This Answer is to correct a misconception that is being put about by some of the other Answers:
For example:
The compiler might substitute x + y with a constant ("xyzabc"), though. @Binkan Salaryman
... and String object 4 [the String that corresponds to concatenation] can be computed by the compiler and turned into an interned constant as well. @dasblinkenlight
This is incorrect. The JLS states this:
15.18.1. String Concatenation Operator +
....
The String object is newly created (§12.5) unless the expression is a constant expression (§15.28).
In order to qualify as a constant expression, the variable names in the expression must be:
Simple names (§6.5.6.1) that refer to constant variables (§4.12.4).
where a "constant variable" is defined as:
A constant variable is a final variable of primitive type or type String that is initialized with a constant expression (§15.28).
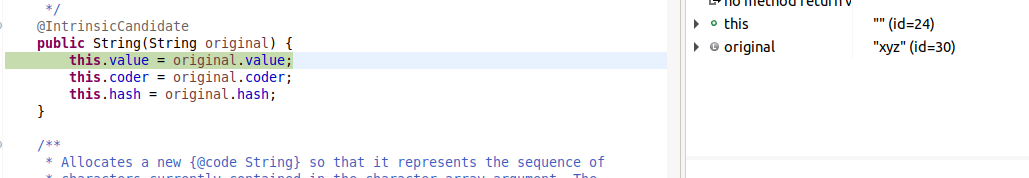
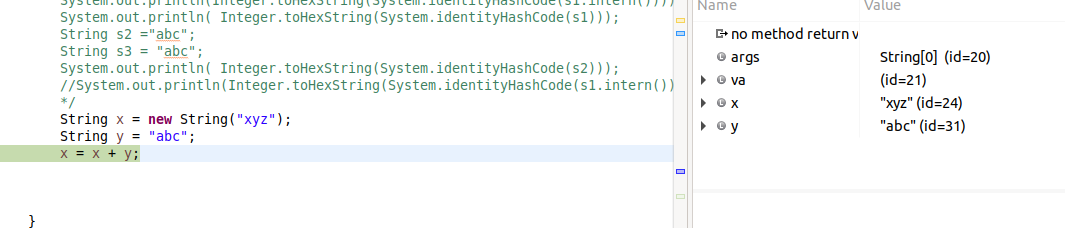
In this example, neither x or y are final so they are not constant variables. And even if they were final, y still wouldn't be a constant variable because of the use of the new operator in its initialization.
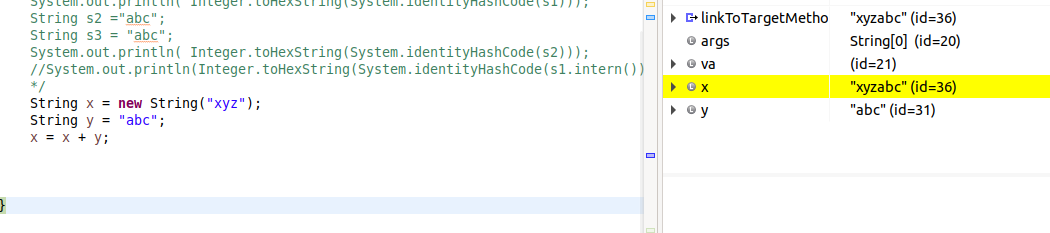
In short, the Java compiler is not permitted to use an intern'd constant "xyzabc" as the result of the concatenation expression.
If I added the following statement at the end:
System.out.println(x == "xyzabc");
it will always print false ... assuming that the compiler is conformant to the Java Language Specification.

xadds an important consideration here. – Slacken