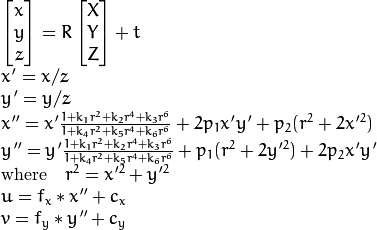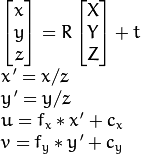Problem statement
I am trying to reproject 2D points to their original 3D coordinates, assuming I know the distance at which each point is. Following the OpenCV documentation, I managed to get it to work with zero-distortions. However, when there are distortions, the result is not correct.
Current approach
So, the idea is to reverse the following:
into the following:
By:
- Geting rid of any distortions using
cv::undistortPoints - Use intrinsics to get back to the normalized camera coordinates by reversing the second equation above
- Multiplying by
zto reverse the normalization.
Questions
Why do I need to subtractThis was my mistake -- I messed up the indexes.f_xandf_yto get back to the normalized camera coordinates (found empirically when testing)? In the code below, in step 2, if I don't subtract -- even the non-distorted result is off- If I include the distortion, the result is wrong -- what am I doing wrong?
Sample code (C++)
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <vector>
std::vector<cv::Point2d> Project(const std::vector<cv::Point3d>& points,
const cv::Mat& intrinsic,
const cv::Mat& distortion) {
std::vector<cv::Point2d> result;
if (!points.empty()) {
cv::projectPoints(points, cv::Mat(3, 1, CV_64F, cvScalar(0.)),
cv::Mat(3, 1, CV_64F, cvScalar(0.)), intrinsic,
distortion, result);
}
return result;
}
std::vector<cv::Point3d> Unproject(const std::vector<cv::Point2d>& points,
const std::vector<double>& Z,
const cv::Mat& intrinsic,
const cv::Mat& distortion) {
double f_x = intrinsic.at<double>(0, 0);
double f_y = intrinsic.at<double>(1, 1);
double c_x = intrinsic.at<double>(0, 2);
double c_y = intrinsic.at<double>(1, 2);
// This was an error before:
// double c_x = intrinsic.at<double>(0, 3);
// double c_y = intrinsic.at<double>(1, 3);
// Step 1. Undistort
std::vector<cv::Point2d> points_undistorted;
assert(Z.size() == 1 || Z.size() == points.size());
if (!points.empty()) {
cv::undistortPoints(points, points_undistorted, intrinsic,
distortion, cv::noArray(), intrinsic);
}
// Step 2. Reproject
std::vector<cv::Point3d> result;
result.reserve(points.size());
for (size_t idx = 0; idx < points_undistorted.size(); ++idx) {
const double z = Z.size() == 1 ? Z[0] : Z[idx];
result.push_back(
cv::Point3d((points_undistorted[idx].x - c_x) / f_x * z,
(points_undistorted[idx].y - c_y) / f_y * z, z));
}
return result;
}
int main() {
const double f_x = 1000.0;
const double f_y = 1000.0;
const double c_x = 1000.0;
const double c_y = 1000.0;
const cv::Mat intrinsic =
(cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << f_x, 0.0, c_x, 0.0, f_y, c_y, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
const cv::Mat distortion =
// (cv::Mat_<double>(5, 1) << 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); // This works!
(cv::Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0.32, 1.24, 0.0013, 0.0013); // This doesn't!
// Single point test.
const cv::Point3d point_single(-10.0, 2.0, 12.0);
const cv::Point2d point_single_projected = Project({point_single}, intrinsic,
distortion)[0];
const cv::Point3d point_single_unprojected = Unproject({point_single_projected},
{point_single.z}, intrinsic, distortion)[0];
std::cout << "Expected Point: " << point_single.x;
std::cout << " " << point_single.y;
std::cout << " " << point_single.z << std::endl;
std::cout << "Computed Point: " << point_single_unprojected.x;
std::cout << " " << point_single_unprojected.y;
std::cout << " " << point_single_unprojected.z << std::endl;
}
Same Code (Python)
import cv2
import numpy as np
def Project(points, intrinsic, distortion):
result = []
rvec = tvec = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
if len(points) > 0:
result, _ = cv2.projectPoints(points, rvec, tvec,
intrinsic, distortion)
return np.squeeze(result, axis=1)
def Unproject(points, Z, intrinsic, distortion):
f_x = intrinsic[0, 0]
f_y = intrinsic[1, 1]
c_x = intrinsic[0, 2]
c_y = intrinsic[1, 2]
# This was an error before
# c_x = intrinsic[0, 3]
# c_y = intrinsic[1, 3]
# Step 1. Undistort.
points_undistorted = np.array([])
if len(points) > 0:
points_undistorted = cv2.undistortPoints(np.expand_dims(points, axis=1), intrinsic, distortion, P=intrinsic)
points_undistorted = np.squeeze(points_undistorted, axis=1)
# Step 2. Reproject.
result = []
for idx in range(points_undistorted.shape[0]):
z = Z[0] if len(Z) == 1 else Z[idx]
x = (points_undistorted[idx, 0] - c_x) / f_x * z
y = (points_undistorted[idx, 1] - c_y) / f_y * z
result.append([x, y, z])
return result
f_x = 1000.
f_y = 1000.
c_x = 1000.
c_y = 1000.
intrinsic = np.array([
[f_x, 0.0, c_x],
[0.0, f_y, c_y],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
])
distortion = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # This works!
distortion = np.array([-0.32, 1.24, 0.0013, 0.0013]) # This doesn't!
point_single = np.array([[-10.0, 2.0, 12.0],])
point_single_projected = Project(point_single, intrinsic, distortion)
Z = np.array([point[2] for point in point_single])
point_single_unprojected = Unproject(point_single_projected,
Z,
intrinsic, distortion)
print "Expected point:", point_single[0]
print "Computed point:", point_single_unprojected[0]
The results for zero-distortion (as mentioned) are correct:
Expected Point: -10 2 12
Computed Point: -10 2 12
But when the distortions are included, the result is off:
Expected Point: -10 2 12
Computed Point: -4.26634 0.848872 12
Update 1. Clarification
This is a camera to image projection -- I am assuming the 3D points are in the camera-frame coordinates.
Update 2. Figured out the first question
OK, I figure out the subtraction of the f_x and f_y -- I was stupid enough to mess up the indexes. Updated the code to correct. The other question still holds.
Update 3. Added Python equivalent code
To increase visibility, adding the Python codes, because it has the same error.