I fitted a mutinomial model using nnet's multinom function using (in this case on data giving the diet preference of male and female and different size classes of alligators in different lakes) :
data=read.csv("https://www.dropbox.com/s/y9elunsbv74p2h6/alligator.csv?dl=1")
head(data)
id size sex lake food
1 1 <2.3 male hancock fish
2 2 <2.3 male hancock fish
3 3 <2.3 male hancock fish
4 4 <2.3 male hancock fish
5 5 <2.3 male hancock fish
6 6 <2.3 male hancock fish
library(nnet)
fit=multinom(food~lake+sex+size, data = data, Hess = TRUE)
The overall significance of my factors I can get using
library(car)
Anova(fit, type="III") # type III tests
Analysis of Deviance Table (Type III tests)
Response: food
LR Chisq Df Pr(>Chisq)
lake 50.318 12 1.228e-06 ***
sex 2.215 4 0.696321
size 17.600 4 0.001477 **
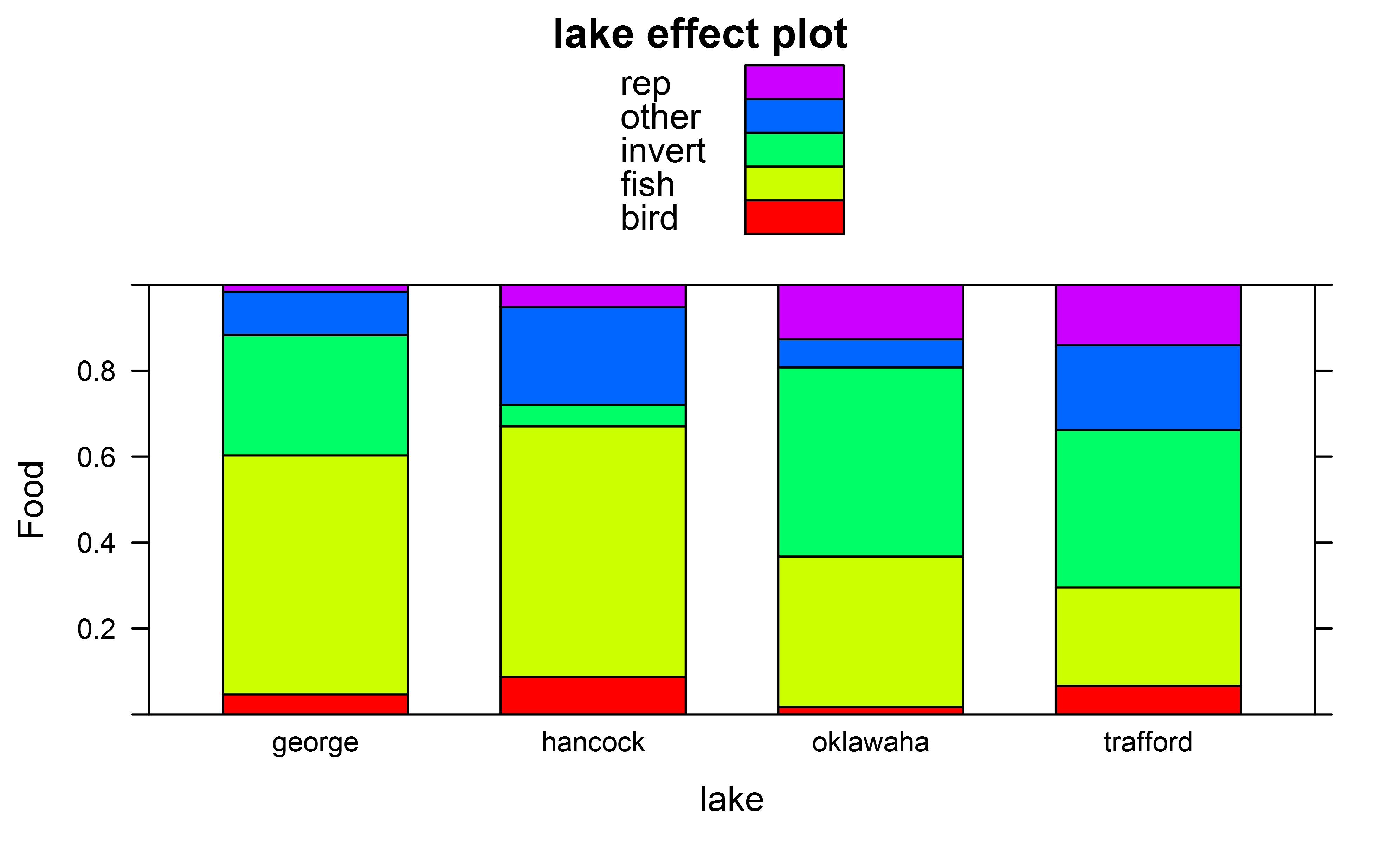
And effect plots I got e.g. for factor "lake" using
library(effects)
plot(effect(fit,term="lake"),ylab="Food",type="probability",style="stacked",colors=rainbow(5))
In addition to the overall Anova tests I would also like to also carry out pairwise Tukey posthoc tests though to test for overall differences in the multinomial distribution of which prey items are eaten, e.g. across different pairs of lakes.
I first thought of using function glht in package multcomp but this does not appear to work, e.g. for factor lake:
library(multcomp)
summary(glht(fit, mcp(lake = "Tukey")))
Error in summary(glht(fit, mcp(lake = "Tukey"))) :
error in evaluating the argument 'object' in selecting a method for function 'summary': Error in glht.matrix(model = list(n = c(6, 0, 5), nunits = 12L, nconn = c(0, :
‘ncol(linfct)’ is not equal to ‘length(coef(model))’
Alternative was to use package lsmeans for this, for which I tried
lsmeans(fit, pairwise ~ lake | food, adjust="tukey", mode = "prob")
$contrasts
food = bird:
contrast estimate SE df t.ratio p.value
george - hancock -0.04397388 0.05451515 24 -0.807 0.8507
george - oklawaha 0.03680712 0.03849268 24 0.956 0.7751
george - trafford -0.02123255 0.05159049 24 -0.412 0.9760
hancock - oklawaha 0.08078100 0.04983303 24 1.621 0.3863
hancock - trafford 0.02274133 0.06242724 24 0.364 0.9831
oklawaha - trafford -0.05803967 0.04503128 24 -1.289 0.5786
food = fish:
contrast estimate SE df t.ratio p.value
george - hancock -0.02311955 0.09310322 24 -0.248 0.9945
george - oklawaha 0.19874095 0.09273047 24 2.143 0.1683
george - trafford 0.32066789 0.08342262 24 3.844 0.0041
hancock - oklawaha 0.22186050 0.09879102 24 2.246 0.1396
hancock - trafford 0.34378744 0.09088119 24 3.783 0.0047
oklawaha - trafford 0.12192695 0.08577365 24 1.421 0.4987
food = invert:
contrast estimate SE df t.ratio p.value
george - hancock 0.23202865 0.06111726 24 3.796 0.0046
george - oklawaha -0.13967425 0.08808698 24 -1.586 0.4053
george - trafford -0.07193252 0.08346283 24 -0.862 0.8242
hancock - oklawaha -0.37170290 0.07492749 24 -4.961 0.0003
hancock - trafford -0.30396117 0.07129577 24 -4.263 0.0014
oklawaha - trafford 0.06774173 0.09384594 24 0.722 0.8874
food = other:
contrast estimate SE df t.ratio p.value
george - hancock -0.12522495 0.06811177 24 -1.839 0.2806
george - oklawaha 0.03499241 0.05141930 24 0.681 0.9035
george - trafford -0.08643898 0.06612383 24 -1.307 0.5674
hancock - oklawaha 0.16021736 0.06759887 24 2.370 0.1103
hancock - trafford 0.03878598 0.08135810 24 0.477 0.9635
oklawaha - trafford -0.12143138 0.06402725 24 -1.897 0.2560
food = rep:
contrast estimate SE df t.ratio p.value
george - hancock -0.03971026 0.03810819 24 -1.042 0.7269
george - oklawaha -0.13086622 0.05735022 24 -2.282 0.1305
george - trafford -0.14106384 0.06037257 24 -2.337 0.1177
hancock - oklawaha -0.09115595 0.06462624 24 -1.411 0.5052
hancock - trafford -0.10135358 0.06752424 24 -1.501 0.4525
oklawaha - trafford -0.01019762 0.07161794 24 -0.142 0.9989
Results are averaged over the levels of: sex, size
P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 4 estimates
This carries out tests for differences in the proportion of each specific type of food item though.
I was wondering if it would also be possible in one way or another to obtain Tukey posthoc tests in which the overall multinomial distributions are compared across the different lakes, i.e. where differences are tested for in the proportion of any of the prey items eaten? I tried with
lsmeans(fit, pairwise ~ lake, adjust="tukey", mode = "prob")
but that doesn't seem to work:
$contrasts
contrast estimate SE df t.ratio p.value
george - hancock 3.252607e-19 1.879395e-10 24 0 1.0000
george - oklawaha -8.131516e-19 1.861245e-10 24 0 1.0000
george - trafford -1.843144e-18 2.504062e-10 24 0 1.0000
hancock - oklawaha -1.138412e-18 NaN 24 NaN NaN
hancock - trafford -2.168404e-18 NaN 24 NaN NaN
oklawaha - trafford -1.029992e-18 NaN 24 NaN NaN
Any thoughts?
Or would anyone know how glht could be made to work for multinom models?

lakeinvolve averaging overfood, which is your multinomial response. Those multinomial probabilities necessarily sum to 1 over food for any fixed setting of the other factors, so when you average over food you always will get $0.2$. So the flaky-looking comparisons are all just of rounding error. That is no way to compare the lakes. If you want pairwise comparisons, then formulate some kind of linear combination of the probabilities for each lake and compare those scores. – Wagoner