Context
After quite some experimenting, I automated generating a nested Sphinx structure of all python source and test files including their classes and functions (which is the main difference with the module overview):
:ref:`modindex`
So I thought I'd share it here, it implements the structure given in the magnifiscent answer by P.G.
Limitations
It assumes the following repository structure:
├── docs
│ ├── build
│ ├── source/conf.py
├── src/projectname/__main__.py
├── src/projectname/some_subdirectory/some_other_file.py
├── test/test_something.py
and it does not include the __main__.py file.
Conf.py
Below is the docs/source/conf.py that automates generating the documentation:
"""Configuration file for the Sphinx documentation builder.
For the full list of built-in configuration values, see the documentation:
https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/configuration.html
-- Project information -----------------------------------------------------
https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/configuration.html#project-information
""" #
import os
import shutil
import sys
from datetime import datetime
from os.path import basename, normpath
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Tuple
# This file only contains a selection of the most common options. For a full
# list see the documentation:
# https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/configuration.html
# -- Path setup --------------------------------------------------------------
# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
#
# This makes the Sphinx documentation tool look at the root of the repository
# for .py files.
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath("../.."))
# -- Project information -----------------------------------------------------
def get_abs_root_path() -> str:
"""Returns the absolute path of the root dir of this repository.
Throws an error if the current path does not end in /docs/source.
"""
current_abs_path: str = os.getcwd()
assert_abs_path_ends_in_docs_source(current_abs_path=current_abs_path)
abs_root_path: str = current_abs_path[:-11]
return abs_root_path
def assert_abs_path_ends_in_docs_source(*, current_abs_path: str) -> None:
"""Asserts the current absolute path ends in /docs/source."""
if current_abs_path[-12:] != "/docs/source":
print(f"current_abs_path={current_abs_path}")
raise ValueError(
"Error, current_abs_path is expected to end in: /docs/source"
)
def split_filepath_into_three(*, filepath: str) -> Tuple[str, str, str]:
"""Split a file path into directory path, filename, and extension.
Args:
filepath (str): The input file path.
Returns:
Tuple[str, str, str]: A tuple containing directory path, filename, and
extension.
"""
path_obj: Path = Path(filepath)
directory_path: str = str(path_obj.parent)
filename = os.path.splitext(path_obj.name)[0]
extension = path_obj.suffix
return directory_path, filename, extension
def loop_over_files(*, abs_search_path: str, extension: str) -> List[str]:
"""Loop over all files in the specified root directory and its child
directories.
Args:
root_directory (str): The root directory to start the traversal from.
"""
filepaths: List[str] = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(abs_search_path):
for filename in files:
extension_len: int = -len(extension)
if filename[extension_len:] == extension:
filepath = os.path.join(root, filename)
filepaths.append(filepath)
return filepaths
def is_unwanted(*, filepath: str) -> bool:
"""Hardcoded filter of unwanted datatypes."""
base_name = os.path.basename(filepath)
if base_name == "__init__.py":
return True
if base_name.endswith("pyc"):
return True
if "something/another" in filepath:
return True
return False
def filter_unwanted_files(*, filepaths: List[str]) -> List[str]:
"""Filters out unwanted files from a list of file paths.
Unwanted files include:
- Files named "init__.py"
- Files ending with "swag.py"
- Files in the subdirectory "something/another"
Args:
filepaths (List[str]): List of file paths.
Returns:
List[str]: List of filtered file paths.
"""
return [
filepath
for filepath in filepaths
if not is_unwanted(filepath=filepath)
]
def get_abs_python_filepaths(
*, abs_root_path: str, extension: str, root_folder_name: str
) -> List[str]:
"""Returns all the Python files in this repo."""
# Get the file lists.
py_files: List[str] = loop_over_files(
abs_search_path=f"{abs_root_path}docs/source/../../{root_folder_name}",
extension=extension,
)
# Merge and filter to preserve the relevant files.
filtered_filepaths: List[str] = filter_unwanted_files(filepaths=py_files)
return filtered_filepaths
def abs_to_relative_python_paths_from_root(
*, abs_py_paths: List[str], abs_root_path: str
) -> List[str]:
"""Converts the absolute Python paths to relative Python filepaths as seen
from the root dir."""
rel_py_filepaths: List[str] = []
for abs_py_path in abs_py_paths:
flattened_filepath = os.path.normpath(abs_py_path)
if abs_root_path not in flattened_filepath:
print(f"abs_root_path={abs_root_path}")
print(f"flattened_filepath={flattened_filepath}")
raise ValueError(
"Error, root dir should be in flattened_filepath."
)
rel_py_filepaths.append(
os.path.relpath(flattened_filepath, abs_root_path)
)
return rel_py_filepaths
def delete_directory(*, directory_path: str) -> None:
"""Deletes a directory and its contents.
Args:
directory_path (Union[str, bytes]): Path to the directory to be
deleted.
Raises:
FileNotFoundError: If the specified directory does not exist.
PermissionError: If the function lacks the necessary permissions to
delete the directory.
OSError: If an error occurs while deleting the directory.
Returns:
None
"""
if os.path.exists(directory_path) and os.path.isdir(directory_path):
shutil.rmtree(directory_path)
def create_relative_path(*, relative_path: str) -> None:
"""Creates a relative path if it does not yet exist.
Args:
relative_path (str): Relative path to create.
Returns:
None
"""
if not os.path.exists(relative_path):
os.makedirs(relative_path)
if not os.path.exists(relative_path):
raise NotADirectoryError(f"Error, did not find:{relative_path}")
def create_rst(
*,
autogen_dir: str,
rel_filedir: str,
filename: str,
py_type: str,
) -> None:
"""Creates a reStructuredText (.rst) file with automodule directives.
Args:
rel_filedir (str): Path to the directory where the .rst file will be
created.
filename (str): Name of the .rst file (without the .rst extension).
Returns:
None
"""
if py_type == "src":
if rel_filedir[:4] != "src/":
raise ValueError(
"Expected relative file dir for src files to start with:src/"
)
prelude = f"{rel_filedir[4:]}.".replace("/", ".")
elif py_type == "test":
prelude = f"{rel_filedir}.".replace("/", ".")
else:
raise ValueError(f"Error, py_type={py_type} is not supported.")
# if filename != "__main__":
title_underline = "=" * len(f"{filename}-module")
rst_content = f"""
.. _{filename}-module:
{filename} Module
{title_underline}
.. automodule:: {prelude}{filename}
:members:
:undoc-members:
:show-inheritance:
"""
rst_filepath: str = os.path.join(
f"{autogen_dir}{rel_filedir}", f"{filename}.rst"
)
with open(rst_filepath, "w", encoding="utf-8") as rst_file:
rst_file.write(rst_content)
def generate_rst_per_code_file(
*,
extension: str,
) -> List[str]:
"""Generates a parameterised .rst file for each .py file of the project, to
automatically include its documentation in Sphinx.
Returns rst filepaths.
"""
abs_root_path: str = get_abs_root_path()
abs_src_py_paths: List[str] = get_abs_python_filepaths(
abs_root_path=abs_root_path,
extension=extension,
root_folder_name="src",
)
abs_test_py_paths: List[str] = get_abs_python_filepaths(
abs_root_path=abs_root_path,
extension=extension,
root_folder_name="test",
)
current_abs_path: str = os.getcwd()
autogen_dir: str = f"{current_abs_path}/autogen/"
prepare_rst_directories(autogen_dir=autogen_dir)
rst_paths: List[str] = []
rst_paths.extend(
create_rst_files(
abs_root_path=abs_root_path,
autogen_dir=autogen_dir,
abs_py_paths=abs_src_py_paths,
py_type="src",
)
)
rst_paths.extend(
create_rst_files(
abs_root_path=abs_root_path,
autogen_dir=autogen_dir,
abs_py_paths=abs_test_py_paths,
py_type="test",
)
)
return rst_paths
def prepare_rst_directories(*, autogen_dir: str) -> None:
"""Creates the output directory for the auto-generated .rst documentation
files."""
delete_directory(directory_path=autogen_dir)
create_relative_path(relative_path=autogen_dir)
def create_rst_files(
*,
abs_root_path: str,
autogen_dir: str,
abs_py_paths: List[str],
py_type: str,
) -> List[str]:
"""Loops over the python files of py_type src or test, and creates the .rst
files that point to the actual .py file such that Sphinx can generate its
documentation on the fly."""
rel_root_py_paths: List[str] = abs_to_relative_python_paths_from_root(
abs_py_paths=abs_py_paths, abs_root_path=abs_root_path
)
rst_paths: List[str] = []
# Create file for each py file.
for rel_root_py_path in rel_root_py_paths:
if "__main__.py" not in rel_root_py_path:
rel_filedir: str
filename: str
rel_filedir, filename, _ = split_filepath_into_three(
filepath=rel_root_py_path
)
create_relative_path(relative_path=f"{autogen_dir}{rel_filedir}")
create_rst(
autogen_dir=autogen_dir,
rel_filedir=rel_filedir,
filename=filename,
py_type=py_type,
)
rst_path: str = os.path.join(
f"autogen/{rel_filedir}", f"{filename}"
)
rst_paths.append(rst_path)
return rst_paths
def generate_index_rst(*, filepaths: List[str], use_flat_list: bool) -> str:
"""Generates the list of all the auto-generated rst files."""
now = datetime.now().strftime("%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y")
# TODO: make filepaths relative nested directories.
content = f"""\
.. jsonmodipy documentation main file, created by
sphinx-quickstart on {now}.
You can adapt this file completely to your liking, but it should at least
contain the root `toctree` directive.
.. include:: manual.rst
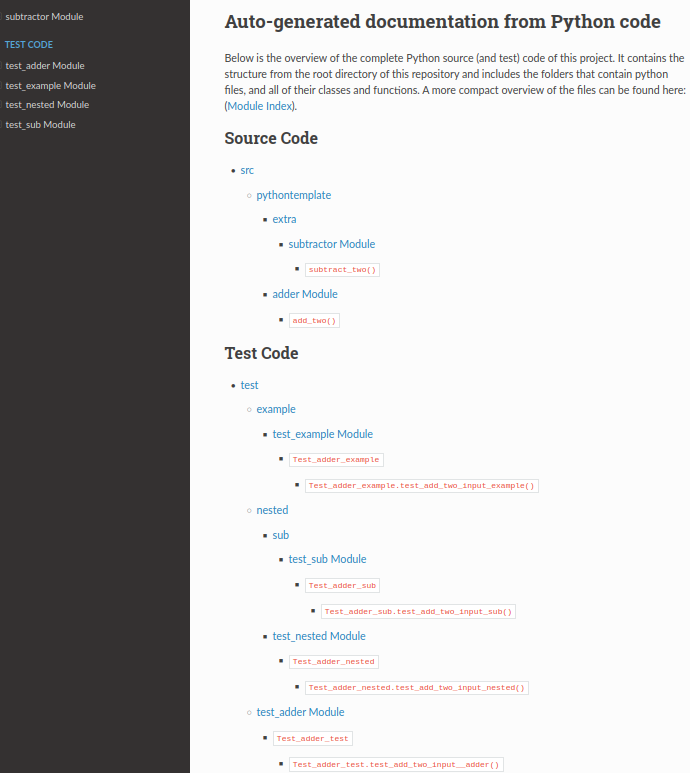
Auto-generated documentation from Python code
=============================================
Below is the overview of the complete Python source (and test) code of this
project. It contains the structure from the root directory of this repository
and includes the folders that contain python files, and all of their classes
and functions. A more compact overview of the files can be found
here:(:ref:`modindex`).
"""
if use_flat_list:
content += get_flat_list_of_file_documentation_rst_content(
filepaths=filepaths
)
else:
content += get_nested_documentation_structure_rst_content()
content += """
Code visualisation
==================
TODO: include auto-generated PlantUML of call graph from main that only
contains functions and classes directly coded in this project (skipping
function calls that are included from an external library).
Indices and tables
==================
* :ref:`genindex`
* :ref:`modindex`
* :ref:`search`
"""
return content
def get_flat_list_of_file_documentation_rst_content(
*, filepaths: List[str]
) -> str:
"""Returns the rst content in the main page for the nested/hierarchical
overview of the source code and test code (separately)."""
content: str = """
.. toctree::
:numbered:
:caption: Source Code
"""
for filepath in filepaths:
if filepath[:12] == "autogen/src/":
content += f"\n {filepath}"
content += """
.. toctree::
:numbered:
:caption: Test Code
"""
for filepath in filepaths:
if filepath[:13] == "autogen/test/":
content += f"\n {filepath}"
return content
def get_nested_documentation_structure_rst_content() -> str:
"""Returns the rst content in the main page for the nested/hierarchical
overview of the source code and test code (separately)."""
create_index_files_per_rst_dir(
abs_rst_path=f"{get_abs_root_path()}docs/source/autogen/src/"
)
create_index_files_per_rst_dir(
abs_rst_path=f"{get_abs_root_path()}docs/source/autogen/test/"
)
return """
.. toctree::
:caption: Source Code
autogen/src/index.rst
.. toctree::
:caption: Test Code
autogen/test/index.rst
"""
def write_index_rst(
*, filepaths: List[str], output_file: str, use_flat_list: bool
) -> None:
"""Creates an index.rst file that is used to generate the Sphinx
documentation."""
index_rst_content = generate_index_rst(
filepaths=filepaths, use_flat_list=use_flat_list
)
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as index_file:
index_file.write(index_rst_content)
def get_dir_structure_as_relative_paths(*, abs_target_path: str) -> List[str]:
"""Replicates the directory structure from abs_path to target_dir,
including nested folders.
Args:
abs_path: The absolute path of the source directory.
target_dir: The absolute path of the destination directory where the
structure will be recreated.
"""
relative_target_subpaths: List[str] = []
for root, _, _ in os.walk(abs_target_path):
# Get relative path from abs_pat
rel_path = os.path.relpath(root, abs_target_path)
if rel_path not in [".", "__pycache__"]:
relative_target_subpaths.append(f"/{rel_path}")
return relative_target_subpaths
def get_child_directories(*, abs_path: str) -> List[str]:
"""Lists all child directories within a given path.
Args:
path: The absolute path to the directory.
Returns:
A list containing the names of all child directories.
"""
# Check if the path is valid and exists
if not os.path.exists(abs_path):
raise ValueError(f"Error: Path '{abs_path}' does not exist.")
# Initialize an empty list to store child directory names
child_dirs: List[str] = []
# Loop through all entries in the path
for some_dir_name in os.listdir(abs_path):
# Construct the full path for the current entry
full_path = os.path.join(abs_path, some_dir_name)
# Check if the entry is a directory
if os.path.isdir(full_path):
# If it's a directory, append its name to the list
child_dirs.append(some_dir_name)
# Return the list of child directory names
return child_dirs
def create_nested_index_file(
*, abs_rst_path: str, child_dirs: List[str], rst_filenames: List[str]
) -> None:
"""Creates an index.rst file for a nested .rst directory."""
currentDirName: str = basename(normpath(abs_rst_path))
title_underline = "=" * len(currentDirName)
rst_content: str = f"""
{currentDirName}
{title_underline}
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
"""
for child_dir in child_dirs:
rst_content += f"\n {child_dir}/index.rst"
for rst_filename in rst_filenames:
rst_content += f"\n {rst_filename}"
with open(f"{abs_rst_path}index.rst", "w", encoding="utf-8") as rst_file:
rst_file.write(rst_content)
def create_index_files_per_rst_dir(*, abs_rst_path: str) -> None:
"""Loops over the child directories in abs_rst_path and in each of those
directories, it creates a index.rst file with a toctree that contains the
.rst files in that directory, and the index.rst files of any of its child
directories."""
child_dirs = get_child_directories(abs_path=abs_rst_path)
# Create list of .rst files in that directory (that are not named
# index.rst)
rst_filenames: List[str] = [
f for f in os.listdir(abs_rst_path) if f.endswith(".rst")
]
# Create the .rst file
create_nested_index_file(
abs_rst_path=abs_rst_path,
child_dirs=child_dirs,
rst_filenames=rst_filenames,
)
for child_dir in child_dirs:
abs_rst_child_dir: str = f"{abs_rst_path}{child_dir}/"
# call this function recursively on the child dir.
create_index_files_per_rst_dir(abs_rst_path=abs_rst_child_dir)
# Call functions to generate rst Sphinx documentation structure.
# Readthedocs sets it to contents.rst, but it is index.rst in the used example.
# -- General configuration ---------------------------------------------------
project: str = "pythontemplate"
main_doc: str = "index"
# pylint:disable=W0622
copyright: str = "2024, a-t-0"
author: str = "a-t-0"
the_rst_paths: List[str] = generate_rst_per_code_file(
extension=".py",
)
if len(the_rst_paths) == 0:
raise ValueError(
"Error, did not find any Python files for which documentation needs"
+ " to be generated."
)
write_index_rst(
filepaths=the_rst_paths, output_file="index.rst", use_flat_list=False
)
# Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be
# extensions coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom
# ones.
extensions: List[str] = [
"sphinx.ext.duration",
"sphinx.ext.doctest",
"sphinx.ext.autodoc",
"sphinx.ext.autosummary",
"sphinx.ext.intersphinx",
# Include markdown files in Sphinx documentation
"myst_parser",
]
# Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
templates_path: List[str] = ["_templates"]
# List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
# directories to ignore when looking for source files.
# This pattern also affects html_static_path and html_extra_path.
exclude_patterns: List[str] = []
# -- Options for HTML output -------------------------------------------------
# The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
# a list of builtin themes.
#
# html_theme: str = "alabaster"
html_theme: str = "sphinx_rtd_theme"
# Theme options are theme-specific and customize the look and feel of a theme
# further. For a list of options available for each theme, see the
# documentation.
html_theme_options = {"collapse_navigation": False}
# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
# html_static_path: List[str] = ["_static"]
For completeness, here is the complete template repository.
Visualisation
![enter image description here]()


:dropdown Animalscommand is incorrect. I want to set arbitrary group sections that drop down into real doc pages – Extradition