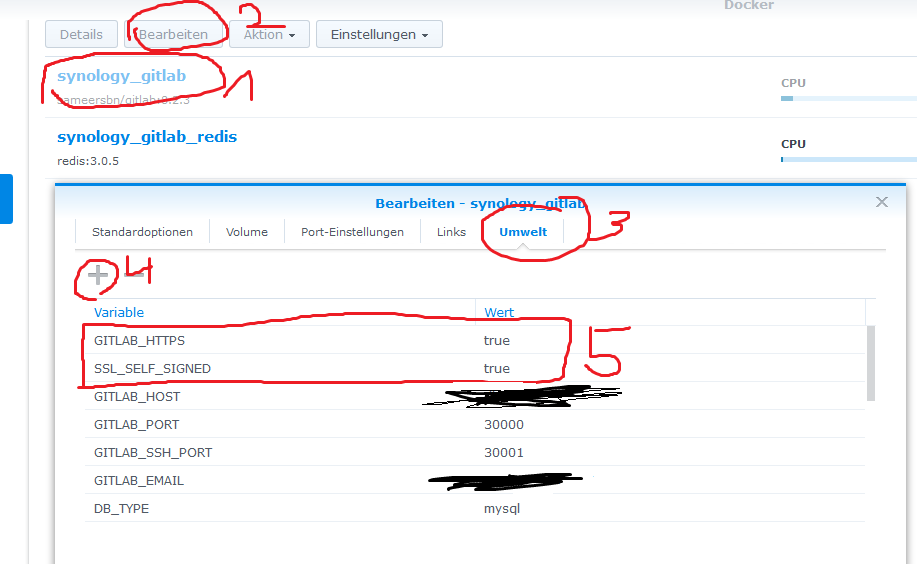
I used @helt solution but looking at the docker info page (https://hub.docker.com/r/sameersbn/gitlab/#ssl), I seen that the certs folder is at "docker/gitlab/gitlab/certs/"...
For the @helt solution, I updated this:
mkdir /volume1/docker/gitlab/gitlab/certs
cd /volume1/docker/gitlab/gitlab/certs
openssl genrsa -out gitlab.key 2048
openssl req -new -key gitlab.key -out gitlab.csr
openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -in gitlab.csr -signkey gitlab.key -out gitlab.crt
openssl dhparam -out dhparam.pem 2048
chmod 400 gitlab.key
When I used only "/volume1/docker/gitlab/certs", when accessing the GitLab page, I had an error page with "PR_END_OF_FILE_ERROR", after using "/volume1/docker/gitlab/gitlab/certs", error disappeared and everything works fine...
My Synology station is a DS718+ running DSM 6.2.2-24922 Update 3.