I would like to convert getdate() in SQL Server to EST time.
UPDATED ANSWER (05-29-2020)
The Azure SQL team has released a new function which makes this even easier. SELECT CURRENT_TIMEZONE_ID() will return your server's timezone. Adding this function into the ORIGINAL ANSWER below yields a single query will work globally on all Azure SQL Servers.
SELECT CONVERT(DATETIME,GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE (SELECT CURRENT_TIMEZONE_ID()) AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time')
This query will work on any Azure SQL Server.
ORIGINAL ANSWER:
There are a lot of answers here that are unnecessarily complex, or that don't account for daylight savings time. No massive CASE statements needed. No new stored procedure, or scalar/user defined functions are needed. As of SQL Server 2016, converting between timezones can be done with a single line of native sql. This has advantages. For example, it can be called from reports or used on databases that are read-only.
SELECT CONVERT(DATETIME,GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time')
That's it. Above, we are using the AT TIME ZONE features, described in more detail here. There may be some functions and features that are new here, so an explanation is warranted. The query above calls GETDATE() and sets it's timezone as UTC using AT TIMEZONE. Implicitly, this is also changing it's datatype from a datetime to datetimeoffset. Next, we'll call AT TIMEZONE again to cut it over to EST. Lastly, we'll wrap the entire thing in CONVERT() to get it back to a datetime, dropping the unneeded +/- hours portion during the process.
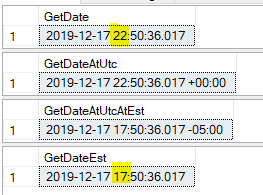
Taking the query step-by-step ...
SELECT [GetDate] = GETDATE()
SELECT [GetDateAtUtc] = GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC'
SELECT [GetDateAtUtcAtEst] = GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time'
SELECT [GetDateEst] = CONVERT(DATETIME,GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time')
SELECT CONVERT(DATETIME,GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time') does not work for me but SELECT CONVERT(DATETIME,GETUTCDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time') does –
Hush GETDATE() vs GETUTCDATE(). Azure SQL is always UTC, so those statements should be equal. Perhaps you are using SQL Server? –
Intraatomic GETUTCDATE() so it works for SQL Server as well. –
Intraatomic Have you considered GETUTCDATE() and performing the offset from there? If you mean EST as in standard time, then that is UTC-5, so
select dateadd(hour,-5,GETUTCDATE())
sys.time_zone_info table. So while this answer is technically correct, I think It's fair to presume the OP wants something that accepts a UTC date and translate it correctly to their current eastern time, whether recgonizing daylight savings or not. For that reason, I believe the other answers here are more useful. Thanks. –
Intraatomic EST is GMT-5 hours while EDT is GMT-4 hours.
To get EST:
select dateadd(hour,-5,GETUTCDATE())
To get EDT :
select dateadd(hour,-4,GETUTCDATE())
SQL server itself has the table current_utc_offset with correct offset for summer and winter time.
Please, try the query select * from current_utc_offset, change the date to different season on your server and review the table again.
So the correct function to get EST would be:
CREATE FUNCTION [dbo].[Getestlocaldatetime] ()
returns DATETIME
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @zz NVARCHAR(12);
DECLARE @hh NVARCHAR(3);
DECLARE @dd DATETIME;
SET @zz = (SELECT current_utc_offset
FROM sys.time_zone_info
WHERE NAME = N'US Eastern Standard Time')
SET @hh = Substring(@zz, 1, 3);
SET @dd = Dateadd(hh, CONVERT(INT, @hh), Getutcdate())
RETURN @dd
END
AT TIME ZONE feature which simplifies this. That feature is also using the sys.time_zone_info table. –
Intraatomic SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR, CONVERT(DATETIME, GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time'), 100) AS [Date_Result]
GetDate() is the system time from the server itself.
Take the hour difference of the GetDate() now and the time it is now in EST use this code where 1 is that said difference ( in this instance the server is in Central Time zone) (This is also assuming your server is accounting for DST)
SELECT Dateadd(hour, 1, Getdate()) AS EST
If you are attempting to output a local time, such as eastern time, with Daylight savings time, you need a function that Detects the start and end of daylight savings time and then applies a variable offset: I've found this: http://joeyiodice.com/convert-sql-azure-getdate-utc-time-to-local-time/ useful.
For those who are using latest version of sql server can create a .net function
A scalar-valued function (SVF) returns a single value, such as a string, integer, or bit value. You can create scalar-valued user-defined functions in managed code using any .NET Framework programming language. These functions are accessible to Transact-SQL or other managed code. For information about the advantages of CLR integration and choosing between managed code and Transact-SQL.
Since .NET has access to all time zone at operating system so you don't have to calculate daylight saving -4 or -5 fundamentals.
var timeUtc = DateTime.UtcNow;
TimeZoneInfo easternZone = TimeZoneInfo.FindSystemTimeZoneById("Eastern Standard Time");
DateTime easternTime = TimeZoneInfo.ConvertTimeFromUtc(timeUtc, easternZone);
Select CONVERT(DATETIME,GETUTCDATE() AT TIME ZONE 'UTC' AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time')
using GETDATE() :
GMT :
DATE WILL BE DISPLAYED:
SELECT GETDATE()
EST :
USE GETDATE() FOR CONVERSION NOW:
SELECT DATEADD(HOUR, -4, CONVERT(varchar(20),GETDATE(),120))
If you want to do this without calling a function, you can do it with a CASE statement as well. The code below converts a UTC field to Mountain Time accounting for daylight savings. For EST, you would just change all the -6 to -4 and change all the -7 to -5.
--Adjust a UTC value, in the example the UTC field is identified as UTC.Field, to account for daylight savings time when converting out of UTC to Mountain time.
CASE
--When it's between March and November, it is summer time which is -6 from UTC
WHEN MONTH ( UTC.Field ) > 3 AND MONTH ( UTC.Field ) < 11
THEN DATEADD ( HOUR , -6 , UTC.Field )
--When its March and the day is greater than the 14, you know it's summer (-6)
WHEN MONTH ( UTC.Field ) = 3
AND DATEPART ( DAY , UTC.Field ) >= 14
THEN
--However, if UTC is before 9am on that Sunday, then it's before 2am Mountain which means it's still Winter daylight time.
CASE
WHEN DATEPART ( WEEKDAY , UTC.Field ) = 1
AND UTC.Field < '9:00'
--Before 2am mountain time so it's winter, -7 hours for Winter daylight time
THEN DATEADD ( HOUR , -7 , UTC.Field )
--Otherwise -6 because it'll be after 2am making it Summer daylight time
ELSE DATEADD ( HOUR , -6 , UTC.Field )
END
WHEN MONTH ( UTC.Field ) = 3
AND ( DATEPART ( WEEKDAY , UTC.Field ) + 7 ) <= DATEPART ( day , UTC.Field )
THEN
--According to the date, it's moved onto Summer daylight, but we need to account for the hours leading up to 2am if it's Sunday
CASE
WHEN DATEPART ( WEEKDAY , UTC.Field ) = 1
AND UTC.Field < '9:00'
--Before 9am UTC is before 2am Mountain so it's winter Daylight, -7 hours
THEN DATEADD ( HOUR , -7 , UTC.Field )
--Otherwise, it's summer daylight, -6 hours
ELSE DATEADD ( HOUR , -6 , UTC.Field )
END
--When it's November and the weekday is greater than the calendar date, it's still Summer so -6 from the time
WHEN MONTH ( UTC.Field ) = 11
AND DATEPART ( WEEKDAY , UTC.Field ) > DATEPART ( DAY , UTC.Field )
THEN DATEADD ( HOUR , -6 , UTC.Field )
WHEN MONTH ( UTC.Field ) = 11
AND DATEPART ( WEEKDAY , UTC.Field ) <= DATEPART ( DAY , UTC.Field )
--If the weekday is less than or equal to the calendar day it's Winter daylight but we need to account for the hours leading up to 2am.
CASE
WHEN DATEPART ( WEEKDAY , UTC.Field ) = 1
AND UTC.Field < '8:00'
--If it's before 8am UTC and it's Sunday in the logic outlined, then it's still Summer daylight, -6 hours
THEN DATEADD ( HOUR , -6 , UTC.Field )
--Otherwise, adjust for Winter daylight at -7
ELSE DATEADD ( HOUR , -7 , UTC.Field )
END
--If the date doesn't fall into any of the above logic, it's Winter daylight, -7
ELSE
DATEADD ( HOUR , -7 , UTC.Field )
END
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.