This question needs a proper answer:
Just use the standard package site, which was made for this job!
and here is how (plagiating my own answer to my own question on the very same topic):
- Open a Python prompt and type
>>> import site
>>> site.USER_SITE
'C:\\Users\\ojdo\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages'
...
(Alternatively, call python -m site --user-site for the same effect.)
- Create this folder if it does not exist yet:
...
>>> import os
>>> os.makedirs(site.USER_SITE)
...
(Or, in Bash, your preferred variant of makedirs -p $(python -m site --user-site).)
- Create a file
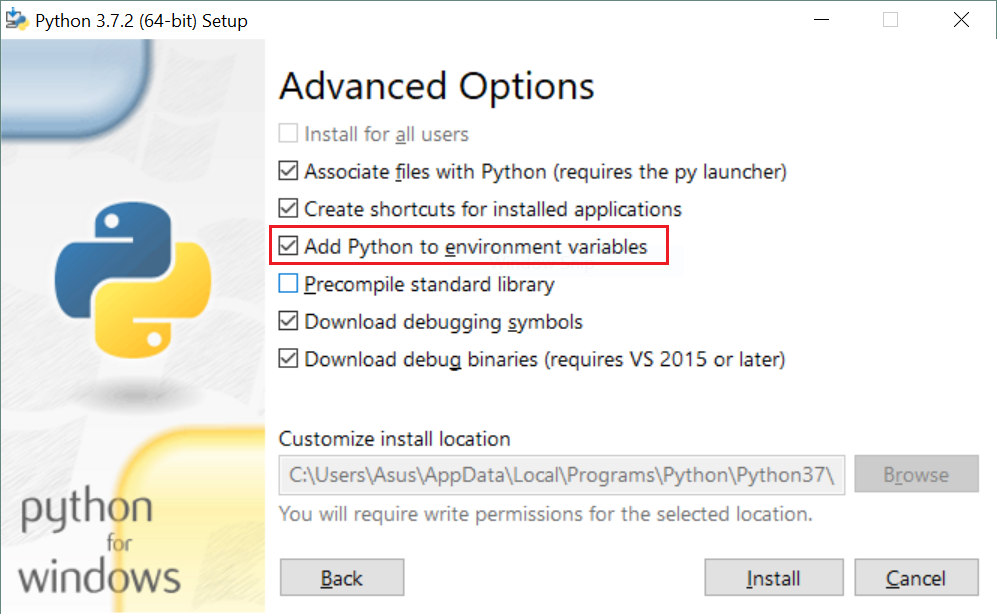
sitecustomize.py (with exactly this filename, or it won't work) in this folder containing the content of FIND_MY_PACKAGES, either manually or using something like the following code. Of course, you have to change C:\My_Projects to the correct path to your custom import location.
...
>>> FIND_MY_PACKAGES = """
import site
site.addsitedir(r'C:\My_Projects')
"""
>>> filename = os.path.join(site.USER_SITE, 'sitecustomize.py')
>>> with open(filename, 'w') as outfile:
... print(FIND_MY_PACKAGES, file=outfile)
And the next time you start Python, C:\My_Projects is present in your sys.path, without having to touch system-wide settings. Bonus: the above steps work on Linux, too!
Why does this work?
From the documentation of standard library package site:
[Then] an attempt is made to import a module named sitecustomize, which can perform arbitrary site-specific customizations. [...].
So if you create a module named sitecustomize anywhere in PYTHONPATH, package site will execute it at Python startup. And by calling site.addsitedir, the sys.path can be safely extended to your liking.






sitemodule. – Tupi