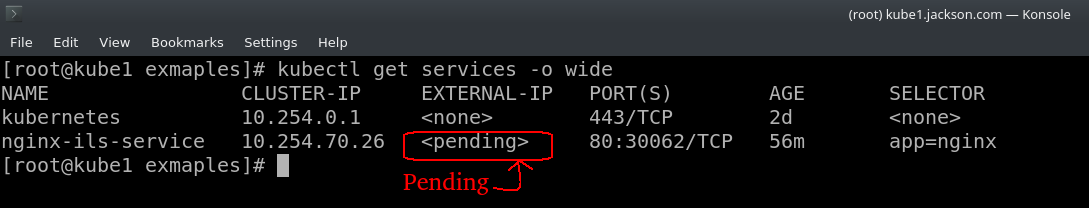
I am trying to deploy nginx on kubernetes, kubernetes version is v1.5.2, I have deployed nginx with 3 replica, YAML file is below,
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deployment-example
spec:
replicas: 3
revisionHistoryLimit: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.10
ports:
- containerPort: 80
and now I want to expose its port 80 on port 30062 of node, for that I created a service below,
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-ils-service
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
nodePort: 30062
selector:
app: nginx
type: LoadBalancer
this service is working good as it should be, but it is showing as pending not only on kubernetes dashboard also on terminal.