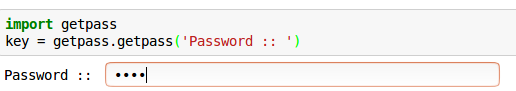
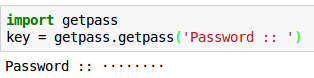
If you want a solution that works on Windows/macOS/Linux and on Python 2 & 3, you can install the pwinput module:
pip install pwinput
Unlike getpass.getpass() (which is in the Python Standard Library), the pwinput module can display *** mask characters as you type.
Example usage:
>>> pwinput.pwinput()
Password: *********
'swordfish'
>>> pwinput.pwinput(mask='X') # Change the mask character.
Password: XXXXXXXXX
'swordfish'
>>> pwinput.pwinput(prompt='PW: ', mask='*') # Change the prompt.
PW: *********
'swordfish'
>>> pwinput.pwinput(mask='') # Don't display anything.
Password:
'swordfish'
Unfortunately this module, like Python's built-in getpass module, doesn't work in IDLE or Jupyter Notebook.
More details at https://pypi.org/project/pwinput/
Note that pwinput is the new name for the stdiomask module.