Let's discuss from the very beginning:
JWT is a very modern, simple and secure approach which extends for Json Web Tokens. Json Web Tokens are a stateless solution for authentication. So there is no need to store any session state on the server, which of course is perfect for restful APIs.
Restful APIs should always be stateless, and the most widely used alternative to authentication with JWTs is to just store the user's log-in state on the server using sessions. But then of course does not follow the principle that says that restful APIs should be stateless and that's why solutions like JWT became popular and effective.
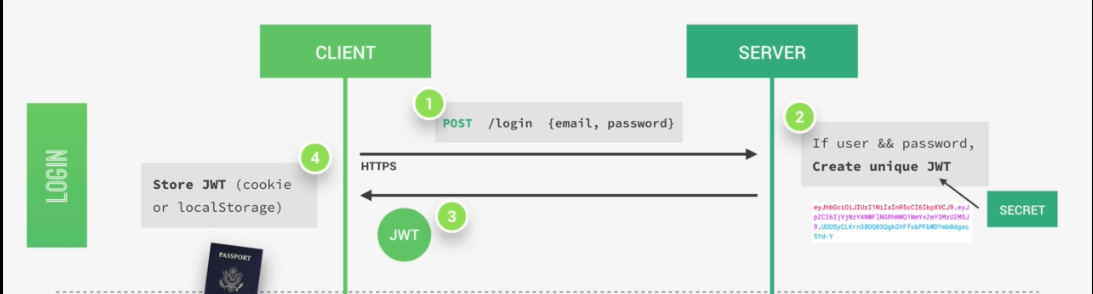
So now let's know how authentication actually works with Json Web Tokens. Assuming we already have a registered user in our database. So the user's client starts by making a post request with the username and the password, the application then checks if the user exists and if the password is correct, then the application will generate a unique Json Web Token for only that user.
The token is created using a secret string that is stored on a server. Next, the server then sends that JWT back to the client which will store it either in a cookie or in local storage.
![enter image description here]()
Just like this, the user is authenticated and basically logged into our application without leaving any state on the server.
So the server does in fact not know which user is actually logged in, but of course, the user knows that he's logged in because he has a valid Json Web Token which is a bit like a passport to access protected parts of the application.
So again, just to make sure you got the idea. A user is logged in as soon as he gets back his unique valid Json Web Token which is not saved anywhere on the server. And so this process is therefore completely stateless.
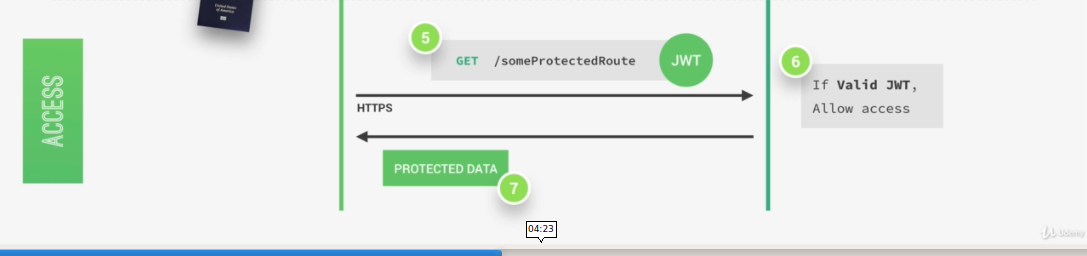
Then, each time a user wants to access a protected route like his user profile data, for example. He sends his Json Web Token along with a request, so it's a bit like showing his passport to get access to that route.
Once the request hits the server, our app will then verify if the Json Web Token is actually valid and if the user is really who he says he is, well then the requested data will be sent to the client and if not, then there will be an error telling the user that he's not allowed to access that resource.
![enter image description here]()
All this communication must happen over https, so secure encrypted Http in order to prevent that anyone can get access to passwords or Json Web Tokens. Only then we have a really secure system.
![enter image description here]()
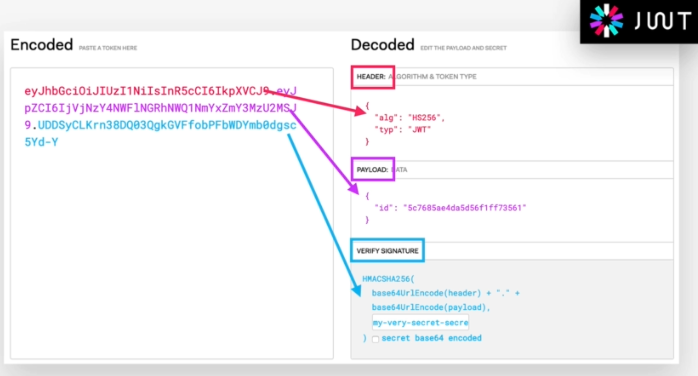
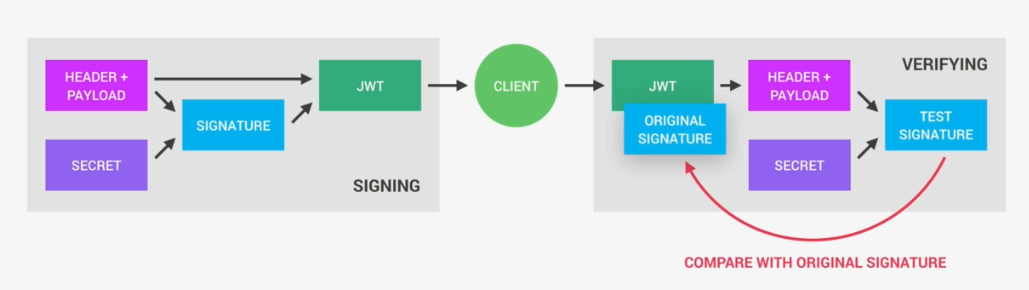
So a Json Web Token looks like left part of this screenshot which was taken from the JWT debugger at jwt.io. So essentially, it's an encoding string made up of three parts. The header, the payload and the signature Now the header is just some metadata about the token itself and the payload is the data that we can encode into the token, any data really that we want. So the more data we want to encode here the bigger the JWT. Anyway, these two parts are just plain text that will get encoded, but not encrypted.
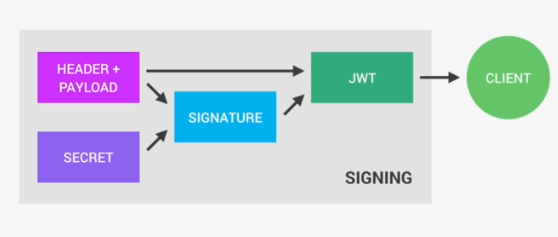
So anyone will be able to decode them and to read them, we cannot store any sensitive data in here. But that's not a problem at all because in the third part, so in the signature, is where things really get interesting. The signature is created using the header, the payload, and the secret that is saved on the server.
And this whole process is then called signing the Json Web Token. The signing algorithm takes the header, the payload, and the secret to create a unique signature. So only this data plus the secret can create this signature, all right?
Then together with the header and the payload, these signature forms the JWT,
which then gets sent to the client.
![enter image description here]()
Once the server receives a JWT to grant access to a protected route, it needs to verify it in order to determine if the user really is who he claims to be. In other words, it will verify if no one changed the header and the payload data of the token. So again, this verification step will check if no third party actually altered either the header or the payload of the Json Web Token.
So, how does this verification actually work? Well, it is actually quite straightforward. Once the JWT is received, the verification will take its header and payload, and together with the secret that is still saved on the server, basically create a test signature.
But the original signature that was generated when the JWT was first created is still in the token, right? And that's the key to this verification. Because now all we have to do is to compare the test signature with the original signature.
And if the test signature is the same as the original signature, then it means that the payload and the header have not been modified.
![enter image description here]()
Because if they had been modified, then the test signature would have to be different. Therefore in this case where there has been no alteration of the data, we can then authenticate the user. And of course, if the two signatures
are actually different, well, then it means that someone tampered with the data.
Usually by trying to change the payload. But that third party manipulating the payload does of course not have access to the secret, so they cannot sign the JWT.
So the original signature will never correspond to the manipulated data.
And therefore, the verification will always fail in this case. And that's the key to making this whole system work. It's the magic that makes JWT so simple,
but also extremely powerful.


md5('original messaged' + secret) != md5('changed message' + secret)thus if someone changes the message you can detect it – Ironclad