I have come across CORS issues multiple times and can usually fix it but I want to really understand by seeing this from a MEAN stack paradigm.
Before I simply added middleware in my express server to catch these things, but it looks like there is some kind of pre-hook that is erroring out my requests.
Request header field Access-Control-Allow-Headers is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers in preflight response
I assumed that I could do this:
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers","*")
})
or the equivalent but this doesn't seem to fix it. I also of course tried
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers","Access-Control-Allow-Headers")
})
Still no luck.


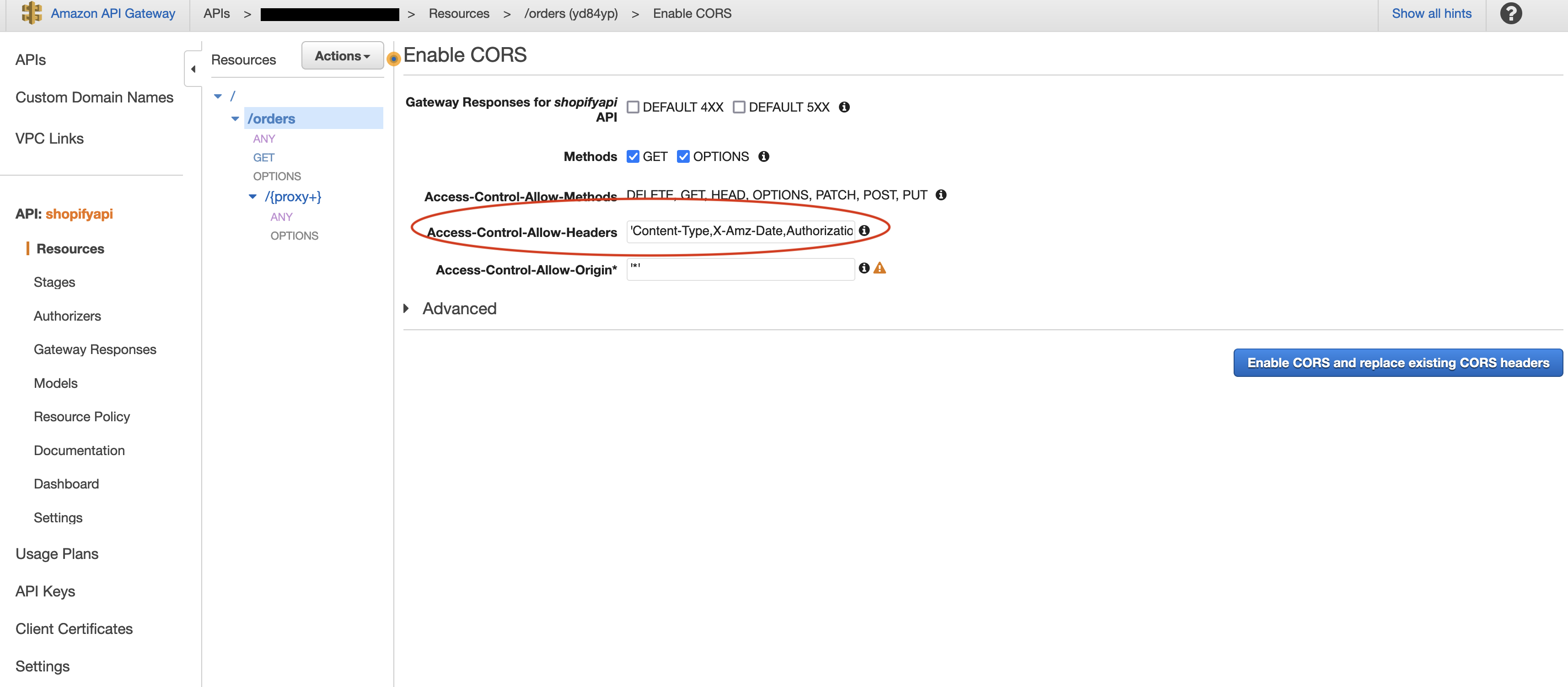
Access-Control-Request-Headers– Revive