I've been reading about code performance and tuning parameters for a long time. Indeed, Android programs are one of my focuses.
Let’s introduce at first the basic or most important concepts in which help us to reach a solution.
As Android Developer Has stated
module can be independently built, tested, and debugged
Therefore, Modules have their own Gradle & Dependencies. And you can explore it in the project Hierarchy Viewer.
Modularization emphasizes Maintenance matters. Unlike Performance Matters. Because Modularization has this important impact:
- Increase Depth of inheritance
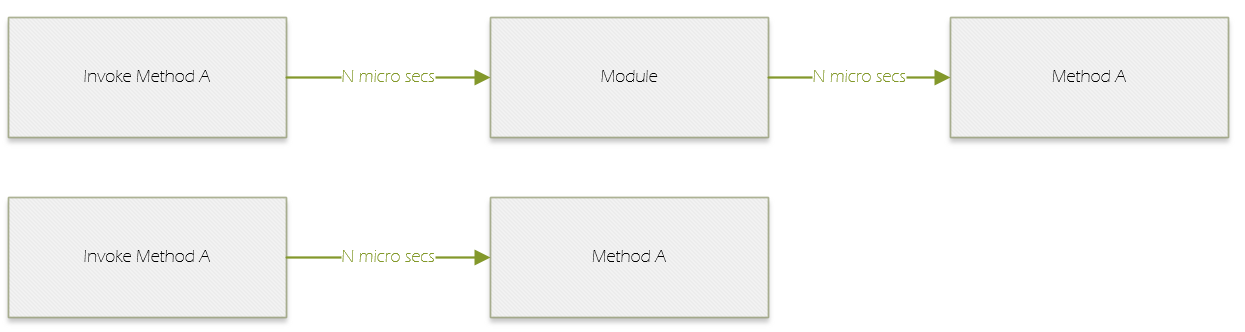
Here is a diagram that I did plot to make it clear. As you can see. while using the discrete module, to invoke Method A there are 2N micro secs compared to N micro secs without discrete module.
![enter image description here]()
This question may come to your mind that Referenced Methods counts what is related to Depth of inheritance?
The answer is: Although using modularization increases Referenced Methods. but, it doesn’t affect the app performance and the main possible issue is Depth of inheritance which in most cases is ignorable.
I do emphasize that increased Referenced Methods in modularization is due to each Module Gradle & Dependencies
How app modularization can increase the referenced method count
drastically so high?
Conditions in which impact APK analyzer importantly Referenced Methods
Also note that minification and code shrinking can each also
considerably change the contents of a DEX file after source code is
compiled.
In addition to the above official statement, I want to add another condition in which impact the APK analyzer that’s:
how much is the developer experienced in modularization?
modularization is like a home that architecture(developer) defines where should be the kitchen and where should be a restroom and where should be WC.
What if the architecture decides to combine WC & Kitchen? Yea this is a disaster.
This may happen while modularization if the developer is not very much experienced.
Answering OP questions in Addition to extra information
Here I answer op asked questions in the comments
Why would separate Gradle add to the referenced method count? And for
separate dependency, if the final result is a single APK then I do not
think duplicate dependencies in 'app' and feature module would add to
referenced method count.
Because modules can be built, tested, and debugged then they MUST have their own Gradle & Dependencies.
While multi-module project is being complied , compiler generates several .dex files including:
- a
.dex file for total-integrated dependencies
- modules
.dexs
dependencies .dex file is an integrate of all the modules gradles
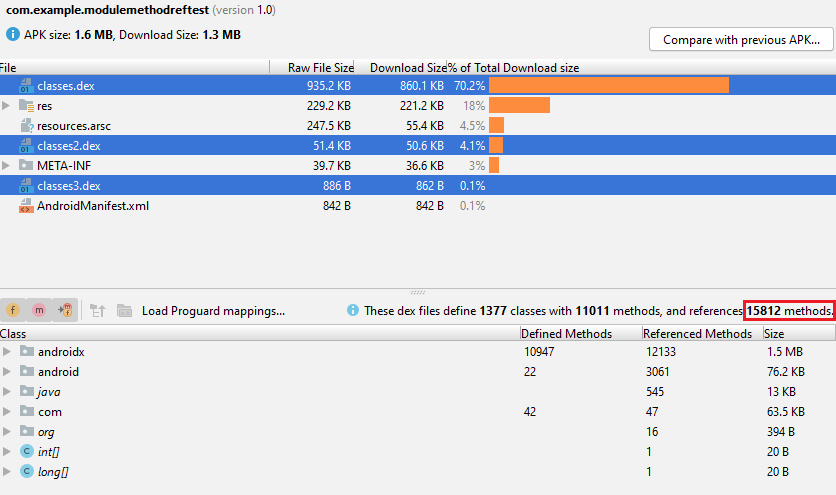
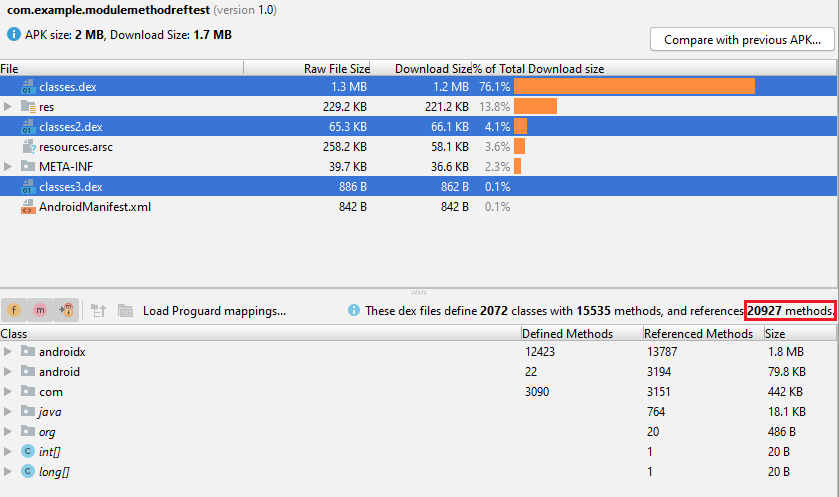
Let's look at how a module gradle impacts final Referenced Methods Count?!
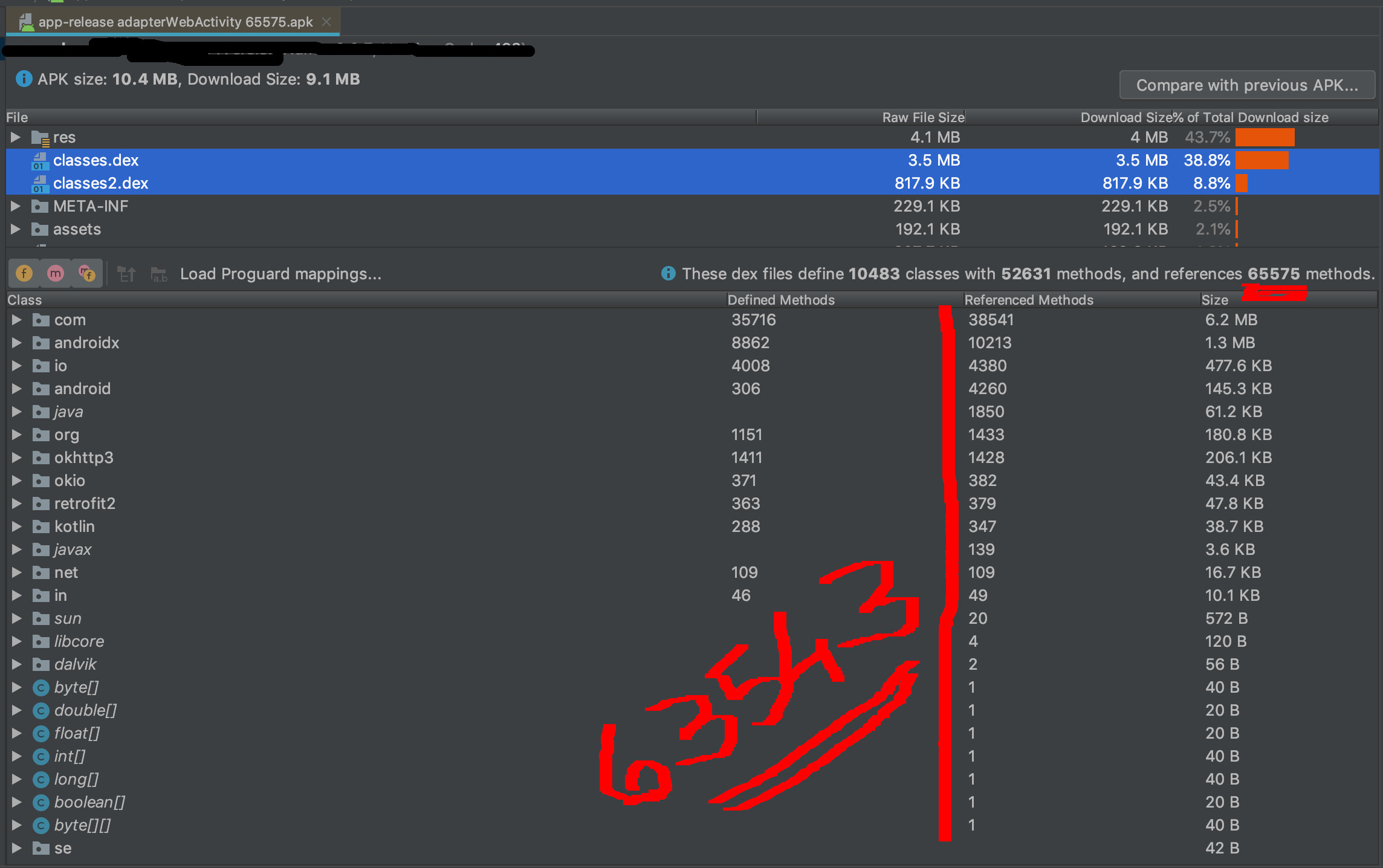
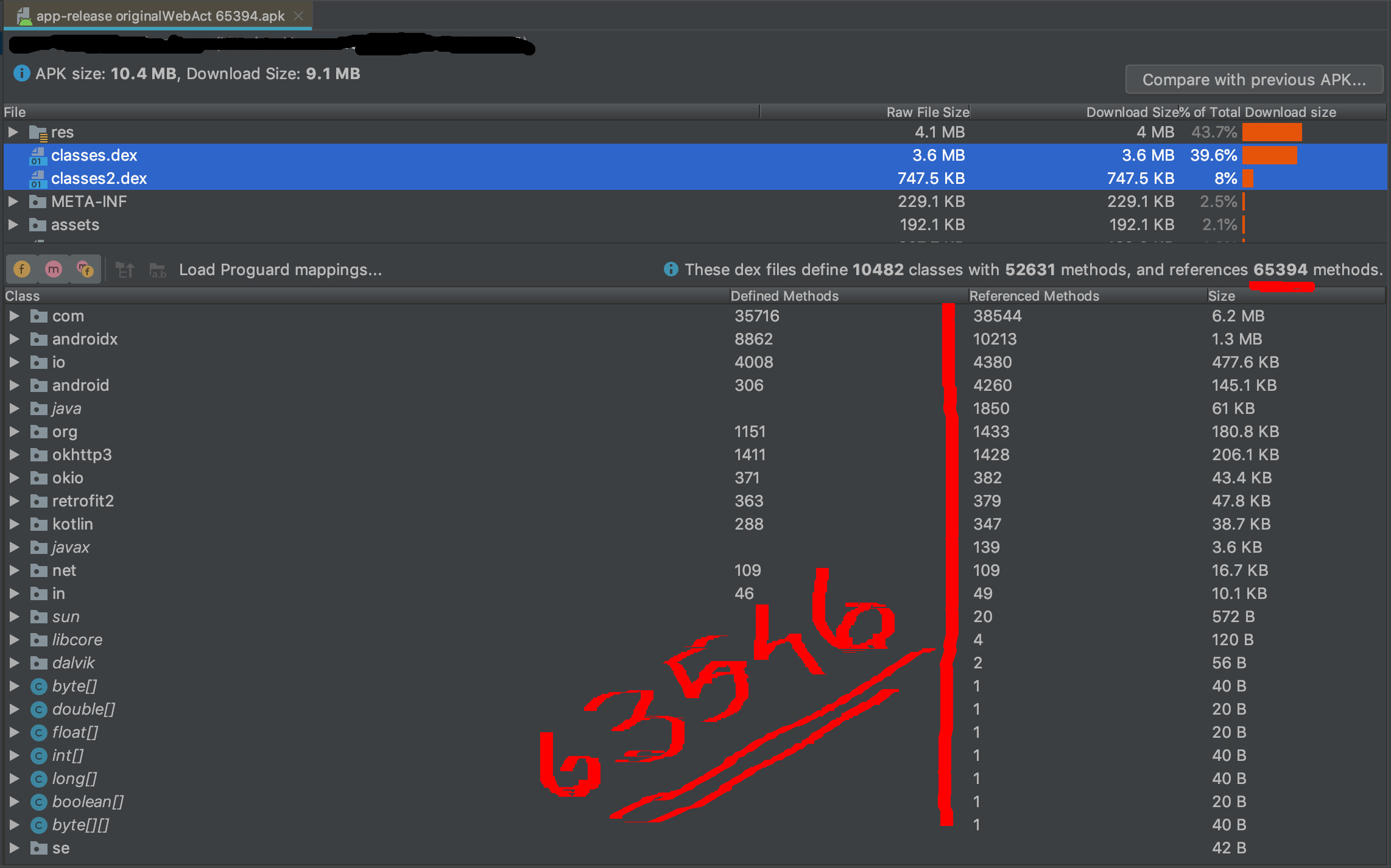
there are 2 APKs with the same result but differences in Referenced Methods counts.
![figure 1]()
![figure 2]()
They are both empty activities that have a 1.7k difference in Referenced Methods Count that is very high depending on their functionality.
The key difference is on their Module's Gradle one of them was configured to
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.1.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'
}
Another one configured to
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.2.0-alpha01'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.0.0-beta4'
}
Although they are just empty activities, a minimal difference in Gradle caused a 1.7k difference in Referenced Method Counts.
And App Gradle is
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.1.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'
implementation project(path: ':module')
}
major concern is why the addition of individually referenced method count
is different than the total referenced method count in Apk Analyzer?
This is just an IDE filter nothing else. for sure, if you only select a .dex file Reference Method Counts is equal to SUM of each row Referenced Method Counts but if you multi-select .dex files, You will see the difference in SUM and actual Count that because of equality in References that Analyzer preferred to filter them.
in your screenshots, you've selected multiple .dex files then Analyzer filter equality.
in our project we are using centralized dependencies. gradle file so
there is no chance of a different version. So, do you think even if we
have the same/exact set of dependencies and their versions in feature
modules, it will increase referenced method count?
Theoretically, it should NOT increase referenced method counts.BUT, As I explained it, Developer Experience highly impacts the final result.
Team Analyzer should check and fix performance issues before release like
- proguard rules
- shrunk & minified resources
- androidManifest.xml
- gradle settings
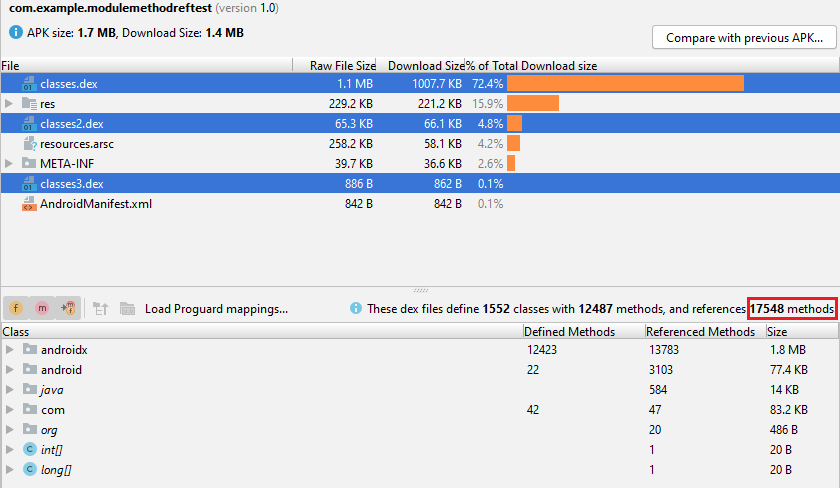
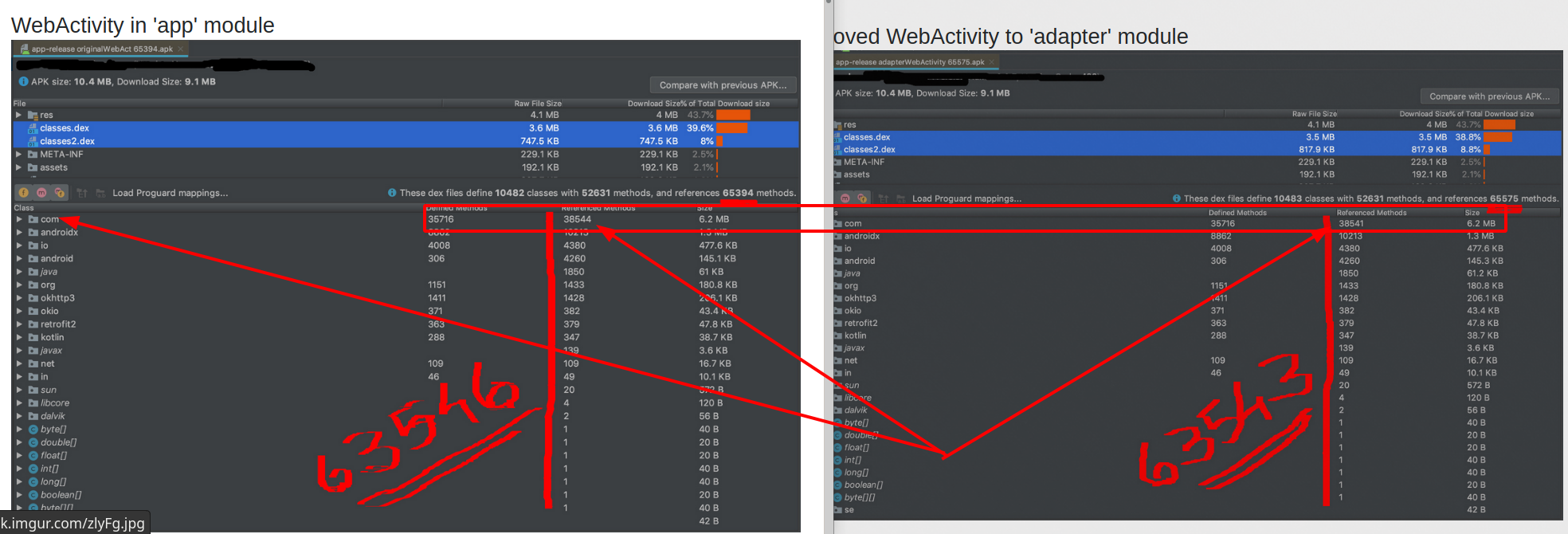
Now I want to clarify how Developer Experience and code maintenance affects the final result. EVEN if your APK uses Centralized Dependencies
![figure 3]()
in the above example, I've increased 5.1k in Referenced Methods Count EVEN IF, I had Centralized Dependencies !!!!!
How it's possible ?
The answer is: I just added a useless and hidden .jar file in the libs directory of the project. just as easy as you can see I affected the final result.
As you can see Developer Experience affects the final result. as a result, Practically it's possible that referenced methods counts to be increased Although Theoretically Should NOT.
And why there is no difference in referenced method count when I
compile only 'app' module by disabling parallel compilation? It should
have decreased as only 'app' module's dependencies would have been
used, right?
the compilation has not any relation to referenced methods counts.it complies with what the developer wants to have complied.
Conclusion
I have covered all the possibilities around the issue. Indeed, it can emerge from different situations, and a developer by using this guideline can fix the issue.
- I would hope that you found why Referenced Methods was increased and
why in some cases it might be drastically increased.
- Modules have their Gradle & Dependencies and modularization increase
modules. therefore, these Method References.
- Modularization impacts app performance ignorable but makes
your app Maintenance highly better.
- Developer experience in modularization also highly impacts the final
result.
IMPORTANT NOTE: almost all of the statements are my investigation & researches. indeed, there may be errors and faults and will be updated to add much more information in the future.