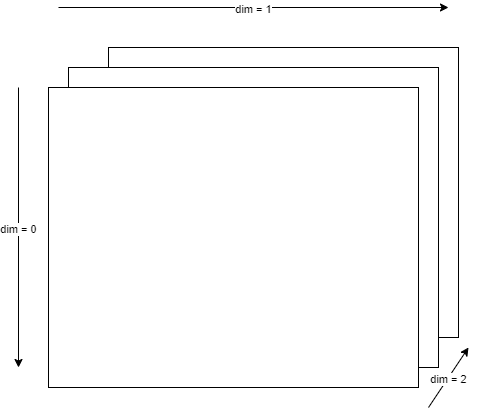
let me take a 2D matrix as example:
mat = torch.arange(9).view(3, -1)
tensor([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
torch.sum(mat, dim=-2)
tensor([ 9, 12, 15])
I find the result of torch.sum(mat, dim=-2) is equal to torch.sum(mat, dim=0) and dim=-1 equal to dim=1. My question is how to understand the negative dimension here. What if the input matrix has 3 or more dimensions?