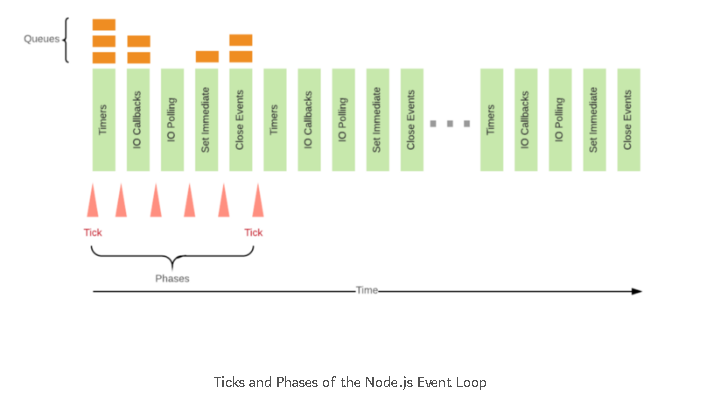
I think I can illustrate this quite nicely. Since nextTick is called at the end of the current operation, calling it recursively can end up blocking the event loop from continuing. setImmediate solves this by firing in the check phase of the event loop, allowing event loop to continue normally.
┌───────────────────────┐
┌─>│ timers │
│ └──────────┬────────────┘
│ ┌──────────┴────────────┐
│ │ I/O callbacks │
│ └──────────┬────────────┘
│ ┌──────────┴────────────┐
│ │ idle, prepare │
│ └──────────┬────────────┘ ┌───────────────┐
│ ┌──────────┴────────────┐ │ incoming: │
│ │ poll │<─────┤ connections, │
│ └──────────┬────────────┘ │ data, etc. │
│ ┌──────────┴────────────┐ └───────────────┘
│ │ check │
│ └──────────┬────────────┘
│ ┌──────────┴────────────┐
└──┤ close callbacks │
└───────────────────────┘
source: https://nodejs.org/en/docs/guides/event-loop-timers-and-nexttick/
Notice that the check phase is immediately after the poll phase. This is because the poll phase and I/O callbacks are the most likely places your calls to setImmediate are going to run. So ideally most of those calls will actually be pretty immediate, just not as immediate as nextTick which is checked after every operation and technically exists outside of the event loop.
Let's take a look at a little example of the difference between setImmediate and process.nextTick:
function step(iteration) {
if (iteration === 10) return;
setImmediate(() => {
console.log(`setImmediate iteration: ${iteration}`);
step(iteration + 1); // Recursive call from setImmediate handler.
});
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log(`nextTick iteration: ${iteration}`);
});
}
step(0);
Let's say we just ran this program and are stepping through the first iteration of the event loop. It will call into the step function with iteration zero. It will then register two handlers, one for setImmediate and one for process.nextTick. We then recursively call this function from the setImmediate handler which will run in the next check phase. The nextTick handler will run at the end of the current operation interrupting the event loop, so even though it was registered second it will actually run first.
The order ends up being: nextTick fires as current operation ends, next event loop begins, normal event loop phases execute, setImmediate fires and recursively calls our step function to start the process all over again. Current operation ends, nextTick fires, etc.
The output of the above code would be:
nextTick iteration: 0
setImmediate iteration: 0
nextTick iteration: 1
setImmediate iteration: 1
nextTick iteration: 2
setImmediate iteration: 2
nextTick iteration: 3
setImmediate iteration: 3
nextTick iteration: 4
setImmediate iteration: 4
nextTick iteration: 5
setImmediate iteration: 5
nextTick iteration: 6
setImmediate iteration: 6
nextTick iteration: 7
setImmediate iteration: 7
nextTick iteration: 8
setImmediate iteration: 8
nextTick iteration: 9
setImmediate iteration: 9
Now let's move our recursive call to step into our nextTick handler instead of the setImmediate.
function step(iteration) {
if (iteration === 10) return;
setImmediate(() => {
console.log(`setImmediate iteration: ${iteration}`);
});
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log(`nextTick iteration: ${iteration}`);
step(iteration + 1); // Recursive call from nextTick handler.
});
}
step(0);
Now that we have moved the recursive call to step into the nextTick handler things will behave in a different order. Our first iteration of the event loop runs and calls step registering a setImmedaite handler as well as a nextTick handler. After the current operation ends our nextTick handler fires which recursively calls step and registers another setImmediate handler as well as another nextTick handler. Since a nextTick handler fires after the current operation, registering a nextTick handler within a nextTick handler will cause the second handler to run immediately after the current handler operation finishes. The nextTick handlers will keep firing, preventing the current event loop from ever continuing. We will get through all our nextTick handlers before we see a single setImmediate handler fire.
The output of the above code ends up being:
nextTick iteration: 0
nextTick iteration: 1
nextTick iteration: 2
nextTick iteration: 3
nextTick iteration: 4
nextTick iteration: 5
nextTick iteration: 6
nextTick iteration: 7
nextTick iteration: 8
nextTick iteration: 9
setImmediate iteration: 0
setImmediate iteration: 1
setImmediate iteration: 2
setImmediate iteration: 3
setImmediate iteration: 4
setImmediate iteration: 5
setImmediate iteration: 6
setImmediate iteration: 7
setImmediate iteration: 8
setImmediate iteration: 9
Note that had we not interrupted the recursive call and aborted it after 10 iterations then the nextTick calls would keep recursing and never letting the event loop continue to the next phase. This is how nextTick can become blocking when used recursively whereas setImmediate will fire in the next event loop and setting another setImmediate handler from within one won't interrupt the current event loop at all, allowing it to continue executing phases of the event loop as normal.
PS - I agree with other commenters that the names of the two functions could easily be swapped since nextTick sounds like it's going to fire in the next event loop rather than the end of the current one, and the end of the current loop is more "immediate" than the beginning of the next loop. Oh well, that's what we get as an API matures and people come to depend on existing interfaces.


nextTickis faster thansetImmediateon large calculations. – IorgossetImmediatedoes in better detail. – UndertrumpsetImmediate, but not beforenextTick? – Use