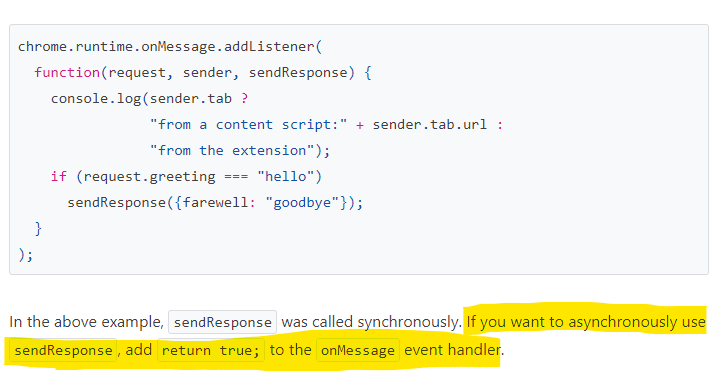
I've always seen Promise work with setTimeout, but I'm trying to make it based on whatever the chrome.runtime.sendMessage returns to the Promise.
I've got a content script that does this function once the script has been done.
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({complete: true});
I've got a background script that loops through every item in an array and uses one of its values to open a URL with chrome.tabs.update.
What I'm trying to do is make the async function wait for the Message the content script is sending and only continue with the next iteration once the message has been received, although I don't know how to implement this since I've only seen examples with setTimeout.
So it should
- Open the first item in the array and stop
- Execute the content script on that page and do a sendMessage at the end.
- Now the background script should be waiting for the sendMessage to be received before going to the next item.
- Once the sendMessage has been received with onMessage it should go to the next and item and repeat from step 2
This is the background script.
chrome.storage.local.get('userItems', function(result) {
console.log(result.userItems);
function delay() {
// I suppose I should do something with onMessage in the delay function
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 500));
}
async function delayedLog(item) {
await delay();
console.log(item);
var url = "http://www.example.com/" + item.Category;
chrome.tabs.update({
url: url
});
}
async function processArray(array) {
for (const item of array) {
await delayedLog(item);
}
}
processArray(result.userItems);
});