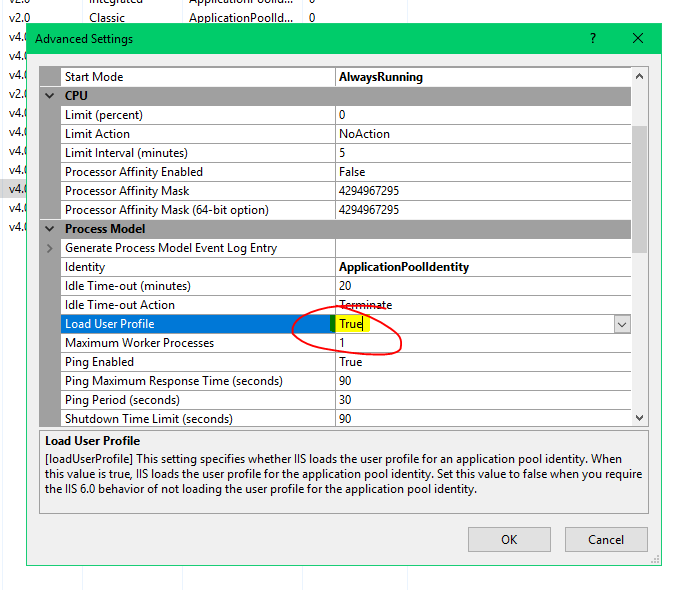
Although I have attended the above, I have come to this point after many attempts.
1- If you want access to the certificate from the store, you can do this as an example
2- It is much easier and cleaner to produce the certificate and use it via a path
Asp.net Core 2.2
OR1:
using Org.BouncyCastle.Asn1;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Asn1.Pkcs;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Asn1.X509;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Generators;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Operators;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Parameters;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Prng;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Math;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Pkcs;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Security;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Utilities;
using Org.BouncyCastle.X509;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Tursys.Pool.Storage.Api.Utility
{
class CertificateManager
{
public static X509Certificate2 GetCertificate(string caller)
{
AsymmetricKeyParameter caPrivateKey = null;
X509Certificate2 clientCert;
X509Certificate2 serverCert;
clientCert = GetCertificateIfExist("CN=127.0.0.1", StoreName.My, StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
serverCert = GetCertificateIfExist("CN=MyROOTCA", StoreName.Root, StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
if (clientCert == null || serverCert == null)
{
var caCert = GenerateCACertificate("CN=MyROOTCA", ref caPrivateKey);
addCertToStore(caCert, StoreName.Root, StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
clientCert = GenerateSelfSignedCertificate("CN=127.0.0.1", "CN=MyROOTCA", caPrivateKey);
var p12 = clientCert.Export(X509ContentType.Pfx);
addCertToStore(new X509Certificate2(p12, (string)null, X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable | X509KeyStorageFlags.PersistKeySet), StoreName.My, StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
}
if (caller == "client")
return clientCert;
return serverCert;
}
public static X509Certificate2 GenerateSelfSignedCertificate(string subjectName, string issuerName, AsymmetricKeyParameter issuerPrivKey)
{
const int keyStrength = 2048;
// Generating Random Numbers
CryptoApiRandomGenerator randomGenerator = new CryptoApiRandomGenerator();
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom(randomGenerator);
// The Certificate Generator
X509V3CertificateGenerator certificateGenerator = new X509V3CertificateGenerator();
// Serial Number
BigInteger serialNumber = BigIntegers.CreateRandomInRange(BigInteger.One, BigInteger.ValueOf(Int64.MaxValue), random);
certificateGenerator.SetSerialNumber(serialNumber);
// Signature Algorithm
//const string signatureAlgorithm = "SHA256WithRSA";
//certificateGenerator.SetSignatureAlgorithm(signatureAlgorithm);
// Issuer and Subject Name
X509Name subjectDN = new X509Name(subjectName);
X509Name issuerDN = new X509Name(issuerName);
certificateGenerator.SetIssuerDN(issuerDN);
certificateGenerator.SetSubjectDN(subjectDN);
// Valid For
DateTime notBefore = DateTime.UtcNow.Date;
DateTime notAfter = notBefore.AddYears(2);
certificateGenerator.SetNotBefore(notBefore);
certificateGenerator.SetNotAfter(notAfter);
// Subject Public Key
AsymmetricCipherKeyPair subjectKeyPair;
var keyGenerationParameters = new KeyGenerationParameters(random, keyStrength);
var keyPairGenerator = new RsaKeyPairGenerator();
keyPairGenerator.Init(keyGenerationParameters);
subjectKeyPair = keyPairGenerator.GenerateKeyPair();
certificateGenerator.SetPublicKey(subjectKeyPair.Public);
// Generating the Certificate
AsymmetricCipherKeyPair issuerKeyPair = subjectKeyPair;
ISignatureFactory signatureFactory = new Asn1SignatureFactory("SHA512WITHRSA", issuerKeyPair.Private, random);
// selfsign certificate
Org.BouncyCastle.X509.X509Certificate certificate = certificateGenerator.Generate(signatureFactory);
// correcponding private key
PrivateKeyInfo info = PrivateKeyInfoFactory.CreatePrivateKeyInfo(subjectKeyPair.Private);
// merge into X509Certificate2
X509Certificate2 x509 = new System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate2(certificate.GetEncoded());
Asn1Sequence seq = (Asn1Sequence)Asn1Object.FromByteArray(info.PrivateKeyAlgorithm.GetDerEncoded());
if (seq.Count != 9)
{
//throw new PemException("malformed sequence in RSA private key");
}
RsaPrivateKeyStructure rsa = RsaPrivateKeyStructure.GetInstance(info.ParsePrivateKey());
RsaPrivateCrtKeyParameters rsaparams = new RsaPrivateCrtKeyParameters(
rsa.Modulus, rsa.PublicExponent, rsa.PrivateExponent, rsa.Prime1, rsa.Prime2, rsa.Exponent1, rsa.Exponent2, rsa.Coefficient);
try
{
var rsap = DotNetUtilities.ToRSA(rsaparams);
x509 = x509.CopyWithPrivateKey(rsap);
//x509.PrivateKey = ToDotNetKey(rsaparams);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
;
}
//x509.PrivateKey = DotNetUtilities.ToRSA(rsaparams);
return x509;
}
public static AsymmetricAlgorithm ToDotNetKey(RsaPrivateCrtKeyParameters privateKey)
{
var cspParams = new CspParameters
{
KeyContainerName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
KeyNumber = (int)KeyNumber.Exchange,
Flags = CspProviderFlags.UseMachineKeyStore
};
var rsaProvider = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(cspParams);
var parameters = new RSAParameters
{
Modulus = privateKey.Modulus.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
P = privateKey.P.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
Q = privateKey.Q.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
DP = privateKey.DP.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
DQ = privateKey.DQ.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
InverseQ = privateKey.QInv.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
D = privateKey.Exponent.ToByteArrayUnsigned(),
Exponent = privateKey.PublicExponent.ToByteArrayUnsigned()
};
rsaProvider.ImportParameters(parameters);
return rsaProvider;
}
public static X509Certificate2 GenerateCACertificate(string subjectName, ref AsymmetricKeyParameter CaPrivateKey)
{
const int keyStrength = 2048;
// Generating Random Numbers
CryptoApiRandomGenerator randomGenerator = new CryptoApiRandomGenerator();
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom(randomGenerator);
// The Certificate Generator
X509V3CertificateGenerator certificateGenerator = new X509V3CertificateGenerator();
// Serial Number
BigInteger serialNumber = BigIntegers.CreateRandomInRange(BigInteger.One, BigInteger.ValueOf(Int64.MaxValue), random);
certificateGenerator.SetSerialNumber(serialNumber);
// Signature Algorithm
//const string signatureAlgorithm = "SHA256WithRSA";
//certificateGenerator.SetSignatureAlgorithm(signatureAlgorithm);
// Issuer and Subject Name
X509Name subjectDN = new X509Name(subjectName);
X509Name issuerDN = subjectDN;
certificateGenerator.SetIssuerDN(issuerDN);
certificateGenerator.SetSubjectDN(subjectDN);
// Valid For
DateTime notBefore = DateTime.UtcNow.Date;
DateTime notAfter = notBefore.AddYears(2);
certificateGenerator.SetNotBefore(notBefore);
certificateGenerator.SetNotAfter(notAfter);
// Subject Public Key
AsymmetricCipherKeyPair subjectKeyPair;
KeyGenerationParameters keyGenerationParameters = new KeyGenerationParameters(random, keyStrength);
RsaKeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = new RsaKeyPairGenerator();
keyPairGenerator.Init(keyGenerationParameters);
subjectKeyPair = keyPairGenerator.GenerateKeyPair();
certificateGenerator.SetPublicKey(subjectKeyPair.Public);
// Generating the Certificate
AsymmetricCipherKeyPair issuerKeyPair = subjectKeyPair;
// selfsign certificate
//Org.BouncyCastle.X509.X509Certificate certificate = certificateGenerator.Generate(issuerKeyPair.Private, random);
ISignatureFactory signatureFactory = new Asn1SignatureFactory("SHA512WITHRSA", issuerKeyPair.Private, random);
// selfsign certificate
Org.BouncyCastle.X509.X509Certificate certificate = certificateGenerator.Generate(signatureFactory);
X509Certificate2 x509 = new System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate2(certificate.GetEncoded());
CaPrivateKey = issuerKeyPair.Private;
return x509;
//return issuerKeyPair.Private;
}
public static bool addCertToStore(System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate2 cert, System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.StoreName st, System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.StoreLocation sl)
{
bool bRet = false;
try
{
X509Store store = new X509Store(st, sl);
store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadWrite);
store.Add(cert);
store.Close();
}
catch
{
}
return bRet;
}
protected internal static X509Certificate2 GetCertificateIfExist(string subjectName, StoreName store, StoreLocation location)
{
using (var certStore = new X509Store(store, location))
{
certStore.Open(OpenFlags.ReadOnly);
var certCollection = certStore.Certificates.Find(
X509FindType.FindBySubjectDistinguishedName, subjectName, false);
X509Certificate2 certificate = null;
if (certCollection.Count > 0)
{
certificate = certCollection[0];
}
return certificate;
}
}
}
}
OR 2:
services.AddDataProtection()
//.PersistKeysToFileSystem(new DirectoryInfo(@"c:\temp-keys"))
.ProtectKeysWithCertificate(
new X509Certificate2(Path.Combine(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(), "clientCert.pfx"), "Password")
)
.UnprotectKeysWithAnyCertificate(
new X509Certificate2(Path.Combine(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(), "clientCert.pfx"), "Password")
);