I'm using a MySQL database.
In which situations should I create a unique key or a primary key?
I'm using a MySQL database.
In which situations should I create a unique key or a primary key?
Primary Key:
NULL - e.g. MySQL adds NOT NULLUnique Key:
NULL valuesNULL ; multiple rows can have NULL values and therefore may not be considered "unique"Unique Key (UK): It's a column or a group of columns that can identify a uniqueness in a row.
Primary Key (PK): It's also a column or group of columns that can identify a uniqueness in a row.
So the Primary key is just another name for unique key, but the default implementation in SQL Server is different for Primary and Unique Key.
By Default:
It really depends what is your aim when deciding whether to create a UK or PK. It follows an analogy like "If there is a team of three people, so all of them are peers, but there will be one of them who will be a pair of peers: PK and UK has similar relation.". I would suggest reading this article: The example given by the author may not seem suitable, but try to get an overall idea.
http://tsqltips.blogspot.com/2012/06/difference-between-unique-key-and.html
[table_name]_pkey) is added to the table (I've heard this referred to as a surrogate key). Source: postgresqltutorial.com/postgresql-primary-key I'm new to all this so I'd appreciate a more knowledgeable poster to point out the nuances I missed. –
Nelidanelie For an organization or a business, there are so many physical entities (such as people, resources, machines, etc.) and virtual entities (their Tasks, transactions, activities). Typically, business needs to record and process information of those business entities. These business entities are identified within a whole business domain by a Key.
As per RDBMS prospective, Key (a.k.a Candidate Key) is a value or set of values that uniquely identifies an entity.
For a DB-Table, there are so many keys are exist and might be eligible for Primary Key. So that all keys, primary key, unique key, etc are collectively called as Candidate Key. However, DBA selected a key from candidate key for searching records is called Primary key.
Difference between Primary Key and Unique key
1. Behavior: Primary Key is used to identify a row (record) in a table, whereas Unique-key is to prevent duplicate values in a column (with the exception of a null entry).
2. Indexing: By default SQL-engine creates Clustered Index on primary-key if not exists and Non-Clustered Index on Unique-key.
3. Nullability: Primary key does not include Null values, whereas Unique-key can.
4. Existence: A table can have at most one primary key, but can have multiple Unique-key.
5. Modifiability: You can’t change or delete primary values, but Unique-key values can.
For more information and Examples:
A primary key must be unique.
A unique key does not have to be the primary key - see candidate key.
That is, there may be more than one combination of columns on a table that can uniquely identify a row - only one of these can be selected as the primary key. The others, though unique are candidate keys.
| Primary Key | Unique Key |
|---|---|
A primary key can't accept NULL values |
Unique key can accept NULL values, so problematic in the context of being unique |
| A primary key cannot contain duplicate values | A unique key also cannot contain duplicate values |
| We can have only one primary key in a table | We can have more than one unique key in a table |
| We can make a primary key from one or more table fields | We can also make a unique key from one or more table fields |
| By default, a primary key creates a clustered index | By default, a unique key creates a non-clustered unique index |
| It is used to identify each record in the table | It prevents storing duplicate entries in a column |
A primary key has the semantic of identifying the row of a database. Therefore there can be only one primary key for a given table, while there can be many unique keys.
Also for the same reason a primary key cannot be NULL (at least in Oracle, not sure about other databases)
Since it identifies the row it should never ever change. Changing primary keys are bound to cause serious pain and probably eternal damnation.
Therefor in most cases you want some artificial id for primary key which isn't used for anything but identifying single rows in the table.
Unique keys on the other hand may change as much as you want.
A Primary key is a unique key.
Each table must have at most ONE primary key but it can have multiple unique key. A primary key is used to uniquely identify a table row. A primary key cannot be NULL since NULL is not a value.
Explaining why rather than how:
Purpose of Primary Key: To identify a row in a database uniquely => A row represents a single instance of the entity type modeled by the table. A primary key enforces integrity of an entity, AKA Entity Integrity. Primary Key would be a clustered index i.e. it defines the order in which data is physically stored in a table.
Purpose of Unique Key: Ok, with the Primary Key we have a way to uniquely identify a row. But I have a business need such that, another column/a set of columns should have unique values. Well, technically, given that this column(s) is unique, it can be a candidate to enforce entity integrity. But for all we know, this column can contain data originating from an external organization that I may have a doubt about being unique. I may not trust it to provide entity integrity. I just make it a unique key to fulfill my business requirement.
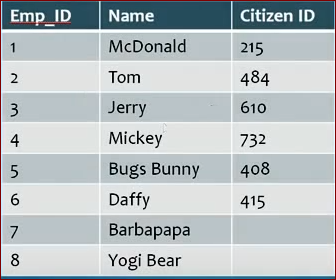
If your Database design is such that their is no need of foreign key, then you can go with Unique key( but remember unique key allow single null value ).
If you database demand foreign key then you leave with no choice you have to go with primary key.
To see the difference between unique and primary key visit here
Unique key:
It should be used when you have to have a unique value. In the case of unique key it means null values are also allowed. Unique keys are those keys which are unique and not similar in that column. For example your pet name. It can be nothing, like null, and if you are asking in context of a database then every null is different from another null in the database. (EXCEPT SQL Server where null=null is true.)
Primary key:
It should be used when you have to give uniquely identify a row. A primary is a key which is unique for every row in a database and doesn't allow null. So you might have seen that the database has a column which is auto incremented and it is the primary key of the table. It can be used as a foreign key in another table. For example: orderId on an order Table, billId in a bill Table.
When to use:
Use a primary key in the column which cannot be null in the table that you are using as foreign key in another table for creating a relationship.
Use a unique key in a table where it doesn't affect whether you take the null for the particular column in the table or in the whole database. For example snacks in the restaurant when it is possible you don't take snacks in a restaurant
difference between Primary Key and Unique Key
Both Primary key and Unique Key are used to uniquely define of a row in a table.
Primary Key creates a clustered index of the column whereas a Unique creates an unclustered index of the column.
A Primary Key doesn’t allow NULL value, however a Unique Key does allow one NULL value.
Simply Primary Key is a unique and can't be null, unique can be null and may not be unique.
may not be unique means here? –
Moria The main purpose of the primary key is to provide a means to identify each record in the table.
The primary key provides a means to identity the row, using data within the row. A primary key can be based on one or more columns, such as first and last name; however, in many designs, the primary key is an auto-generated number from an identity column.
A primary key has the following characteristics:
A unique key is also called a unique constraint. A unique constraint can be used to ensure rows are unique within the database.
Don’t we already do that with the primary key? Yep, we do, but a table may have several sets of columns which you want unique.
In SQL Server the unique key has the following characteristics:
source : here
A primary key’s main features are:
It must contain a unique value for each row of data. It cannot contain null values. Only one Primary key in a table.
A Unique key’s main features are:
It can also contain a unique value for each row of data.
It can also contain null values.
Multiple Unique keys in a table.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.
PRIMARY KEY = UNIQUE KEY + Not Null CONSTRAINT– Iden