NSAttributedString.Key.attachment instead. –
Usable I follow this version,
Swift 4:
import Foundation
class AELinkedClickableUILabel: UILabel {
typealias YourCompletion = () -> Void
var linkedRange: NSRange!
var completion: YourCompletion?
@objc func linkClicked(sender: UITapGestureRecognizer){
if let completionBlock = completion {
let textView = UITextView(frame: self.frame)
textView.text = self.text
textView.attributedText = self.attributedText
let index = textView.layoutManager.characterIndex(for: sender.location(in: self),
in: textView.textContainer,
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
if linkedRange.lowerBound <= index && linkedRange.upperBound >= index {
completionBlock()
}
}
}
/**
* This method will be used to set an attributed text specifying the linked text with a
* handler when the link is clicked
*/
public func setLinkedTextWithHandler(text:String, link: String, handler: @escaping ()->()) -> Bool {
let attributextText = NSMutableAttributedString(string: text)
let foundRange = attributextText.mutableString.range(of: link)
if foundRange.location != NSNotFound {
self.linkedRange = foundRange
self.completion = handler
attributextText.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.link, value: text, range: foundRange)
self.isUserInteractionEnabled = true
self.addGestureRecognizer(UITapGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(linkClicked(sender:))))
return true
}
return false
}
}
Call Example:
button.setLinkedTextWithHandler(text: "This website (stackoverflow.com) is awesome", link: "stackoverflow.com")
{
// show popup or open to link
}
I found a other solution:
I find a way to detect the link in a html text that you find from the internet you transform it into nsattributeString with :
func htmlAttributedString(fontSize: CGFloat = 17.0) -> NSAttributedString? {
let fontName = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: fontSize).fontName
let string = self.appending(String(format: "<style>body{font-family: '%@'; font-size:%fpx;}</style>", fontName, fontSize))
guard let data = string.data(using: String.Encoding.utf16, allowLossyConversion: false) else { return nil }
guard let html = try? NSMutableAttributedString (
data: data,
options: [NSAttributedString.DocumentReadingOptionKey.documentType: NSAttributedString.DocumentType.html],
documentAttributes: nil) else { return nil }
return html
}
My method allows you to detect the hyperlink without having to specify them.
first you create an extension of the tapgesturerecognizer :
extension UITapGestureRecognizer { func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool { guard let attrString = label.attributedText else { return false } let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager() let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: .zero) let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: attrString) layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer) textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager) textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0 textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines let labelSize = label.bounds.size textContainer.size = labelSize let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.location(in: label) let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer) let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(x: (labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x, y: (labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y) let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x, y: locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y) let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil) return NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange) }}
then in you view controller you created a list of url and ranges to store all the links and the range that the attribute text contain:
var listurl : [String] = []
var listURLRange : [NSRange] = []
to find the URL and the URLRange you can use :
fun findLinksAndRange(attributeString : NSAttributeString){
notification.enumerateAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.link , in: NSMakeRange(0, notification.length), options: [.longestEffectiveRangeNotRequired]) { value, range, isStop in
if let value = value {
print("\(value) found at \(range.location)")
let stringValue = "\(value)"
listurl.append(stringValue)
listURLRange.append(range)
}
}
westlandNotifcationLabel.addGestureRecognizer(UITapGestureRecognizer(target : self, action: #selector(handleTapOnLabel(_:))))
}
then you implementing the handle tap :
@objc func handleTapOnLabel(_ recognizer: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
for index in 0..<listURLRange.count{
if recognizer.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: westlandNotifcationLabel, inRange: listURLRange[index]) {
goToWebsite(url : listurl[index])
}
}
}
func goToWebsite(url : String){
if let websiteUrl = URL(string: url){
if #available(iOS 10, *) {
UIApplication.shared.open(websiteUrl, options: [:],
completionHandler: {
(success) in
print("Open \(websiteUrl): \(success)")
})
} else {
let success = UIApplication.shared.openURL(websiteUrl)
print("Open \(websiteUrl): \(success)")
}
}
}
and here we go!
I hope this solution help you like it help me.
I'm extending @samwize's answer to handle multi-line UILabel and give an example on using for a UIButton
extension UITapGestureRecognizer {
func didTapAttributedTextInButton(button: UIButton, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
guard let label = button.titleLabel else { return false }
return didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label, inRange: targetRange)
}
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
// Create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: label.attributedText!)
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
let labelSize = label.bounds.size
textContainer.size = labelSize
// Find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.locationInView(label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRectForTextContainer(textContainer)
let textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake((locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x),
0 );
// Adjust for multiple lines of text
let lineModifier = Int(ceil(locationOfTouchInLabel.y / label.font.lineHeight)) - 1
let rightMostFirstLinePoint = CGPointMake(labelSize.width, 0)
let charsPerLine = layoutManager.characterIndexForPoint(rightMostFirstLinePoint, inTextContainer: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndexForPoint(locationOfTouchInTextContainer, inTextContainer: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let adjustedRange = indexOfCharacter + (lineModifier * charsPerLine)
return NSLocationInRange(adjustedRange, targetRange)
}
}
For fully custom links, you'll need to use a UIWebView - you can intercept the calls out, so that you can go to some other part of your app instead when a link is pressed.
based on Charles Gamble answer, this what I used (I removed some lines that confused me and gave me wrong indexed) :
- (BOOL)didTapAttributedTextInLabel:(UILabel *)label inRange:(NSRange)targetRange TapGesture:(UIGestureRecognizer*) gesture{
NSParameterAssert(label != nil);
// create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
NSLayoutManager *layoutManager = [[NSLayoutManager alloc] init];
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:label.attributedText];
// configure layoutManager and textStorage
[textStorage addLayoutManager:layoutManager];
// configure textContainer for the label
NSTextContainer *textContainer = [[NSTextContainer alloc] initWithSize:CGSizeMake(label.frame.size.width, label.frame.size.height)];
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0;
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode;
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines;
// find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
CGPoint locationOfTouchInLabel = [gesture locationInView:label];
[layoutManager addTextContainer:textContainer]; //(move here, not sure it that matter that calling this line after textContainer is set
NSInteger indexOfCharacter = [layoutManager characterIndexForPoint:locationOfTouchInLabel
inTextContainer:textContainer
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints:nil];
if (NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange)) {
return YES;
} else {
return NO;
}
}
Here's a drop-in Objective-C category that enables clickable links in existing UILabel.attributedText strings, exploiting the existing NSLinkAttributeName attribute.
@interface UILabel (GSBClickableLinks) <UIGestureRecognizerDelegate>
@property BOOL enableLinks;
@end
#import <objc/runtime.h>
static const void *INDEX;
static const void *TAP;
@implementation UILabel (GSBClickableLinks)
- (void)setEnableLinks:(BOOL)enableLinks
{
UITapGestureRecognizer *tap = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &TAP); // retreive tap
if (enableLinks && !tap) { // add a gestureRegonzier to the UILabel to detect taps
tap = [UITapGestureRecognizer.alloc initWithTarget:self action:@selector(openLink)];
tap.delegate = self;
[self addGestureRecognizer:tap];
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &TAP, tap, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC); // save tap
}
self.userInteractionEnabled = enableLinks; // note - when false UILAbel wont receive taps, hence disable links
}
- (BOOL)enableLinks
{
return (BOOL)objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &TAP); // ie tap != nil
}
// First check whether user tapped on a link within the attributedText of the label.
// If so, then the our label's gestureRecogizer will subsequently fire, and open the corresponding NSLinkAttributeName.
// If not, then the tap will get passed along, eg to the enclosing UITableViewCell...
// Note: save which character in the attributedText was clicked so that we dont have to redo everything again in openLink.
- (BOOL)gestureRecognizerShouldBegin:(UIGestureRecognizer *)gestureRecognizer
{
if (gestureRecognizer != objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &TAP)) return YES; // dont block other gestures (eg swipe)
// Re-layout the attributedText to find out what was tapped
NSTextContainer *textContainer = [NSTextContainer.alloc initWithSize:self.frame.size];
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0;
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = self.numberOfLines;
textContainer.lineBreakMode = self.lineBreakMode;
NSLayoutManager *layoutManager = NSLayoutManager.new;
[layoutManager addTextContainer:textContainer];
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [NSTextStorage.alloc initWithAttributedString:self.attributedText];
[textStorage addLayoutManager:layoutManager];
NSUInteger index = [layoutManager characterIndexForPoint:[gestureRecognizer locationInView:self]
inTextContainer:textContainer
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints:NULL];
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &INDEX, @(index), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC); // save index
return (BOOL)[self.attributedText attribute:NSLinkAttributeName atIndex:index effectiveRange:NULL]; // tapped on part of a link?
}
- (void)openLink
{
NSUInteger index = [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &INDEX) unsignedIntegerValue]; // retrieve index
NSURL *url = [self.attributedText attribute:NSLinkAttributeName atIndex:index effectiveRange:NULL];
if (url && [UIApplication.sharedApplication canOpenURL:url]) [UIApplication.sharedApplication openURL:url];
}
@end
This would be a bit cleaner done via a UILabel subclass (ie none of the objc_getAssociatedObject mess), but if you are like me you prefer to avoid having to make unnecessary (3rd party) subclasses just to add some extra function to existing UIKit classes. Also, this has the beauty that it adds clickable-links to any existing UILabel, eg existing UITableViewCells!
I've tried to make it as minimally invasive as possible by using the existing NSLinkAttributeName attribute stuff already available in NSAttributedString. So its a simple as:
NSURL *myURL = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.google.com"];
NSMutableAttributedString *myString = [NSMutableAttributedString.alloc initWithString:@"This string has a clickable link: "];
[myString appendAttributedString:[NSAttributedString.alloc initWithString:@"click here" attributes:@{NSLinkAttributeName:myURL}]];
...
myLabel.attributedText = myString;
myLabel.enableLinks = YES; // yes, that's all! :-)
Basically, it works by adding a UIGestureRecognizer to your UILabel. The hard work is done in gestureRecognizerShouldBegin:, which re-layouts the attributedText string to find out which character was tapped on. If this character was part of a NSLinkAttributeName then the gestureRecognizer will subsequently fire, retrieve the corresponding URL (from the NSLinkAttributeName value), and open the link per the usual [UIApplication.sharedApplication openURL:url] process.
Note - by doing all this in gestureRecognizerShouldBegin:, if you dont happen to tap on a link in the label, the event is passed along. So, for example, your UITableViewCell will capture taps on links, but otherwise behave normally (select cell, unselect, scroll, ...).
I've put this in a GitHub repository here. Adapted from Kai Burghardt's SO posting here.
Yes this is possible albeit very confusing to figure out at first. I will go a step further and show you how you can even click on any area in the text as well.
With this method you can have UI Label tha is:
- Multiline Friendly
- Autoshrink Friendly
- Clickable Friendly (yes, even individual characters)
- Swift 5
Step 1:
Make the UILabel have the properties for Line Break of 'Truncate Tail' and set a minimum font scale.
If you are unfamiliar with font scale just remember this rule:
minimumFontSize/defaultFontSize = fontscale
In my case I wanted 7.2 to be the minimum font size and my starting font size was 36. Therefore, 7.2 / 36 = 0.2
Step 2:
If you do not care about the labels being clickable and just wanted a working multiline label you are done!
HOWEVER, if you want the labels to be clickable read on...
Add this following extension I created
extension UILabel {
func setOptimalFontSize(maxFontSize:CGFloat,text:String){
let width = self.bounds.size.width
var font_size:CGFloat = maxFontSize //Set the maximum font size.
var stringSize = NSString(string: text).size(withAttributes: [.font : self.font.withSize(font_size)])
while(stringSize.width > width){
font_size = font_size - 1
stringSize = NSString(string: text).size(withAttributes: [.font : self.font.withSize(font_size)])
}
self.font = self.font.withSize(font_size)//Forcefully change font to match what it would be graphically.
}
}
It's used like this (just replace <Label> with your actual label name):
<Label>.setOptimalFontSize(maxFontSize: 36.0, text: formula)
This extension is needed because auto shrink does NOT change the 'font' property of the label after it auto-shrinks so you have to deduce it by calculating it the same way it does by using .size(withAttributes) function which simulates what it's size would be with that particular font.
This is necessary because the solution for detecting where to click on the label requires the exact font size to be known.
Step 3:
Add the following extension:
extension UITapGestureRecognizer {
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
// Create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
let mutableAttribString = NSMutableAttributedString(attributedString: label.attributedText!)
mutableAttribString.addAttributes([NSAttributedString.Key.font: label.font!], range: NSRange(location: 0, length: label.attributedText!.length))
let paragraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
paragraphStyle.lineSpacing = 6
paragraphStyle.lineBreakMode = .byTruncatingTail
paragraphStyle.alignment = .center
mutableAttribString.addAttributes([.paragraphStyle: paragraphStyle], range: NSMakeRange(0, mutableAttribString.string.count))
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: mutableAttribString)
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
let labelSize = label.bounds.size
textContainer.size = labelSize
// Find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.location(in: label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer)
//let textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
//(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(x: (labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x, y: (labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y)
//let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake(locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x,
// locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y);
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x, y: locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
print("IndexOfCharacter=",indexOfCharacter)
print("TargetRange=",targetRange)
return NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange)
}
}
You will need to modify this extension for your particular multiline situation. In my case you will notice that I use a paragraph style.
let paragraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
paragraphStyle.lineSpacing = 6
paragraphStyle.lineBreakMode = .byTruncatingTail
paragraphStyle.alignment = .center
mutableAttribString.addAttributes([.paragraphStyle: paragraphStyle], range: NSMakeRange(0, mutableAttribString.string.count))
Make sure to change this in the extension to what you are actually using for your line spacing so that everything calculates correctly.
Step 4:
Add the gestureRecognizer to the label in viewDidLoad or where you think is appropriate like so (just replace <Label> with your label name again:
<Label>.addGestureRecognizer(UITapGestureRecognizer(target:self, action: #selector(tapLabel(gesture:))))
Here is a simplified example of my tapLabel function (just replace <Label> with your UILabel name):
@IBAction func tapLabel(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
guard let text = <Label>.attributedText?.string else {
return
}
let click_range = text.range(of: "(α/β)")
if gesture.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: <Label>, inRange: NSRange(click_range!, in: text)) {
print("Tapped a/b")
}else {
print("Tapped none")
}
}
Just a note in my example, my string is BED = N * d * [ RBE + ( d / (α/β) ) ], so I was just getting the range of the α/β in this case. You could add "\n" to the string to add a newline and whatever text you wanted after and test this to find a string on the next line and it will still find it and detect the click correctly!
That's it! You are done. Enjoy a multiline clickable label.
Create the class with the following .h and .m files. In the .m file there is the following function
- (void)linkAtPoint:(CGPoint)location
Inside this function we will check the ranges of substrings for which we need to give actions. Use your own logic to put your ranges.
And following is the usage of the subclass
TaggedLabel *label = [[TaggedLabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 100)];
[self.view addSubview:label];
label.numberOfLines = 0;
NSMutableAttributedString *attributtedString = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString : @"My name is @jjpp" attributes : @{ NSFontAttributeName : [UIFont systemFontOfSize:10],}];
//Do not forget to add the font attribute.. else it wont work.. it is very important
[attributtedString addAttribute:NSForegroundColorAttributeName
value:[UIColor redColor]
range:NSMakeRange(11, 5)];//you can give this range inside the .m function mentioned above
following is the .h file
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface TaggedLabel : UILabel<NSLayoutManagerDelegate>
@property(nonatomic, strong)NSLayoutManager *layoutManager;
@property(nonatomic, strong)NSTextContainer *textContainer;
@property(nonatomic, strong)NSTextStorage *textStorage;
@property(nonatomic, strong)NSArray *tagsArray;
@property(readwrite, copy) tagTapped nameTagTapped;
@end
following is the .m file
#import "TaggedLabel.h"
@implementation TaggedLabel
- (id)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
{
self = [super initWithFrame:frame];
if (self)
{
self.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
}
return self;
}
- (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder
{
self = [super initWithCoder:aDecoder];
if (self)
{
self.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
}
return self;
}
- (void)setupTextSystem
{
_layoutManager = [[NSLayoutManager alloc] init];
_textContainer = [[NSTextContainer alloc] initWithSize:CGSizeZero];
_textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:self.attributedText];
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
[_layoutManager addTextContainer:_textContainer];
[_textStorage addLayoutManager:_layoutManager];
// Configure textContainer
_textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0;
_textContainer.lineBreakMode = NSLineBreakByWordWrapping;
_textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = 0;
self.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
self.textContainer.size = self.bounds.size;
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
if (!_layoutManager)
{
[self setupTextSystem];
}
// Get the info for the touched link if there is one
CGPoint touchLocation = [[touches anyObject] locationInView:self];
[self linkAtPoint:touchLocation];
}
- (void)linkAtPoint:(CGPoint)location
{
// Do nothing if we have no text
if (_textStorage.string.length == 0)
{
return;
}
// Work out the offset of the text in the view
CGPoint textOffset = [self calcGlyphsPositionInView];
// Get the touch location and use text offset to convert to text cotainer coords
location.x -= textOffset.x;
location.y -= textOffset.y;
NSUInteger touchedChar = [_layoutManager glyphIndexForPoint:location inTextContainer:_textContainer];
// If the touch is in white space after the last glyph on the line we don't
// count it as a hit on the text
NSRange lineRange;
CGRect lineRect = [_layoutManager lineFragmentUsedRectForGlyphAtIndex:touchedChar effectiveRange:&lineRange];
if (CGRectContainsPoint(lineRect, location) == NO)
{
return;
}
// Find the word that was touched and call the detection block
NSRange range = NSMakeRange(11, 5);//for this example i'm hardcoding the range here. In a real scenario it should be iterated through an array for checking all the ranges
if ((touchedChar >= range.location) && touchedChar < (range.location + range.length))
{
NSLog(@"range-->>%@",self.tagsArray[i][@"range"]);
}
}
- (CGPoint)calcGlyphsPositionInView
{
CGPoint textOffset = CGPointZero;
CGRect textBounds = [_layoutManager usedRectForTextContainer:_textContainer];
textBounds.size.width = ceil(textBounds.size.width);
textBounds.size.height = ceil(textBounds.size.height);
if (textBounds.size.height < self.bounds.size.height)
{
CGFloat paddingHeight = (self.bounds.size.height - textBounds.size.height) / 2.0;
textOffset.y = paddingHeight;
}
if (textBounds.size.width < self.bounds.size.width)
{
CGFloat paddingHeight = (self.bounds.size.width - textBounds.size.width) / 2.0;
textOffset.x = paddingHeight;
}
return textOffset;
}
@end
Drop-in solution as a category on UILabel (this assumes your UILabel uses an attributed string with some NSLinkAttributeName attributes in it):
@implementation UILabel (Support)
- (BOOL)openTappedLinkAtLocation:(CGPoint)location {
CGSize labelSize = self.bounds.size;
NSTextContainer* textContainer = [[NSTextContainer alloc] initWithSize:CGSizeZero];
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0;
textContainer.lineBreakMode = self.lineBreakMode;
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = self.numberOfLines;
textContainer.size = labelSize;
NSLayoutManager* layoutManager = [[NSLayoutManager alloc] init];
[layoutManager addTextContainer:textContainer];
NSTextStorage* textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:self.attributedText];
[textStorage addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName value:self.font range:NSMakeRange(0, textStorage.length)];
[textStorage addLayoutManager:layoutManager];
CGRect textBoundingBox = [layoutManager usedRectForTextContainer:textContainer];
CGPoint textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
CGPoint locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake(location.x - textContainerOffset.x, location.y - textContainerOffset.y);
NSInteger indexOfCharacter = [layoutManager characterIndexForPoint:locationOfTouchInTextContainer inTextContainer:textContainer fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints:nullptr];
if (indexOfCharacter >= 0) {
NSURL* url = [textStorage attribute:NSLinkAttributeName atIndex:indexOfCharacter effectiveRange:nullptr];
if (url) {
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:url];
return YES;
}
}
return NO;
}
@end
This generic method works too !
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
guard let strAttributedText = self.attributedText else {
return false
}
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: strAttributedText)
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = Constants.lineFragmentPadding
textContainer.lineBreakMode = self.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = self.numberOfLines
let labelSize = self.bounds.size
textContainer.size = CGSize(width: labelSize.width, height: CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude)
// Find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = gesture.location(in: self)
let xCordLocationOfTouchInTextContainer = locationOfTouchInLabel.x
let yCordLocationOfTouchInTextContainer = locationOfTouchInLabel.y
let locOfTouch = CGPoint(x: xCordLocationOfTouchInTextContainer ,
y: yCordLocationOfTouchInTextContainer)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locOfTouch, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
guard let strLabel = text else {
return false
}
let charCountOfLabel = strLabel.count
if indexOfCharacter < (charCountOfLabel - 1) {
return NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange)
} else {
return false
}
}
And you can call the method with
let text = yourLabel.text
let termsRange = (text as NSString).range(of: fullString)
if yourLabel.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer, inRange: termsRange) {
showCorrespondingViewController()
}
UITapGestureRecognizer come from? Is it an outlet? A property you setup? –
Confiscate Here is my answer based on @Luca Davanzo's answer, override the touchesBegan event instead of a tap gesture:
import UIKit
public protocol TapableLabelDelegate: NSObjectProtocol {
func tapableLabel(_ label: TapableLabel, didTapUrl url: String, atRange range: NSRange)
}
public class TapableLabel: UILabel {
private var links: [String: NSRange] = [:]
private(set) var layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
private(set) var textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
private(set) var textStorage = NSTextStorage() {
didSet {
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
}
}
public weak var delegate: TapableLabelDelegate?
public override var attributedText: NSAttributedString? {
didSet {
if let attributedText = attributedText {
textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: attributedText)
} else {
textStorage = NSTextStorage()
links = [:]
}
}
}
public override var lineBreakMode: NSLineBreakMode {
didSet {
textContainer.lineBreakMode = lineBreakMode
}
}
public override var numberOfLines: Int {
didSet {
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = numberOfLines
}
}
public override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
setup()
}
public required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: aDecoder)
setup()
}
public override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
textContainer.size = bounds.size
}
/// addLinks
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - text: text of link
/// - url: link url string
public func addLink(_ text: String, withURL url: String) {
guard let theText = attributedText?.string as? NSString else {
return
}
let range = theText.range(of: text)
guard range.location != NSNotFound else {
return
}
links[url] = range
}
private func setup() {
isUserInteractionEnabled = true
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = numberOfLines
}
public override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
guard let locationOfTouch = touches.first?.location(in: self) else {
return
}
textContainer.size = bounds.size
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.glyphIndex(for: locationOfTouch, in: textContainer)
for (urlString, range) in links {
if NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, range), let url = URL(string: urlString) {
delegate?.tapableLabel(self, didTapUrl: urlString, atRange: range)
}
}
}}
Modified @timbroder code to handle multiple line correctly for swift4.2
extension UITapGestureRecognizer {
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
// Create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: label.attributedText!)
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
let labelSize = label.bounds.size
textContainer.size = labelSize
// Find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.location(in: label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer)
let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(x: (labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
y: (labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: (locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x),
y: 0 );
// Adjust for multiple lines of text
let lineModifier = Int(ceil(locationOfTouchInLabel.y / label.font.lineHeight)) - 1
let rightMostFirstLinePoint = CGPoint(x: labelSize.width, y: 0)
let charsPerLine = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: rightMostFirstLinePoint, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let adjustedRange = indexOfCharacter + (lineModifier * charsPerLine)
var newTargetRange = targetRange
if lineModifier > 0 {
newTargetRange.location = targetRange.location+(lineModifier*Int(ceil(locationOfTouchInLabel.y)))
}
return NSLocationInRange(adjustedRange, newTargetRange)
}
}
UILabel Code
let tapAction = UITapGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(self.tapLabel(gesture:)))
let quote = "For full details please see our privacy policy and cookie policy."
let attributedString = NSMutableAttributedString(string: quote)
let string1: String = "privacy policy", string2: String = "cookie policy"
// privacy policy
let rangeString1 = quote.range(of: string1)!
let indexString1: Int = quote.distance(from: quote.startIndex, to: rangeString1.lowerBound)
attributedString.addAttributes(
[.font: <UIfont>,
.foregroundColor: <UI Color>,
.underlineStyle: 0, .underlineColor:UIColor.clear
], range: NSRange(location: indexString1, length: string1.count));
// cookie policy
let rangeString2 = quote.range(of: string2)!
let indexString2: Int = quote.distance(from: quote.startIndex, to: rangeString2.lowerBound )
attributedString.addAttributes(
[.font: <UIfont>,
.foregroundColor: <UI Color>,
.underlineStyle: 0, .underlineColor:UIColor.clear
], range: NSRange(location: indexString2, length: string2.count));
let label = UILabel()
label.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 200, width: 375, height: 100)
label.isUserInteractionEnabled = true
label.addGestureRecognizer(tapAction)
label.attributedText = attributedString
Code to recognise the Tap
@objc
func tapLabel(gesture: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
if gesture.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: <UILabel>, inRange: termsLabelRange {
print("Terms of service")
} else if gesture.didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label:<UILabel> inRange: privacyPolicyLabelRange) {
print("Privacy policy")
} else {
print("Tapped none")
}
}
We use the convenient solution from zekel with the UITapGestureRecognizer category.
This uses NSTextContainer, like many answers to this question do.
However, this returned wrong character indexes. Apparently because NSTextContainer was missing information about the font style, as indicated by these other posts:
- https://mcmap.net/q/101815/-get-index-of-character-in-uilabel-from-tap
- https://mcmap.net/q/101815/-get-index-of-character-in-uilabel-from-tap
After changing:
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:label.attributedText];
To:
// Apply the font of the label to the attributed text:
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedText = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithAttributedString:label.attributedText];
NSMutableParagraphStyle *paragraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle.new;
paragraphStyle.alignment = self.label.textAlignment;
[attributedText addAttributes:@{NSFontAttributeName: label.font, NSParagraphStyleAttributeName: paragraphStyle}
range:NSMakeRange(0, label.attributedText.string.length)];
// Init with attributed text from label:
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:attributedText];
The result was significantly better, the tap area was now correctly starting at the first character of our target string. But the last character returned still NO. We expected that this was related to the fact that our target string has attributes to set the font weight to UIFontWeightSemibold. While the above code improvement applies label.font on the entire string, which has a regular weight.
To solve this we improved the above code snippet even further, by iterating over all attributed ranges, in order to support multiple font styles in the text:
// According to https://mcmap.net/q/101815/-get-index-of-character-in-uilabel-from-tap it's required to apply the paragraph style and font of the UILabel.
// However, the attributed string might contain font formatting as well, e.g. to emphasize a word in a different font style.
// Therefor copy all attributes:
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedText = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithAttributedString:label.attributedText];
[label.attributedText enumerateAttributesInRange:NSMakeRange(0, label.attributedText.length)
options:0
usingBlock:^(NSDictionary<NSAttributedStringKey,id> * _Nonnull attrs, NSRange range, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
// Add each attribute:
[attributedText addAttributes:attrs
range:range];
// In case the attributes of this range do NOT contain a font specifier, apply the font from the UILabel:
if (![attrs objectForKey:NSFontAttributeName]) {
[attributedText addAttributes:@{ NSFontAttributeName : label.font }
range:range];
}
}];
// Init the storage with the font attributed text:
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:attributedText];
Now the method returns YES for every character in the semi-bold string range, which is the expected result.
TAGS #Swift2.0
I take inspiration on - excellent - @NAlexN's answer and I decide to write by myself a wrapper of UILabel.
I also tried TTTAttributedLabel but I can't make it works.
Hope you can appreciate this code, any suggestions are welcome!
import Foundation
@objc protocol TappableLabelDelegate {
optional func tappableLabel(tabbableLabel: TappableLabel, didTapUrl: NSURL, atRange: NSRange)
}
/// Represent a label with attributed text inside.
/// We can add a correspondence between a range of the attributed string an a link (URL)
/// By default, link will be open on the external browser @see 'openLinkOnExternalBrowser'
class TappableLabel: UILabel {
// MARK: - Public properties -
var links: NSMutableDictionary = [:]
var openLinkOnExternalBrowser = true
var delegate: TappableLabelDelegate?
// MARK: - Constructors -
override func awakeFromNib() {
super.awakeFromNib()
self.enableInteraction()
}
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
self.enableInteraction()
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: aDecoder)
}
private func enableInteraction() {
self.userInteractionEnabled = true
self.addGestureRecognizer(UITapGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: Selector("didTapOnLabel:")))
}
// MARK: - Public methods -
/**
Add correspondence between a range and a link.
- parameter url: url.
- parameter range: range on which couple url.
*/
func addLink(url url: String, atRange range: NSRange) {
self.links[url] = range
}
// MARK: - Public properties -
/**
Action rised on user interaction on label.
- parameter tapGesture: gesture.
*/
func didTapOnLabel(tapGesture: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
let labelSize = self.bounds.size;
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSizeZero)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: self.attributedText!)
// configure textContainer for the label
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = self.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = self.numberOfLines
textContainer.size = labelSize;
// configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
// find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = tapGesture.locationInView(self)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRectForTextContainer(textContainer)
let textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y)
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake(locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x,
locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndexForPoint(locationOfTouchInTextContainer,
inTextContainer:textContainer,
fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
for (url, value) in self.links {
if let range = value as? NSRange {
if NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, range) {
let url = NSURL(string: url as! String)!
if self.openLinkOnExternalBrowser {
UIApplication.sharedApplication().openURL(url)
}
self.delegate?.tappableLabel?(self, didTapUrl: url, atRange: range)
}
}
}
}
}
0 cause that locationOfTouchInTextContainer.x was negative. I try to use let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.glyphIndex(for: locationOfTouch, in: textContainer) instead, and works well. –
Defunct - (BOOL)didTapAttributedTextInLabel:(UILabel *)label inRange:(NSRange)targetRange{
NSLayoutManager *layoutManager = [NSLayoutManager new];
NSTextContainer *textContainer = [[NSTextContainer alloc] initWithSize:CGSizeZero];
NSTextStorage *textStorage = [[NSTextStorage alloc] initWithAttributedString:label.attributedText];
[layoutManager addTextContainer:textContainer];
[textStorage addLayoutManager:layoutManager];
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0;
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode;
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines;
CGSize labelSize = label.bounds.size;
textContainer.size = labelSize;
CGPoint locationOfTouchInLabel = [self locationInView:label];
CGRect textBoundingBox = [layoutManager usedRectForTextContainer:textContainer];
CGPoint textContainerOffset = CGPointMake((labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
(labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * 0.5 - textBoundingBox.origin.y);
CGPoint locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPointMake(locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x,
locationOfTouchInLabel.y - textContainerOffset.y);
NSUInteger indexOfCharacter =[layoutManager characterIndexForPoint:locationOfTouchInTextContainer inTextContainer:textContainer fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints:nil];
return NSLocationInRange(indexOfCharacter, targetRange);
}
This is a Xamarin.iOS c# implementation based on Kedar's answer.
MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme implementation with ShouldInteractWithUrl override:
// Inspired from https://mcmap.net/q/101816/-shouldchangetextinrange-is-not-called-for-uitextview
internal class MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme : UITextView, IUITextViewDelegate
{
public MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme()
{
Initialize();
}
public MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme(Foundation.NSCoder coder) : base(coder)
{
Initialize();
}
public MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme(Foundation.NSObjectFlag t) : base(t)
{
Initialize();
}
public MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme(IntPtr handle) : base(handle)
{
Initialize();
}
public MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme(CoreGraphics.CGRect frame) : base(frame)
{
Initialize();
}
public MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme(CoreGraphics.CGRect frame, NSTextContainer textContainer) : base(frame, textContainer)
{
Initialize();
}
void Initialize()
{
Delegate = this;
}
[Export("textView:shouldInteractWithURL:inRange:")]
public new bool ShouldInteractWithUrl(UITextView textView, NSUrl URL, NSRange characterRange)
{
if (URL.Scheme.CompareTo(@"username") == 0)
{
// Launch the Activity
return false;
}
// The system will handle the URL
return base.ShouldInteractWithUrl(textView, URL, characterRange);
}
}
Converted objective-C code in c# becomes:
MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme uiHabitTile = new MyClickableTextViewWithCustomUrlScheme();
uiHabitTile.Selectable = true;
uiHabitTile.ScrollEnabled = false;
uiHabitTile.Editable = false;
// https://mcmap.net/q/99746/-create-tap-able-quot-links-quot-in-the-nsattributedstring-of-a-uilabel
string wholeTitle = @"This is an example by marcelofabri";
NSMutableAttributedString attributedString = new NSMutableAttributedString(wholeTitle);
attributedString.AddAttribute(UIStringAttributeKey.Link,
new NSString("username://marcelofabri"),
attributedString.Value.RangeOfString(@"marcelofabri")
);
NSMutableDictionary<NSString, NSObject> linkAttributes = new NSMutableDictionary<NSString, NSObject>();
linkAttributes[UIStringAttributeKey.ForegroundColor] = UIColor.Green;
linkAttributes[UIStringAttributeKey.UnderlineColor] = UIColor.LightGray;
linkAttributes[UIStringAttributeKey.UnderlineStyle] = new NSNumber((short)NSUnderlineStyle.PatternSolid);
uiHabitTile.AttributedText = attributedString;
Make sure to set Editable = false and Selectable = true to be able to click the link.
Also ScrollEnabled = true allows the textview to size its height correctly.
Swift 5.2
I've found several issues with multiline text labels in previous answers, so I give my final working solution.
It solves the issues with multilines and text alignment.
func didTapAttributedTextInLabel(label: UILabel, inRange targetRange: NSRange) -> Bool {
// Create instances of NSLayoutManager, NSTextContainer and NSTextStorage
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(size: CGSize.zero)
let textStorage = NSTextStorage(attributedString: label.attributedText!)
// Configure layoutManager and textStorage
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
// Configure textContainer
textContainer.lineFragmentPadding = 0.0
textContainer.lineBreakMode = label.lineBreakMode
textContainer.maximumNumberOfLines = label.numberOfLines
let labelSize = label.bounds.size
textContainer.size = labelSize
// Find the tapped character location and compare it to the specified range
let locationOfTouchInLabel = self.location(in: label)
let textBoundingBox = layoutManager.usedRect(for: textContainer)
let textAligmentOffset = aligmentOffset(for: label)
let textContainerOffset = CGPoint(x: (labelSize.width - textBoundingBox.size.width) * textAligmentOffset - textBoundingBox.origin.x,
y: (labelSize.height - textBoundingBox.size.height) * textAligmentOffset - textBoundingBox.origin.y)
let locationOfTouchInTextContainer = CGPoint(x: (locationOfTouchInLabel.x - textContainerOffset.x),
y: 0 )
// Adjust for multiple lines of text
let lineModifier = Int(floor(locationOfTouchInLabel.y / label.font.lineHeight)) - 1
let rightMostFirstLinePoint = CGPoint(x: labelSize.width,
y: 0)
let charsPerLine = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: rightMostFirstLinePoint, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let indexOfCharacter = layoutManager.characterIndex(for: locationOfTouchInTextContainer, in: textContainer, fractionOfDistanceBetweenInsertionPoints: nil)
let adjustedRange = indexOfCharacter + (lineModifier * charsPerLine)
return NSLocationInRange(adjustedRange, targetRange)
}
private func aligmentOffset(for label: UILabel) -> CGFloat {
switch label.textAlignment {
case .left, .natural, .justified:
return 0.0
case .center:
return 0.5
case .right:
return 1.0
@unknown default:
return 0.0
}
}
Starting from iOS 15, SwiftUI comes with built-in support Markdown markup language so text in Markdown:
Text("You can [click this link](https://www.example.com) to visit the website.")
Or as a simplest example with using SwiftUI you can do it like this:
HStack() {
Text("Open the")
.foregroundColor(.black)
Link(destination: URL(string: "https://www.example.com/TOS.html")!) {
Text("link")
.foregroundColor(.blue)
.underline()
}
Text("in browser")
.foregroundColor(.black)
}
NSString *string = name;
NSError *error = NULL;
NSDataDetector *detector =
[NSDataDetector dataDetectorWithTypes:(NSTextCheckingTypes)NSTextCheckingTypeLink | NSTextCheckingTypePhoneNumber
error:&error];
NSArray *matches = [detector matchesInString:string
options:0
range:NSMakeRange(0, [string length])];
for (NSTextCheckingResult *match in matches)
{
if (([match resultType] == NSTextCheckingTypePhoneNumber))
{
NSString *phoneNumber = [match phoneNumber];
NSLog(@" Phone Number is :%@",phoneNumber);
label.enabledTextCheckingTypes = NSTextCheckingTypePhoneNumber;
}
if(([match resultType] == NSTextCheckingTypeLink))
{
NSURL *email = [match URL];
NSLog(@"Email is :%@",email);
label.enabledTextCheckingTypes = NSTextCheckingTypeLink;
}
if (([match resultType] == NSTextCheckingTypeLink))
{
NSURL *url = [match URL];
NSLog(@"URL is :%@",url);
label.enabledTextCheckingTypes = NSTextCheckingTypeLink;
}
}
label.text =name;
}
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.


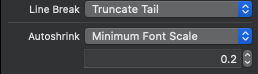


Swift 4solution. It usesUITextViewbut makes it behave like aUILabel. I tried the solutions on here, and failed to get accurate link detection. – BurrusUITextView, it has delegateshouldInteractWiththat you can customize how the action should be. – Beaty