EDIT: New Library
An updated library exists which can be installed via the following command:
pip install finance-byu
Documentation here: https://fin-library.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
The new library includes Fama Macbeth regression implementations and a Regtable class that can be helpful for reporting results.
This page in the documentation outlines the Fama Macbeth functions: https://fin-library.readthedocs.io/en/latest/fama_macbeth.html
There is an implementation which is very similar to Karl D.'s implementation above with numpy's linear algebra functions, an implementation that utilizes joblib for parallelization to increase performance when a large number of time periods in the data, and an implementation using numba for optimization that shaves off an order of magnitude on small data sets.
Here is an example with a small simulated data set as in the documentation:
>>> from finance_byu.fama_macbeth import fama_macbeth, fama_macbeth_parallel, fm_summary, fama_macbeth_numba
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import time
>>> import numpy as np
>>>
>>> n_jobs = 5
>>> n_firms = 1.0e2
>>> n_periods = 1.0e2
>>>
>>> def firm(fid):
>>> f = np.random.random((int(n_periods),4))
>>> f = pd.DataFrame(f)
>>> f['period'] = f.index
>>> f['firmid'] = fid
>>> return f
>>> df = [firm(i) for i in range(int(n_firms))]
>>> df = pd.concat(df).rename(columns={0:'ret',1:'exmkt',2:'smb',3:'hml'})
>>> df.head()
ret exmkt smb hml period firmid
0 0.766593 0.002390 0.496230 0.992345 0 0
1 0.346250 0.509880 0.083644 0.732374 1 0
2 0.787731 0.204211 0.705075 0.313182 2 0
3 0.904969 0.338722 0.437298 0.669285 3 0
4 0.121908 0.827623 0.319610 0.455530 4 0
>>> result = fama_macbeth(df,'period','ret',['exmkt','smb','hml'],intercept=True)
>>> result.head()
intercept exmkt smb hml
period
0 0.655784 -0.160938 -0.109336 0.028015
1 0.455177 0.033941 0.085344 0.013814
2 0.410705 -0.084130 0.218568 0.016897
3 0.410537 0.010719 0.208912 0.001029
4 0.439061 0.046104 -0.084381 0.199775
>>> fm_summary(result)
mean std_error tstat
intercept 0.506834 0.008793 57.643021
exmkt 0.004750 0.009828 0.483269
smb -0.012702 0.010842 -1.171530
hml 0.004276 0.010530 0.406119
>>> %timeit fama_macbeth(df,'period','ret',['exmkt','smb','hml'],intercept=True)
123 ms ± 117 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each
>>> %timeit fama_macbeth_parallel(df,'period','ret',['exmkt','smb','hml'],intercept=True,n_jobs=n_jobs,memmap=False)
146 ms ± 16.9 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
>>> %timeit fama_macbeth_numba(df,'period','ret',['exmkt','smb','hml'],intercept=True)
5.04 ms ± 5.2 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
Note: Turning off the memmap makes for fair comparison without generating new data at each run. With the memmap, the parallel implementation would simply pull cached results.
Here are a couple simple implementations of the table class also using simulated data:
>>> from finance_byu.regtables import Regtable
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
>>> import numpy as np
>>>
>>>
>>> nobs = 1000
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random((nobs,3))).rename(columns={0:'age',1:'bmi',2:'hincome'})
>>> df['age'] = df['age']*100
>>> df['bmi'] = df['bmi']*30
>>> df['hincome'] = df['hincome']*100000
>>> df['hincome'] = pd.qcut(df['hincome'],16,labels=False)
>>> df['rich'] = df['hincome'] > 13
>>> df['gender'] = np.random.choice(['M','F'],nobs)
>>> df['race'] = np.random.choice(['W','B','H','O'],nobs)
>>>
>>> regformulas = ['bmi ~ age',
>>> 'bmi ~ np.log(age)',
>>> 'bmi ~ C(gender) + np.log(age)',
>>> 'bmi ~ C(gender) + C(race) + np.log(age)',
>>> 'bmi ~ C(gender) + rich + C(gender)*rich + C(race) + np.log(age)',
>>> 'bmi ~ -1 + np.log(age)',
>>> 'bmi ~ -1 + C(race) + np.log(age)']
>>> reg = [smf.ols(f,df).fit() for f in regformulas]
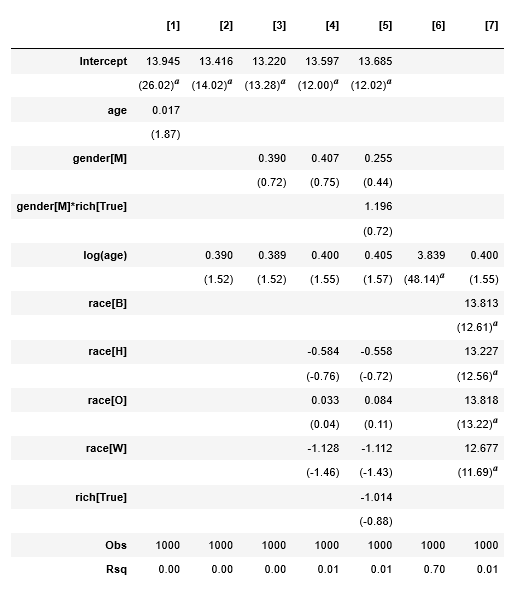
>>> tbl = Regtable(reg)
>>> tbl.render()
Produces the following:
![enter image description here]()
>>> df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random((nobs,10)))
>>> df2.columns = ['t0_vw','t4_vw','et_vw','t0_ew','t4_ew','et_ew','mktrf','smb','hml','umd']
>>> regformulas2 = ['t0_vw ~ mktrf',
>>> 't0_vw ~ mktrf + smb + hml',
>>> 't0_vw ~ mktrf + smb + hml + umd',
>>> 't4_vw ~ mktrf',
>>> 't4_vw ~ mktrf + smb + hml',
>>> 't4_vw ~ mktrf + smb + hml + umd',
>>> 'et_vw ~ mktrf',
>>> 'et_vw ~ mktrf + smb + hml',
>>> 'et_vw ~ mktrf + smb + hml + umd',
>>> 't0_ew ~ mktrf',
>>> 't0_ew ~ mktrf + smb + hml',
>>> 't0_ew ~ mktrf + smb + hml + umd',
>>> 't4_ew ~ mktrf',
>>> 't4_ew ~ mktrf + smb + hml',
>>> 't4_ew ~ mktrf + smb + hml + umd',
>>> 'et_ew ~ mktrf',
>>> 'et_ew ~ mktrf + smb + hml',
>>> 'et_ew ~ mktrf + smb + hml + umd'
>>> ]
>>> regnames = ['Small VW','','',
>>> 'Large VW','','',
>>> 'Spread VW','','',
>>> 'Small EW','','',
>>> 'Large EW','','',
>>> 'Spread EW','',''
>>> ]
>>> reg2 = [smf.ols(f,df2).fit() for f in regformulas2]
>>>
>>> tbl2 = Regtable(reg2,orientation='horizontal',regnames=regnames,sig='coeff',intercept_name='alpha',nobs=False,rsq=False,stat='se')
>>> tbl2.render()
Produces the following:
![]()
The documentation for the Regtable class is here: https://byu-finance-library-finance-byu.readthedocs.io/en/latest/regtables.html
These tables can be exported to LaTeX for easy incorporation into writing:
tbl.to_latex()


summary_colfunction but it is missing some options (and bells and whistles) github.com/statsmodels/statsmodels/issues/1637 – Inveightexregor stata'soutreg2. I guess I will have to switch to R for output – Torey