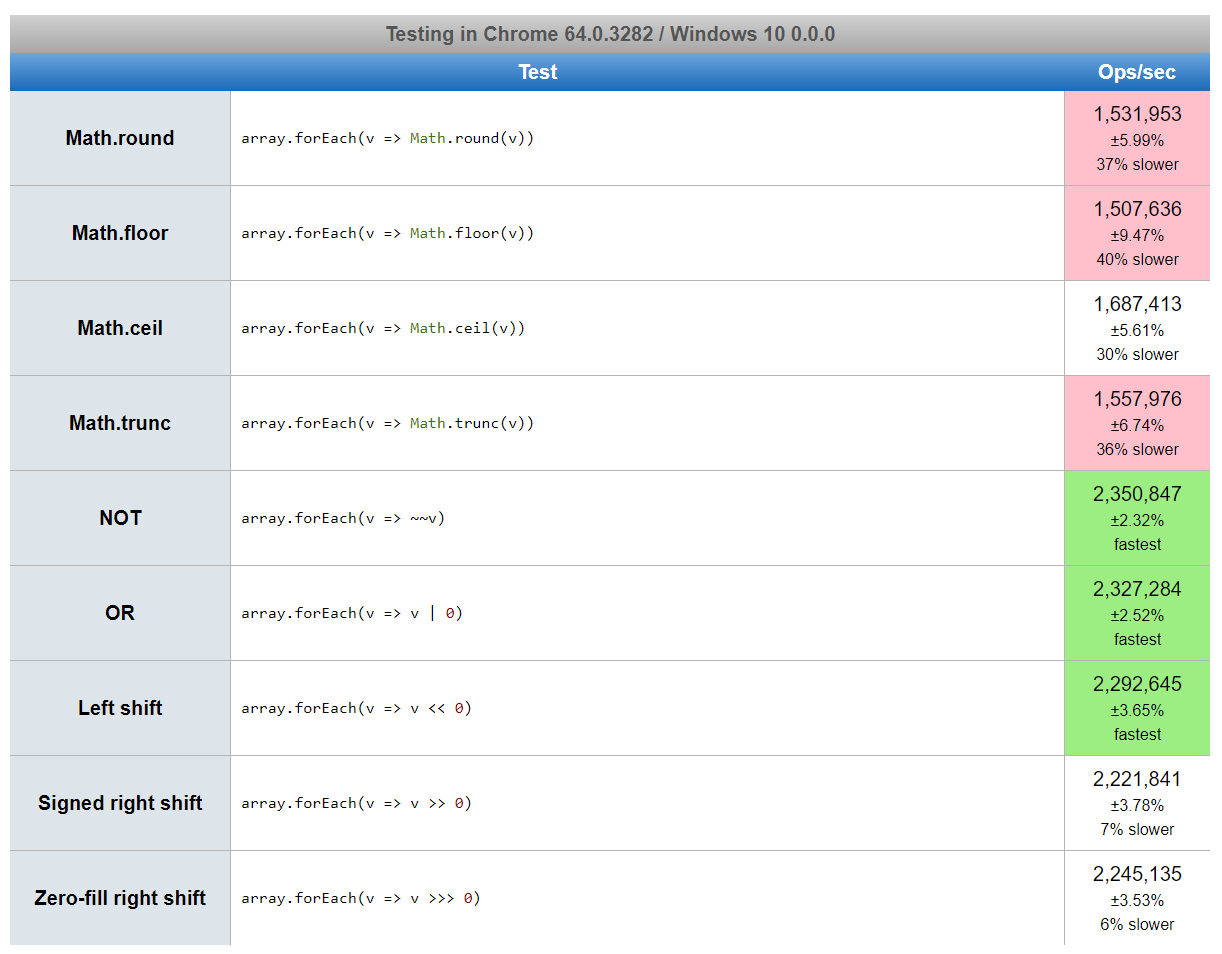
Actually, there is much more alternative ways to remove the decimals from a number. But it's a tradeoff of readability and speed.
Choosing the right one depends on what you need. If you just need to just remove decimals, always use trunc() or bitwise operators.
The floor(), ceil() and round() are conceptually very different from trunc().
Math library
You already know these. Always use them in a standard, non-critical code.
var v = 3.14; [Math.trunc(v), Math.round(v), Math.floor(v), Math.ceil(v)]
// prints results
for different input values you get these results
v t r f c
3.87 : [ 3, 4, 3, 4]
3.14 : [ 3, 3, 3, 4]
-3.14 : [-3, -3, -4, -3]
-3.87 : [-3, -4, -4, -3]
Math.trunc() cuts away (truncates) the decimal places.
Math.round() rounds towards closest integer number.
Math.floor() rounds towards closest lower integer number. 3.5 -> 3 -3.5 -> -4
Math.ceil() rounds towards closest higher integer number. 3.5 -> 4 -3.5 -> -3
But this is more fun :)
If you look at them in the code, it might not be apparent from the first glance what they do, so don't use them in normal code. Though in some cases, they might be useful. For example calculating coordinates in a <canvas/>. They are much faster, but come with limitations.
Conceptually, they work this way:
- The operands are converted to 32-bit signed integers and thus lose all decimal fractions.
ATTENTION:
Numbers with more than 32 bits get their most significant (leftmost) bits discarded and the leftmost bit becomes the new sign bit.
[
0b011100110111110100000000000000110000000000001, // 15872588537857
~~0b011100110111110100000000000000110000000000001, // -1610588159
~~0b10100000000000000110000000000001, // -1610588159
]
Bitwise logical operators
- Each bit in the first operand is paired with the corresponding bit in the second operand. (First bit to first bit, second bit to second bit, and so on.)
- The operator is applied to each pair of bits, and the result is constructed bitwise.
Bitwise shift operators
- These operators take a
value to be shifted and a number of bit positions to shift the value by.
truncating
However, when truncating, we always use a 0, zero, a false as a second operand, that doesn't do anything to the original value, except for converting to integer, in these cases:
~ NOT ~~v
| OR v | 0
<< Left shift v << 0
>> Signed right shift v >> 0
>>> Zero-fill right shift v >>> 0
var v = 3.78;
[ ~~v , v | 0 , v << 0 , v >> 0 , v >>> 0 ]
// prints these results
3.78 : [ 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]
3.14 : [ 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]
-3.74 : [-3, -3, -3, -3, 4294967293]
-3.14 : [-3, -3, -3, -3, 4294967293]
Performance
https://jsperf.com/number-truncating-methods/1
![enter image description here]()

Math.trunc, you’d be wrong.Math.truncis very new and not supported in every browser. – Corolla