What are the iterator invalidation rules for C++ containers?
(Note: This Q&A is an entry in Stack Overflow's C++ FAQ. Meta-discussion about the question itself should be posted on the Meta question that started all of this, not here.)C++17 (All references are from the final working draft of CPP17 - n4659)
Insertion
Sequence Containers
vector: The functionsinsert,emplace_back,emplace,push_backcause reallocation if the new size is greater than the old capacity. Reallocation invalidates all the references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements in the sequence. If no reallocation happens, all the iterators and references before the insertion point remain valid. [26.3.11.5/1]
With respect to thereservefunction, reallocation invalidates all the references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements in the sequence. No reallocation shall take place during insertions that happen after a call toreserve()until the time when an insertion would make the size of the vector greater than the value ofcapacity(). [26.3.11.3/6]deque: An insertion in the middle of the deque invalidates all the iterators and references to elements of the deque. An insertion at either end of the deque invalidates all the iterators to the deque, but has no effect on the validity of references to elements of the deque. [26.3.8.4/1]list: Does not affect the validity of iterators and references. If an exception is thrown there are no effects. [26.3.10.4/1].
Theinsert,emplace_front,emplace_back,emplace,push_front,push_backfunctions are covered under this rule.forward_list: None of the overloads ofinsert_aftershall affect the validity of iterators and references [26.3.9.5/1]array: As a rule, iterators to an array are never invalidated throughout the lifetime of the array. One should take note, however, that during swap, the iterator will continue to point to the same array element, and will thus change its value.
Associative Containers
All Associative Containers: Theinsertandemplacemembers shall not affect the validity of iterators and references to the container [26.2.6/9]
Unordered Associative Containers
All Unordered Associative Containers: Rehashing invalidates iterators, changes ordering between elements, and changes which buckets elements appear in, but does not invalidate pointers or references to elements. [26.2.7/9]
Theinsertandemplacemembers shall not affect the validity of references to container elements, but may invalidate all iterators to the container. [26.2.7/14]
Theinsertandemplacemembers shall not affect the validity of iterators if(N+n) <= z * B, whereNis the number of elements in the container prior to the insert operation,nis the number of elements inserted,Bis the container’s bucket count, andzis the container’s maximum load factor. [26.2.7/15]All Unordered Associative Containers: In case of a merge operation (e.g.,a.merge(a2)), iterators referring to the transferred elements and all iterators referring toawill be invalidated, but iterators to elements remaining ina2will remain valid. (Table 91 — Unordered associative container requirements)
Container Adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
Erasure
Sequence Containers
vector: The functionseraseandpop_backinvalidate iterators and references at or after the point of the erase. [26.3.11.5/3]deque: An erase operation that erases the last element of adequeinvalidates only the past-the-end iterator and all iterators and references to the erased elements. An erase operation that erases the first element of adequebut not the last element invalidates only iterators and references to the erased elements. An erase operation that erases neither the first element nor the last element of adequeinvalidates the past-the-end iterator and all iterators and references to all the elements of thedeque. [ Note:pop_frontandpop_backare erase operations. —end note ] [26.3.8.4/4]list: Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.10.4/3]. This applies toerase,pop_front,pop_back,clearfunctions.
removeandremove_ifmember functions: Erases all the elements in the list referred by a list iteratorifor which the following conditions hold:*i == value,pred(*i) != false. Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements [26.3.10.5/15].
uniquemember function - Erases all but the first element from every consecutive group of equal elements referred to by the iteratoriin the range[first + 1, last)for which*i == *(i-1)(for the version of unique with no arguments) orpred(*i, *(i - 1))(for the version of unique with a predicate argument) holds. Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.10.5/19]forward_list:erase_aftershall invalidate only iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.9.5/1].
removeandremove_ifmember functions - Erases all the elements in the list referred by a list iterator i for which the following conditions hold:*i == value(forremove()),pred(*i)is true (forremove_if()). Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.9.6/12].
uniquemember function - Erases all but the first element from every consecutive group of equal elements referred to by the iterator i in the range [first + 1, last) for which*i == *(i-1)(for the version with no arguments) orpred(*i, *(i - 1))(for the version with a predicate argument) holds. Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.9.6/16]All Sequence Containers:clearinvalidates all references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements of a and may invalidate the past-the-end iterator (Table 87 — Sequence container requirements). But forforward_list,cleardoes not invalidate past-the-end iterators. [26.3.9.5/32]All Sequence Containers:assigninvalidates all references, pointers and iterators referring to the elements of the container. Forvectoranddeque, also invalidates the past-the-end iterator. (Table 87 — Sequence container requirements)
Associative Containers
All Associative Containers: Theerasemembers shall invalidate only iterators and references to the erased elements [26.2.6/9]All Associative Containers: Theextractmembers invalidate only iterators to the removed element; pointers and references to the removed element remain valid [26.2.6/10]
Container Adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
General container requirements relating to iterator invalidation:
Unless otherwise specified (either explicitly or by defining a function in terms of other functions), invoking a container member function or passing a container as an argument to a library function shall not invalidate iterators to, or change the values of, objects within that container. [26.2.1/12]
no
swap()function invalidates any references, pointers, or iterators referring to the elements of the containers being swapped. [ Note: The end() iterator does not refer to any element, so it may be invalidated. —end note ] [26.2.1/(11.6)]
As examples of the above requirements:
transformalgorithm: Theopandbinary_opfunctions shall not invalidate iterators or subranges, or modify elements in the ranges [28.6.4/1]accumulatealgorithm: In the range [first, last],binary_opshall neither modify elements nor invalidate iterators or subranges [29.8.2/1]reducealgorithm: binary_op shall neither invalidate iterators or subranges, nor modify elements in the range [first, last]. [29.8.3/5]
and so on...
std::string? I think it's different from std::vector due to SSO –
Tucana string fails the second general requirement listed above. So I did not include it. Also tried to stick to the same pattern of the previous FAQ entries. –
Enduring "invalidated" can mean "no longer points to what it used to", not just "may not point to any valid element" as @Marshall Clow described in this answer ? Or it just indicates only 1 of the 2 condtions? –
Labors C++03 (Source: Iterator Invalidation Rules (C++03))
Insertion
Sequence containers
vector: all iterators and references before the point of insertion are unaffected, unless the new container size is greater than the previous capacity (in which case all iterators and references are invalidated) [23.2.4.3/1]deque: all iterators and references are invalidated, unless the inserted member is at an end (front or back) of the deque (in which case all iterators are invalidated, but references to elements are unaffected) [23.2.1.3/1]list: all iterators and references unaffected [23.2.2.3/1]
Associative containers
[multi]{set,map}: all iterators and references unaffected [23.1.2/8]
Container adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
Erasure
Sequence containers
vector: every iterator and reference after the point of erase is invalidated [23.2.4.3/3]deque: all iterators and references are invalidated, unless the erased members are at an end (front or back) of the deque (in which case only iterators and references to the erased members are invalidated) [23.2.1.3/4]list: only the iterators and references to the erased element is invalidated [23.2.2.3/3]
Associative containers
[multi]{set,map}: only iterators and references to the erased elements are invalidated [23.1.2/8]
Container adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
Resizing
vector: as per insert/erase [23.2.4.2/6]deque: as per insert/erase [23.2.1.2/1]list: as per insert/erase [23.2.2.2/1]
Note 1
Unless otherwise specified (either explicitly or by defining a function in terms of other functions), invoking a container member function or passing a container as an argument to a library function shall not invalidate iterators to, or change the values of, objects within that container. [23.1/11]
Note 2
It's not clear in C++2003 whether "end" iterators are subject to the above rules; you should assume, anyway, that they are (as this is the case in practice).
Note 3
The rules for invalidation of pointers are the sames as the rules for invalidation of references.
'' meaning "same as above") it looked a bit weird and confusing. I didn't think of placing them in a single line :( @Matthieu: Unless the containers provide a means to check it, there's no way to know if a rehash will happen. –
Carduaceous swap() does not invalidate iterators [23.1/10], even though the result will be that they essentially now point to different elements. –
Fouquiertinville insert() causes the size of the vector to reach the the value specified in the previous reserve() call (which could well be smaller than the current capacity()), any subsequent insert() could cause reallocation and invalidate all the iterators. In C++11, it won't. –
Kinase C++11 (Source: Iterator Invalidation Rules (C++0x))
Insertion
Sequence containers
vector: all iterators and references before the point of insertion are unaffected, unless the new container size is greater than the previous capacity (in which case all iterators and references are invalidated) [23.3.6.5/1]deque: all iterators and references are invalidated, unless the inserted member is at an end (front or back) of the deque (in which case all iterators are invalidated, but references to elements are unaffected) [23.3.3.4/1]list: all iterators and references unaffected [23.3.5.4/1]forward_list: all iterators and references unaffected (applies toinsert_after) [23.3.4.5/1]array: (n/a)
Associative containers
[multi]{set,map}: all iterators and references unaffected [23.2.4/9]
Unsorted associative containers
unordered_[multi]{set,map}: all iterators invalidated when rehashing occurs, but references unaffected [23.2.5/8]. Rehashing does not occur if the insertion does not cause the container's size to exceedz * Bwherezis the maximum load factor andBthe current number of buckets. [23.2.5/14]
Container adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
Erasure
Sequence containers
vector: every iterator and reference at or after the point of erase is invalidated [23.3.6.5/3]deque: erasing the last element invalidates only iterators and references to the erased elements and the past-the-end iterator; erasing the first element invalidates only iterators and references to the erased elements; erasing any other elements invalidates all iterators and references (including the past-the-end iterator) [23.3.3.4/4]list: only the iterators and references to the erased element is invalidated [23.3.5.4/3]forward_list: only the iterators and references to the erased element is invalidated (applies toerase_after) [23.3.4.5/1]array: (n/a)
Associative containers
[multi]{set,map}: only iterators and references to the erased elements are invalidated [23.2.4/9]
Unordered associative containers
unordered_[multi]{set,map}: only iterators and references to the erased elements are invalidated [23.2.5/13]
Container adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
Resizing
vector: as per insert/erase [23.3.6.5/12]deque: as per insert/erase [23.3.3.3/3]list: as per insert/erase [23.3.5.3/1]forward_list: as per insert/erase [23.3.4.5/25]array: (n/a)
Note 1
Unless otherwise specified (either explicitly or by defining a function in terms of other functions), invoking a container member function or passing a container as an argument to a library function shall not invalidate iterators to, or change the values of, objects within that container. [23.2.1/11]
Note 2
no swap() function invalidates any references, pointers, or iterators referring to the elements of the containers being swapped. [ Note: The end() iterator does not refer to any element, so it may be invalidated. —end note ] [23.2.1/10]
Note 3
Other than the above caveat regarding swap(), it's not clear whether "end" iterators are subject to the above listed per-container rules; you should assume, anyway, that they are.
Note 4
vector and all unordered associative containers support reserve(n) which guarantees that no automatic resizing will occur at least until the size of the container grows to n. Caution should be taken with unordered associative containers because a future proposal will allow the specification of a minimum load factor, which would allow rehashing to occur on insert after enough erase operations reduce the container size below the minimum; the guarantee should be considered potentially void after an erase.
swap(), what's the rules for iterator validity upon copy/move assignment? –
Gastrectomy a=il; in which il designates an object of type initializer_list<value_type>, and it says:"Assigns the range [il.begin(),il.end()) into a. All existing elements of a are either assigned to or destroyed." For those elements got assigned but not destroyed (e.g. if destination and source has the exact same size and capacity), I really doubt their iterators are invalidated. This form of assignment at least can be comparable to the actual copy assignment. –
Gastrectomy all existing elements of a are either move assigned to or destroyed" for move-assignment, and specifies only one post-condition r==a for copy-assignment. I have already asked this as a separate question two days ago: #22253855 No reliable answer so far. You are welcome to provide an answer if you can find strong support from the standard. –
Gastrectomy std::basic_string<>? –
Wineglass std::basic_string does not seem to be counted as a container, and certainly not a container in the section of the standard that note applies to. Still, where does it say SSO is disallowed (I know COW is)? –
Wineglass C++17 (All references are from the final working draft of CPP17 - n4659)
Insertion
Sequence Containers
vector: The functionsinsert,emplace_back,emplace,push_backcause reallocation if the new size is greater than the old capacity. Reallocation invalidates all the references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements in the sequence. If no reallocation happens, all the iterators and references before the insertion point remain valid. [26.3.11.5/1]
With respect to thereservefunction, reallocation invalidates all the references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements in the sequence. No reallocation shall take place during insertions that happen after a call toreserve()until the time when an insertion would make the size of the vector greater than the value ofcapacity(). [26.3.11.3/6]deque: An insertion in the middle of the deque invalidates all the iterators and references to elements of the deque. An insertion at either end of the deque invalidates all the iterators to the deque, but has no effect on the validity of references to elements of the deque. [26.3.8.4/1]list: Does not affect the validity of iterators and references. If an exception is thrown there are no effects. [26.3.10.4/1].
Theinsert,emplace_front,emplace_back,emplace,push_front,push_backfunctions are covered under this rule.forward_list: None of the overloads ofinsert_aftershall affect the validity of iterators and references [26.3.9.5/1]array: As a rule, iterators to an array are never invalidated throughout the lifetime of the array. One should take note, however, that during swap, the iterator will continue to point to the same array element, and will thus change its value.
Associative Containers
All Associative Containers: Theinsertandemplacemembers shall not affect the validity of iterators and references to the container [26.2.6/9]
Unordered Associative Containers
All Unordered Associative Containers: Rehashing invalidates iterators, changes ordering between elements, and changes which buckets elements appear in, but does not invalidate pointers or references to elements. [26.2.7/9]
Theinsertandemplacemembers shall not affect the validity of references to container elements, but may invalidate all iterators to the container. [26.2.7/14]
Theinsertandemplacemembers shall not affect the validity of iterators if(N+n) <= z * B, whereNis the number of elements in the container prior to the insert operation,nis the number of elements inserted,Bis the container’s bucket count, andzis the container’s maximum load factor. [26.2.7/15]All Unordered Associative Containers: In case of a merge operation (e.g.,a.merge(a2)), iterators referring to the transferred elements and all iterators referring toawill be invalidated, but iterators to elements remaining ina2will remain valid. (Table 91 — Unordered associative container requirements)
Container Adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
Erasure
Sequence Containers
vector: The functionseraseandpop_backinvalidate iterators and references at or after the point of the erase. [26.3.11.5/3]deque: An erase operation that erases the last element of adequeinvalidates only the past-the-end iterator and all iterators and references to the erased elements. An erase operation that erases the first element of adequebut not the last element invalidates only iterators and references to the erased elements. An erase operation that erases neither the first element nor the last element of adequeinvalidates the past-the-end iterator and all iterators and references to all the elements of thedeque. [ Note:pop_frontandpop_backare erase operations. —end note ] [26.3.8.4/4]list: Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.10.4/3]. This applies toerase,pop_front,pop_back,clearfunctions.
removeandremove_ifmember functions: Erases all the elements in the list referred by a list iteratorifor which the following conditions hold:*i == value,pred(*i) != false. Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements [26.3.10.5/15].
uniquemember function - Erases all but the first element from every consecutive group of equal elements referred to by the iteratoriin the range[first + 1, last)for which*i == *(i-1)(for the version of unique with no arguments) orpred(*i, *(i - 1))(for the version of unique with a predicate argument) holds. Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.10.5/19]forward_list:erase_aftershall invalidate only iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.9.5/1].
removeandremove_ifmember functions - Erases all the elements in the list referred by a list iterator i for which the following conditions hold:*i == value(forremove()),pred(*i)is true (forremove_if()). Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.9.6/12].
uniquemember function - Erases all but the first element from every consecutive group of equal elements referred to by the iterator i in the range [first + 1, last) for which*i == *(i-1)(for the version with no arguments) orpred(*i, *(i - 1))(for the version with a predicate argument) holds. Invalidates only the iterators and references to the erased elements. [26.3.9.6/16]All Sequence Containers:clearinvalidates all references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements of a and may invalidate the past-the-end iterator (Table 87 — Sequence container requirements). But forforward_list,cleardoes not invalidate past-the-end iterators. [26.3.9.5/32]All Sequence Containers:assigninvalidates all references, pointers and iterators referring to the elements of the container. Forvectoranddeque, also invalidates the past-the-end iterator. (Table 87 — Sequence container requirements)
Associative Containers
All Associative Containers: Theerasemembers shall invalidate only iterators and references to the erased elements [26.2.6/9]All Associative Containers: Theextractmembers invalidate only iterators to the removed element; pointers and references to the removed element remain valid [26.2.6/10]
Container Adaptors
stack: inherited from underlying containerqueue: inherited from underlying containerpriority_queue: inherited from underlying container
General container requirements relating to iterator invalidation:
Unless otherwise specified (either explicitly or by defining a function in terms of other functions), invoking a container member function or passing a container as an argument to a library function shall not invalidate iterators to, or change the values of, objects within that container. [26.2.1/12]
no
swap()function invalidates any references, pointers, or iterators referring to the elements of the containers being swapped. [ Note: The end() iterator does not refer to any element, so it may be invalidated. —end note ] [26.2.1/(11.6)]
As examples of the above requirements:
transformalgorithm: Theopandbinary_opfunctions shall not invalidate iterators or subranges, or modify elements in the ranges [28.6.4/1]accumulatealgorithm: In the range [first, last],binary_opshall neither modify elements nor invalidate iterators or subranges [29.8.2/1]reducealgorithm: binary_op shall neither invalidate iterators or subranges, nor modify elements in the range [first, last]. [29.8.3/5]
and so on...
std::string? I think it's different from std::vector due to SSO –
Tucana string fails the second general requirement listed above. So I did not include it. Also tried to stick to the same pattern of the previous FAQ entries. –
Enduring "invalidated" can mean "no longer points to what it used to", not just "may not point to any valid element" as @Marshall Clow described in this answer ? Or it just indicates only 1 of the 2 condtions? –
Labors It is probably worth adding that an insert iterator of any kind (std::back_insert_iterator, std::front_insert_iterator, std::insert_iterator) is guaranteed to remain valid as long as all insertions are performed through this iterator and no other independent iterator-invalidating event occurs.
For example, when you are performing a series of insertion operations into a std::vector by using std::insert_iterator it is quite possible that these insertions will trigger vector reallocation, which will invalidate all iterators that "point" into that vector. However, the insert iterator in question is guaranteed to remain valid, i.e. you can safely continue the sequence of insertions. There's no need to worry about triggering vector reallocation at all.
This, again, applies only to insertions performed through the insert iterator itself. If iterator-invalidating event is triggered by some independent action on the container, then the insert iterator becomes invalidated as well in accordance with the general rules.
For example, this code
std::vector<int> v(10);
std::vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin() + 5;
std::insert_iterator<std::vector<int> > it_ins(v, it);
for (unsigned n = 20; n > 0; --n)
*it_ins++ = rand();
is guaranteed to perform a valid sequence of insertions into the vector, even if the vector "decides" to reallocate somewhere in the middle of this process. Iterator it will obviously become invalid, but it_ins will continue to remain valid.
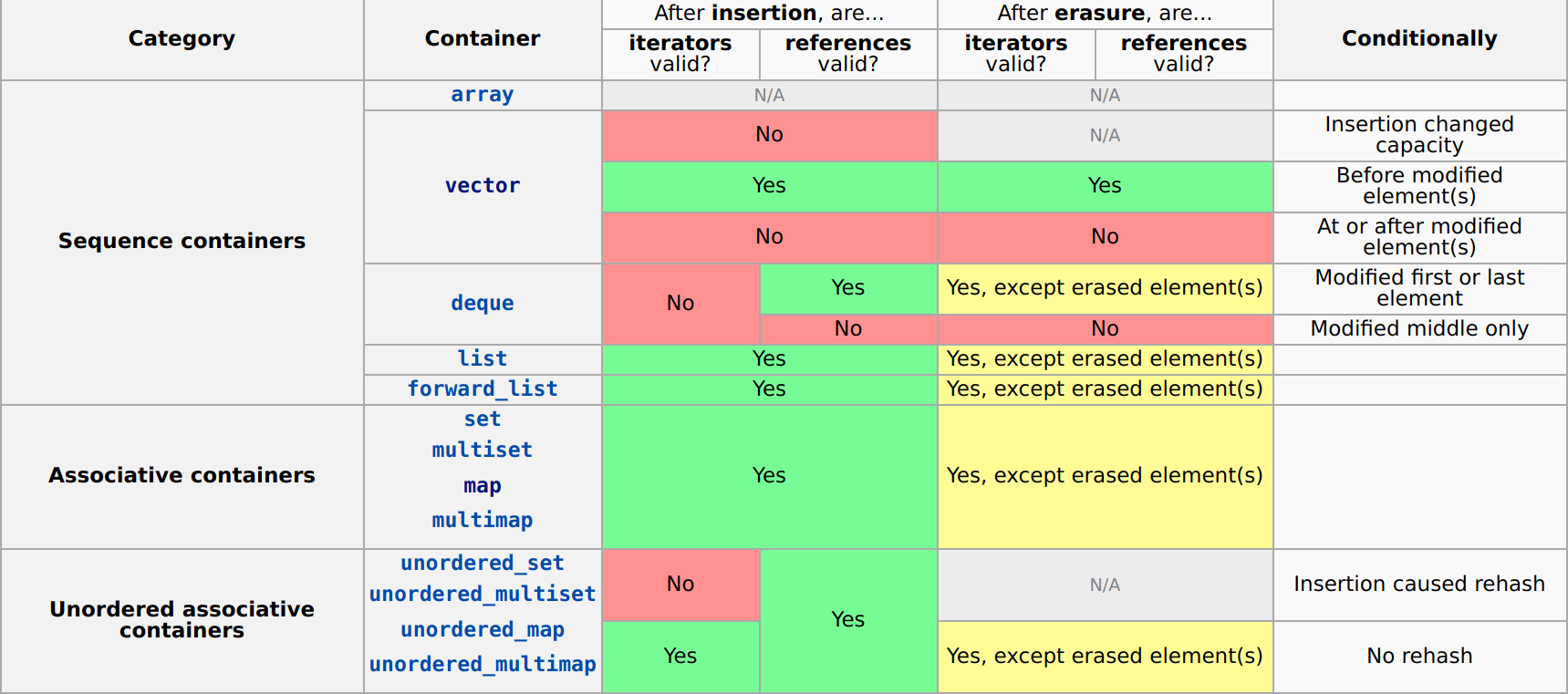
Here is a nice summary table from cppreference.com:
Here, insertion refers to any method which adds one or more elements to the container and erasure refers to any method which removes one or more elements from the container.
Since this question draws so many votes and kind of becomes an FAQ, I guess it would be better to write a separate answer to mention one significant difference between C++03 and C++11 regarding the impact of std::vector's insertion operation on the validity of iterators and references with respect to reserve() and capacity(), which the most upvoted answer failed to notice.
C++ 03:
Reallocation invalidates all the references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements in the sequence. It is guaranteed that no reallocation takes place during insertions that happen after a call to reserve() until the time when an insertion would make the size of the vector greater than the size specified in the most recent call to reserve().
C++11:
Reallocation invalidates all the references, pointers, and iterators referring to the elements in the sequence. It is guaranteed that no reallocation takes place during insertions that happen after a call to reserve() until the time when an insertion would make the size of the vector greater than the value of capacity().
So in C++03, it is not "unless the new container size is greater than the previous capacity (in which case all iterators and references are invalidated)" as mentioned in the other answer, instead, it should be "greater than the size specified in the most recent call to reserve()". This is one thing that C++03 differs from C++11. In C++03, once an insert() causes the size of the vector to reach the value specified in the previous reserve() call (which could well be smaller than the current capacity() since a reserve() could result a bigger capacity() than asked for), any subsequent insert() could cause reallocation and invalidate all the iterators and references. In C++11, this won't happen and you can always trust capacity() to know with certainty that the next reallocation won't take place before the size overpasses capacity().
In conclusion, if you are working with a C++03 vector and you want to make sure a reallocation won't happen when you perform insertion, it's the value of the argument you previously passed to reserve() that you should check the size against, not the return value of a call to capacity(), otherwise you may get yourself surprised at a "premature" reallocation.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.