I have an Excel file with data in it. I want to write some specific rows of it to another Excel file that I created by code. By the way I have the indexes of these rows in a list. How can i do that?
MS provides the OpenXML SDK V 2.5 - see https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb448854(v=office.15).aspx
This can read+write MS Office files (including Excel)...
Another option see http://www.codeproject.com/KB/office/OpenXML.aspx
IF you need more like rendering, formulas etc. then there are different commercial libraries like Aspose and Flexcel...
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Excel.Application xlApp ;
Excel.Workbook xlWorkBook ;
Excel.Worksheet xlWorkSheet ;
object misValue = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
xlApp = new Excel.ApplicationClass();
xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Add(misValue);
xlWorkSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)xlWorkBook.Worksheets.get_Item(1);
xlWorkSheet.Cells[1, 1] = "http://csharp.net-informations.com";
xlWorkBook.SaveAs("csharp-Excel.xls", Excel.XlFileFormat.xlWorkbookNormal, misValue, misValue, misValue, misValue, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlExclusive, misValue, misValue, misValue, misValue, misValue);
xlWorkBook.Close(true, misValue, misValue);
xlApp.Quit();
releaseObject(xlWorkSheet);
releaseObject(xlWorkBook);
releaseObject(xlApp);
MessageBox.Show("Excel file created , you can find the file c:\\csharp-Excel.xls");
}
private void releaseObject(object obj)
{
try
{
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(obj);
obj = null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
obj = null;
MessageBox.Show("Exception Occured while releasing object " + ex.ToString());
}
finally
{
GC.Collect();
}
}
The above code is taken directly off csharp.net please take a look on the site.
Have you ever hear NPOI, a .NET library that can read/write Office formats without Microsoft Office installed. No COM+, no interop. Github Page
This is my Excel Export class
/*
* User: TMPCSigit [email protected]
* Date: 25/11/2019
* Time: 11:28
*
*/
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using NPOI.HSSF.UserModel;
using NPOI.SS.UserModel;
using NPOI.XSSF.UserModel;
namespace Employee_Manager
{
public static class ExportHelper
{
public static void WriteCell( ISheet sheet, int columnIndex, int rowIndex, string value )
{
var row = sheet.GetRow( rowIndex ) ?? sheet.CreateRow( rowIndex );
var cell = row.GetCell( columnIndex ) ?? row.CreateCell( columnIndex );
cell.SetCellValue( value );
}
public static void WriteCell( ISheet sheet, int columnIndex, int rowIndex, double value )
{
var row = sheet.GetRow( rowIndex ) ?? sheet.CreateRow( rowIndex );
var cell = row.GetCell( columnIndex ) ?? row.CreateCell( columnIndex );
cell.SetCellValue( value );
}
public static void WriteCell( ISheet sheet, int columnIndex, int rowIndex, DateTime value )
{
var row = sheet.GetRow( rowIndex ) ?? sheet.CreateRow( rowIndex );
var cell = row.GetCell( columnIndex ) ?? row.CreateCell( columnIndex );
cell.SetCellValue( value );
}
public static void WriteStyle( ISheet sheet, int columnIndex, int rowIndex, ICellStyle style )
{
var row = sheet.GetRow( rowIndex ) ?? sheet.CreateRow( rowIndex );
var cell = row.GetCell( columnIndex ) ?? row.CreateCell( columnIndex );
cell.CellStyle = style;
}
public static IWorkbook CreateNewBook( string filePath )
{
IWorkbook book;
var extension = Path.GetExtension( filePath );
// HSSF => Microsoft Excel(xls形式)(excel 97-2003)
// XSSF => Office Open XML Workbook形式(xlsx形式)(excel 2007以降)
if( extension == ".xls" ) {
book = new HSSFWorkbook();
}
else if( extension == ".xlsx" ) {
book = new XSSFWorkbook();
}
else {
throw new ApplicationException( "CreateNewBook: invalid extension" );
}
return book;
}
public static void createXls(DataGridView dg){
try {
string filePath = "";
SaveFileDialog sfd = new SaveFileDialog();
sfd.Filter = "Excel XLS (*.xls)|*.xls";
sfd.FileName = "Export.xls";
if (sfd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
filePath = sfd.FileName;
var book = CreateNewBook( filePath );
book.CreateSheet( "Employee" );
var sheet = book.GetSheet( "Employee" );
int columnCount = dg.ColumnCount;
string columnNames = "";
string[] output = new string[dg.RowCount + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++)
{
WriteCell( sheet, i, 0, SplitCamelCase(dg.Columns[i].Name.ToString()) );
}
for (int i = 0; i < dg.RowCount; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < columnCount; j++)
{
var celData = dg.Rows[i].Cells[j].Value;
if(celData == "" || celData == null){
celData = "-";
}
if(celData.ToString() == "System.Drawing.Bitmap"){
celData = "Ada";
}
WriteCell( sheet, j, i+1, celData.ToString() );
}
}
var style = book.CreateCellStyle();
style.DataFormat = book.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat( "yyyy/mm/dd" );
WriteStyle( sheet, 0, 4, style );
using( var fs = new FileStream( filePath, FileMode.Create ) ) {
book.Write( fs );
}
}
}
catch( Exception ex ) {
Console.WriteLine( ex );
}
}
public static string SplitCamelCase(string input)
{
return Regex.Replace(input, "(?<=[a-z])([A-Z])", " $1", RegexOptions.Compiled);
}
}
}
I used interop to open Excel and to modify the column widths once the data was done. If you use interop to spit the data into a new Excel workbook (if this is what you want), it will be terribly slow. Instead, I generated a .CSV, then opened the .CSV in Excel. This has its own problems, but I've found this the quickest method.
First, convert the .CSV:
// Convert array data into CSV format.
// Modified from http://csharphelper.com/blog/2018/04/write-a-csv-file-from-an-array-in-c/.
private string GetCSV(List<string> Headers, List<List<double>> Data)
{
// Get the bounds.
var rows = Data[0].Count;
var cols = Data.Count;
var row = 0;
// Convert the array into a CSV string.
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// Add the first field in this row.
sb.Append(Headers[0]);
// Add the other fields in this row separated by commas.
for (int col = 1; col < cols; col++)
sb.Append("," + Headers[col]);
// Move to the next line.
sb.AppendLine();
for (row = 0; row < rows; row++)
{
// Add the first field in this row.
sb.Append(Data[0][row]);
// Add the other fields in this row separated by commas.
for (int col = 1; col < cols; col++)
sb.Append("," + Data[col][row]);
// Move to the next line.
sb.AppendLine();
}
// Return the CSV format string.
return sb.ToString();
}
Then, export it to Excel:
public void ExportToExcel()
{
// Initialize app and pop Excel on the screen.
var excelApp = new Excel.Application { Visible = true };
// I use unix time to give the files a unique name that's almost somewhat useful.
DateTime dateTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
long unixTime = ((DateTimeOffset)dateTime).ToUnixTimeSeconds();
var path = @"C:\Users\my\path\here" + unixTime + ".csv";
var csv = GetCSV();
File.WriteAllText(path, csv);
// Create a new workbook and get its active sheet.
excelApp.Workbooks.Open(path);
var workSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelApp.ActiveSheet;
// iterate over each value and throw it in the chart
for (var column = 0; column < Data.Count; column++)
{
((Excel.Range)workSheet.Columns[column + 1]).AutoFit();
}
currentSheet = workSheet;
}
You'll have to install some stuff, too...
Right click on the solution from solution explorer and select "Manage NuGet Packages." - add
Microsoft.Office.Interop.ExcelIt might actually work right now if you created the project the way interop wants you to. If it still doesn't work, I had to create a new project in a different category. Under New > Project, select Visual C# > Windows Desktop > Console App. Otherwise, the interop tools won't work.
In case I forgot anything, here's my 'using' statements:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
You can use ExcelDataReader to read existing Excel file:
using (var stream = File.Open("C:\\temp\\input.xlsx", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read))
{
using (var reader = ExcelReaderFactory.CreateReader(stream))
{
while (reader.Read())
{
for (var i = 0; i < reader.FieldCount; i++)
{
var value = reader.GetValue(i)?.ToString();
}
}
}
}
After you collected all data needed you can try my SwiftExcel library to export it to the new Excel file:
using (var ew = new ExcelWriter("C:\\temp\\output.xlsx"))
{
for (var i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
ew.Write("your_data", i, 1);
}
}
Nuget commands to install both libraries:
Install-Package ExcelDataReader
Install-Package SwiftExcel
I was also struggling with a similar issue dealing with exporting data into an Excel spreadsheet using C#. I tried many different methods working with external DLLs and had no luck.
For the export functionality you do not need to use anything dealing with the external DLLs. Instead, just maintain the header and content type of the response.
Here is an article that I found rather helpful. The article talks about how to export data to Excel spreadsheets using ASP.NET.
http://www.icodefor.net/2016/07/export-data-to-excel-sheet-in-asp-dot-net-c-sharp.html
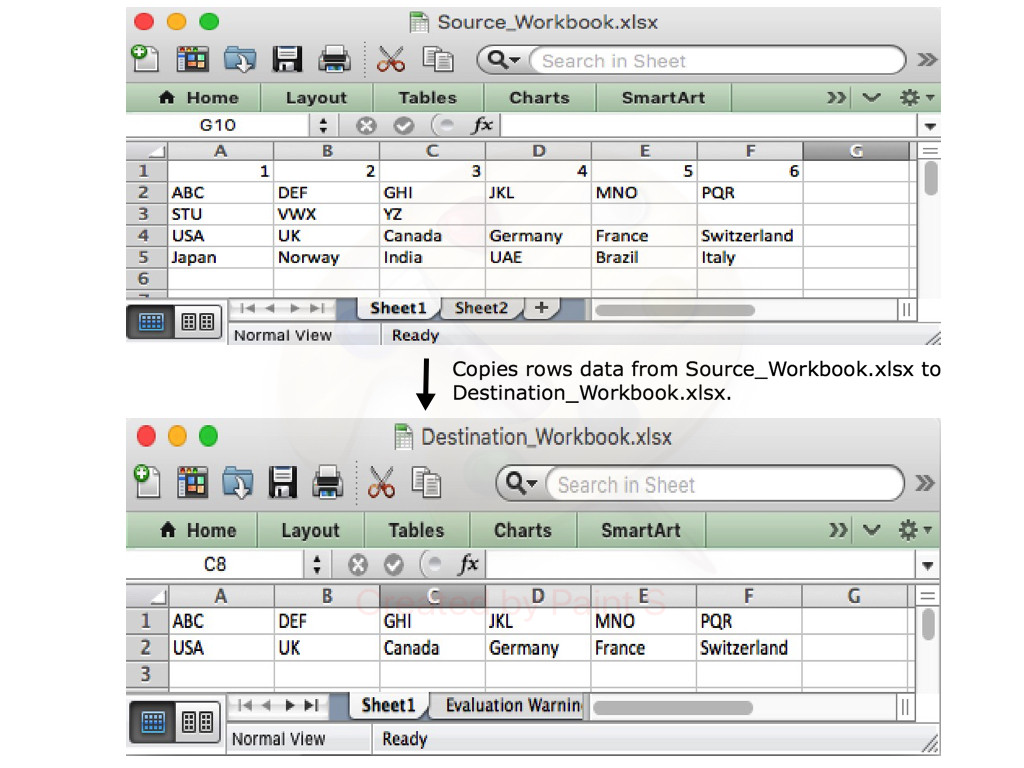
With Aspose.Cells library for .NET, you can easily export data of specific rows and columns from one Excel document to another. The following code sample shows how to do this in C# language.
// Open the source excel file.
Workbook srcWorkbook = new Workbook("Source_Workbook.xlsx");
// Create the destination excel file.
Workbook destWorkbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet of the source workbook.
Worksheet srcWorksheet = srcWorkbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the first worksheet of the destination workbook.
Worksheet desWorksheet = destWorkbook.Worksheets[0];
// Copy the second row of the source Workbook to the first row of destination Workbook.
desWorksheet.Cells.CopyRow(srcWorksheet.Cells, 1, 0);
// Copy the fourth row of the source Workbook to the second row of destination Workbook.
desWorksheet.Cells.CopyRow(srcWorksheet.Cells, 3, 1);
// Save the destination excel file.
destWorkbook.Save("Destination_Workbook.xlsx");
The following blog post explains in detail how to export data from different sources to an Excel document.
https://blog.conholdate.com/2020/08/10/export-data-to-excel-in-csharp/
© 2022 - 2025 — McMap. All rights reserved.