All SQL server instances are stored in the Windows Registry. You can query the registry by using the Windows tool C:\Windows\System32\Regedt32.exe and browse/search there, you can do it by using a language, like C# (see Example 1 there) or even T-SQL (also known as Transact-SQL).
In this answer, I'll show you how to do it with T-SQL. Use this script, which I found here, to determine ServerName, InstanceName, HostName and PortNumber:
set nocount on
Declare @key Varchar(100), @PortNumber varchar(20)
if charindex('\',CONVERT(char(20), SERVERPROPERTY('servername')),0) <>0 begin
set @key = 'SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\Microsoft SQL Server\'+@@servicename+'\MSSQLServer\Supersocketnetlib\TCP'
end else begin
set @key = 'SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\MSSQLServer\MSSQLServer\Supersocketnetlib\TCP'
end
EXEC master..xp_regread @rootkey = 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', @key = @key,
@value_name = 'Tcpport', @value = @PortNumber OUTPUT
SELECT CONVERT(char(20), SERVERPROPERTY('servername')) ServerName,
CONVERT(char(20), SERVERPROPERTY('InstanceName')) InstanceName,
CONVERT(char(20), SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName')) as HostName,
convert(varchar(10), @PortNumber) PortNumber
If the InstanceName is null, it means there is no named instance configured, then you have two, non-exclusive options:
- Specify the
ServerName to access the default instance
- or -
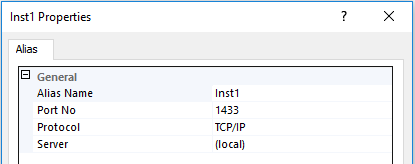
- Use the Sql Server Configuration Manager -> SQL Native Client XX.Y Configuration -> Aliases to define an alias. For example:
![Define_Alias]()
will set up alias Inst1 for the local SQL server. Specify (local)\Inst1,1433 to access it. Of course, instead of (local) you can also use the ServerName.
IMPORTANT: After setting up the alias, you need to restart the SQL service of the related instance or reboot your PC, otherwise it will not be accessible immediately. If you're using a port other than the default port 1433, you might need to open your local firewall in order to get this working.
Note: If you don't have it in the start menu, the SQL Server Configuration Manager can be found in C:\Windows\System32. Look for SqlServerManagerXX.msc (where XX is the SQL version, e.g. XX=11 or XX=13).