I spent too much time on this poorly documented process, that I decided to create some documentation for myself and future developers. I hope it helps.
CodeBuild + CodePipeline
This will connect CodeBuild and CodePipeline such that changes to your GitHub repository triggers CodePipeline to do a Full clone of your repository, that is then passed to CodeBuild which just transforms the local .git folder metadata to be poiting to the correct branch, and then all of the source code plus the Git metadata is deployed to Elastic Beanstalk.
More information about this process can be found here.
- Start creating a CodePipeline pipeline. In the middle of its creation, you wull be prompted to create a CodeBuild project; do it.
- Feel free to select a specific location for the Artifact store (custom S3 bucket).
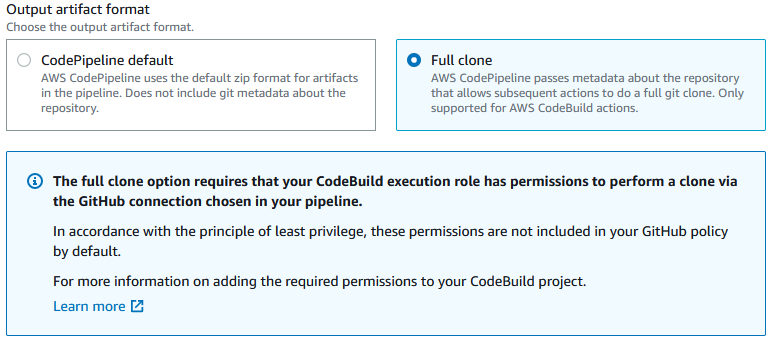
- Select GitHub (Version 2) as the source provider, check "Start the pipeline on source code change", and select Full cone as the output artifact format.
- Select AWS CodeBuild as the Build provider.
- For the Project Name, click onthe "Create project" button and select the below options:
a. Environment image: Managed image
b. Operating system: Amazon Linux 2
c. Runtime(s): Standard
d. For the Buildspec, select "Insert build commands" and click on "Switch to editor". Then paste the below Buildspec code.
e. Enable CloudWatch logs.
- In the Environment variables, insert:
BranchName: #{SourceVariables.BranchName} as Plaintext
CommitId: #{SourceVariables.CommitId} as Plaintext
- Select Single build as the Build type.
- Select AWS Elastic Beanstalk as the Deploy provider.
- Review operation and create the pipeline.
- Create and add a new policy to the newly created
CodeBuildServiceRole role. Choose a name, like projectName-connection-permission and attach the following JSON to it (tutorial):
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "codestar-connections:UseConnection",
"Resource": "arn:aws:codestar-connections:eu-central-1:123456789123:connection/sample-1908-4932-9ecc-2ddacee15095"
}
]
}
PS: Change the Resource value arn:aws:codestar-connections:eu-central-1:123456789123:connection/sample-1908-4932-9ecc-2ddacee15095 from the JSON to your connection ARN. To find the connection ARN for your pipeline, open your pipeline and click the (i) icon on your source action.
- Create and add a new policy to the newly created
CodeBuildServiceRole role. Choose a name, like projectName-s3-access and attach the following JSON to it:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::my-s3-bucket-codepipeline",
"arn:aws:s3:::my-s3-bucket-codepipeline/*"
],
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectVersion",
"s3:GetBucketAcl",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
]
}
]
}
PS: Change the Resource values my-s3-bucket-codepipeline to match with your S3 bucket name for your CodePipeline.
- Edit the inline policy for your
CodePipelineServiceRole role by adding the following object to your Statement array:
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:*"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
- Done.
Buildspec code
version: 0.2
#env:
#variables:
# key: "value"
# key: "value"
#parameter-store:
# key: "value"
# key: "value"
#secrets-manager:
# key: secret-id:json-key:version-stage:version-id
# key: secret-id:json-key:version-stage:version-id
#exported-variables:
# - variable
# - variable
#git-credential-helper: yes
#batch:
#fast-fail: true
#build-list:
#build-matrix:
#build-graph:
phases:
#install:
#If you use the Ubuntu standard image 2.0 or later, you must specify runtime-versions.
#If you specify runtime-versions and use an image other than Ubuntu standard image 2.0, the build fails.
#runtime-versions:
# name: version
# name: version
#commands:
# - command
# - command
#pre_build:
#commands:
# - command
# - command
build:
commands:
- echo Branch - $BranchName
- echo Commit - $CommitId
- echo Checking out branch - $BranchName
- git checkout $BranchName
# - command
# - command
#post_build:
#commands:
# - command
# - command
#reports:
#report-name-or-arn:
#files:
# - location
# - location
#base-directory: location
#discard-paths: yes
#file-format: JunitXml | CucumberJson
#artifacts:
#files:
# - location
# - location
#name: $(date +%Y-%m-%d)
#discard-paths: yes
#base-directory: location
artifacts:
files:
- '**/*'
#cache:
#paths:
# - paths
Additional Info
- Never edit the inline policy that was created by CodePipeline! Only create and add new policies to a role. See this issue.
- The Environment Variables for CodeBuild must be set from
CodePipeline -> Edit: Build -> Environment variables - optional. If you set these variables in CodeBuild -> Edit -> Environment -> Additional configuration -> Environment variables it WON'T WORK!
- For a bigger list of Environment variables during CodeBuild, see Variables List, Action Variables, and CodeBuild variables.
- The Git Full clone option on CodePipeline is not available without CodeBuild. This is a known annoying limitation.
- You can include the
buildspec.yml in your root (top level) project directory. See this.
- The Full clone that CodePipeline does leaves the local repository
.git in a detached HEAD state, meaning that in order to get the branch name you will have to either get it with the help of CodeBuild environment variables to retrieve it from CodePipeline, or to execute the following command (see this):
git branch -a --contains HEAD | sed -n 2p | awk '{ printf $1 }'