I am using pywin32 to read/write to an Excel file. I have some dates in Excel, stored in format yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss. I would like to import those into Python as datetime.datetime objects. Here is the line of code I started with:
prior_datetime = datetime.strptime(excel_ws.Cells(2, 4).Value, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
That didn't work. I got the error:
strptime() argument 1 must be str, not pywintypes.datetime
I tried casting it to a string, like so:
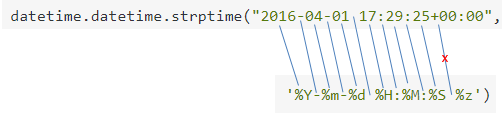
prior_datetime = datetime.strptime(str(excel_ws.Cells(2, 4).Value), '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
That didn't work either. I got the error:
ValueError: unconverted data remains: +00:00
So then I tried something a little different:
prior_datetime = datetime.fromtimestamp(int(excel_ws.Cells(2, 4).Value))
Still no luck. Error:
TypeError: a float is required.
Casting to a float didn't help. Nor integer. (Hey, I was desperate at this point.)
I might be looking in the wrong plce, but I'm having a terrible time finding any good documentation on pywin32 in general or pywintypes or pywintypes.datetime in particular.
Any help?

str(excel_ws.Cells(2, 4).Value)– Antiquateopenpyxl? It doesn't require a version of Excel to be installed or automated and handles converting cells with dates to the native python datetime for you... – Phosphatasepywintypes.Timeinstead of.datetimebut worth a shot. timgolden.me.uk/python/win32_how_do_i/… – Mauromaurois