A Background
The ADO.NET Framework supports two models of Data Access Architecture:
- Connection Oriented
- Disconnected
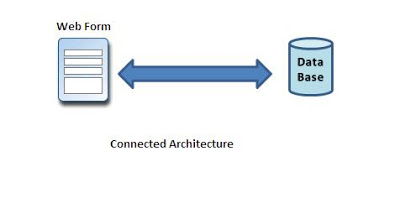
In Connection Oriented Data Access Architecture the application makes a connection to the Data Source and then interact with it through SQL requests using the same connection (e.g. an open connection must be maintained between your application and the Data Source even when it is not using any Database Operations).
Connected architecture is when you constantly make trips to the database for any CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operation you wish to do. This creates more traffic to the database but is normally much faster as you should be doing smaller transactions.
It's built on the classes Connection, Command, DataReader and Transaction.
![enter image description here]()
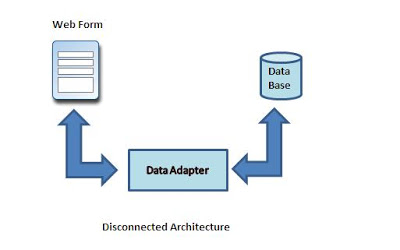
In Disconnected Data Access Architecture the ADO.net uses in-memory data store that can hold multiple tables at the same time (they're fetched before).
Disconnected architecture is a method of retrieving a record set from the database and storing it giving you the ability to do many CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operations on the data in memory, then it can be re-synchronized with the database when reconnecting.
It's Built on classes Connection, DataAdapter, CommandBuilder, DataSet and DataView.
![enter image description here]()
Some key Classes of Connected and Disconnected architecture
DataReader is Connected Architecture since it keeps the
connection open until all rows are fetched one by one.DataSet is Disconnected Architecture since all the records are
brought at once and there is no need to keep the connection alive.DataAdapter acts as a bridge between the Connected and
Disconnected Objects. It manages connections between Data Source and
Dataset by fill the data from Data Source to the Dataset.
which one is better in desired situation?
Connected Mode
- connection oriented
- we read data from a database by using a
DataReader object
- Its methods provide faster performance
- It can hold the data of single table
- It's read only, we can't update the data
Disconnected mode
- It's disconnected connection oriented.
- we read data from a database by using a
DataSet object.
- It get low in speed and performance.
- It can hold multiple tables of data.
- we can perform all option as like update, insert, delete etc.
Answer of your questions
Now I read some articles about connected model and disconnected model
in EF and I'm confused why should I attach explicitly the entities to
the context in disconnected model? I had read also that the default
behavior in web is disconnected model and in WPF is connected model !
Web application could be connected or disconnected, and, in fact ASP.NET applications are disconnected, due to ADO.NET disconnected model. Disconnected model is getting more popular due to simple implementation and easier troubleshooting. Good design with ASP.NET application would close all the database connections as soon as data manipulation is complete regardless if it is 15 hit per month or 15 hits per second.
Could someone explain in easy manner with an an analogy of real life
what's the difference between the two models?
Yes, Suppose you have some important tips to tell/aware a friend. Disconnected means the way you've awaited to see him or you're spending time to obtain more tips to say. Connected is the way when you live with him or having an online/RealTime communication to him for telling every tip each time you want.
How we could handle both models in EF with simple example?
EF uses the Disconnected model. since you work with data and make desired changes and then you perform the SaveChanges :)
Is there a relationship between the type of app (web form , MVC, WPF,
WCF) and the dedicated model used in the EF?
It's based on application logic. RealTime applications need to be connected as they need on-time propagation and updates rather than another application types.
When to use connected model and when to use disconnected model (using
EF) ?
I've answered this. Just I would like to say By keeping connections open for only a minimum period of time, ADO.NET conserves system resources and provides maximum security for databases and also has less impact on system performance. It's based on your application strategy/type, you can make a good decision yourself.
Update:
but if i was in a disconnected model, Could you tell me how the EF can
handle multiple operations (INSERTs,UPDATEs,DELETEs) from many users
at the same time?
Take a look at ObjectStateManager which is responsible for everything related to object tracking in the context. If some users perform concurrent updates to the same entry, By default, the Entity Framework implements an optimistic concurrency model. This means that locks are not held on data in the data source between when the data is queried and the data is updated. The Entity Framework saves object changes to the database without checking for concurrency. For entities that might experience a high degree of concurrency (like banking system), we recommend that the entity define a property in the conceptual layer with an attribute of ConcurrencyMode="fixed", as shown in the following example:
<Property Name="Status" Type="Byte" Nullable="false" ConcurrencyMode="Fixed" />
When this attribute is used, the Entity Framework checks for changes in the database before saving changes to the database. Any conflicting changes will cause an OptimisticConcurrencyException which can also occur when you define an Entity Data Model that uses stored procedures to make updates to the data source. In this case, the exception is raised when the stored procedure that is used to perform updates reports that zero rows were updated. For more information visit Saving Changes and Managing Concurrency