I spent quite sometime figuring how to set up adb on Mac, so I figure writing how to set it up might be useful to some people. adb is the command line tool to install and run android apps on your phone/emulator
Note: this was originally written on Installing ADB on macOS but that question was closed as a duplicate of this one.
Note for zsh users: replace all references to ~/.bash_profile with ~/.zshrc.
Option 1 - Using Homebrew
This is the easiest way and will provide automatic updates.
Install homebrew
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)"Install adb
brew install android-platform-toolsor try a cask install depending on your settings:
brew install --cask android-platform-toolsStart using adb
adb devices
Option 2 - Manually (just the platform tools)
This is the easiest way to get a manual installation of ADB and Fastboot.
Delete your old installation (optional)
rm -rf ~/.android-sdk-macosx/Navigate to https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/platform-tools.html and click on the
SDK Platform-Tools for Maclink.Go to your Downloads folder
cd ~/Downloads/Unzip the tools you downloaded
unzip platform-tools-latest*.zipMove them somewhere you won't accidentally delete them
mkdir ~/.android-sdk-macosx mv platform-tools/ ~/.android-sdk-macosx/platform-toolsAdd
platform-toolsto your pathecho 'export PATH=$PATH:~/.android-sdk-macosx/platform-tools/' >> ~/.bash_profileRefresh your bash profile (or restart your terminal app)
source ~/.bash_profileStart using adb
adb devices
Option 3 - If you already have Android Studio installed
Add
platform-toolsto your pathecho 'export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk' >> ~/.bash_profile echo 'export PATH="$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools"' >> ~/.bash_profileRefresh your bash profile (or restart your terminal app)
source ~/.bash_profileStart using adb
adb devices
Option 4 - MacPorts
Install the Android SDK:
sudo port install androidRun the SDK manager:
sh /opt/local/share/java/android-sdk-macosx/tools/androidUncheck everything but
Android SDK Platform-tools(optional)Install the packages, accepting licenses. Close the SDK Manager.
Add
platform-toolsto your path; in MacPorts, they're in/opt/local/share/java/android-sdk-macosx/platform-tools. E.g., for bash:echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/opt/local/share/java/android-sdk-macosx/platform-tools"' >> ~/.bash_profileRefresh your bash profile (or restart your terminal/shell):
source ~/.bash_profile
Start using adb:
adb devices
Option 5 - Manually (with SDK Manager)
Delete your old installation (optional)
rm -rf ~/.android-sdk-macosx/Download the Mac SDK Tools from the Android developer site under "Get just the command line tools". Make sure you save them to your Downloads folder.
Go to your Downloads folder
cd ~/Downloads/Unzip the tools you downloaded
unzip tools_r*-macosx.zipMove them somewhere you won't accidentally delete them
mkdir ~/.android-sdk-macosx mv tools/ ~/.android-sdk-macosx/toolsRun the SDK Manager
sh ~/.android-sdk-macosx/tools/androidUncheck everything but
Android SDK Platform-tools(optional)Click
Install Packages, accept licenses, clickInstall. Close the SDK Manager window.Add
platform-toolsto your pathecho 'export PATH="$PATH:~/.android-sdk-macosx/platform-tools/"' >> ~/.bash_profileRefresh your bash profile (or restart your terminal app)
source ~/.bash_profileStart using adb
adb devices
homebrew is the recommended option. it may be the easiest option to install but for a novice developer it should be skipped in favor of the official Google binaries (options #2 and #3) –
Quintonquintuple echo "export PATH=\$PATH:/Users/${USER}/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/" >> ~/.bash_profile && source ~/.bash_profile
If you put the android-sdks folder in other directory, replace the path with the directory android-sdks/platform-tools is in
zsh instead bash, you'll need to add this to ~/.zshrc –
Ens source ~/.bash_profile. –
Cia which and other basic commands went after reloading the shell (source ~/.bash_profile) : that should read as export PATH=$PATH:/Users/${USER}/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools –
Doctrinal echo "export PATH=\$PATH:/Users/${USER}/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/" >> ~/.zshrc && source ~/.zshrc –
Byplay Only for zsh users in Terminal or iterm2 in macOS
type the following two commands to add the android sdk and platform-tools to your zsh in Terminal or iterm2 in macOS
echo 'export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk' >> ~/.zshrc
echo 'export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools' >> ~/.zshrc
After adding the two command to ~/.zshrc you need to source the zsh.
source ~/.zshrc
$user/Library and also have you set your ANDROID_HOME as well prior to trying this? –
Paradisiacal This Works Flawless....
In terminal Run both commands next to each other
export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk
export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools
sdk folder has been removed. If those two commands were run, adb devices won't work. Should be the following for latest android studio ` export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools ` –
Gonzalez adb devices be globally recognized in terminal? Because it didn't. I have Android Studio installed. Closed and opened a new Terminal window. –
Tull 2022 Solution
If you have Android Studio installed already and Terminal isn't picking up ADB, here's a one-liner that should fix it:
sudo ln -s ~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/adb /usr/local/bin
It creates a symbolic link (essentially a shortcut) for the adb executable. It's added to /usr/local/bin which is one of the default locations where Terminal looks for command line tools.
ln and -s? –
Zoba NOTE: Path for adb has changed since Android Studio 1.0.xx
For bash shell, use:
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:'$HOME'/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools' >> ~/.bash_profile
For tcsh shell, use:
echo 'setenv PATH $PATH\:'$HOME'/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools' >> ~/.tcshrc
~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools –
Willenewillet If you are using zsh shell and after trying all this solutions, you still need to set $PATH and $ANDROID_HOME every time you open new terminal instance, then here is your answer:
step 1: in terminal run nano ~/.zshrc
step 2: paste following command at the end of the file
export ANDROID_HOME=~/Library/Android/sdk
export PATH=$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools:$PATH
export PATH=$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$PATH
export PATH=$ANDROID_HOME/tools/bin:$PATH
step 3: After copying the lines above, to save hit control + X. and to confirm hit Y. It will ask you if you wish to change the file name but don't change the name so directly hit enter
step 4: Restart your terminal and execute the adb command.
Bingo!
Personally I just source my .bashrc in my .bash_profile:
echo 'source ~/.bashrc' >> ~/.bash_profile
So I put it in my .bashrc. And I'm using Android Studio, so it was a different path.
echo 'PATH=$PATH:$HOME/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/' >> ~/.bashrc
You may also want the following:
echo 'ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Library/Android/sdk' >> ~/.bashrc
Here is a step wise information :
Step-1
Start up Terminal and go to your home folder.
cd ~/
Step-2
Open and edit .bash_profile file
$ open -e .bash_profile
If you don’t have .bash_profile file in your computer path, then create one. Enter below command to create a new file. Once created follow Step-2.
touch .bash_profile
Step-3
Save the below line)
export PATH=${PATH}:/Applications/adt-bundle-mac-x86_64-20140321/sdk/tools
export PATH=${PATH}:/Applications/adt-bundle-mac-x86_64-20140321/sdk/platform-tools
Step-4
Refresh the file using below command
$ source .bash_profile
$ echo $PATH
You should see your android path set in the output now.
The simplest way to use adb command on your Mac systems would be to add the path to the platform-tools (where adb lives) into your bash_profile.
Steps to add the adb path: 1. open the bash_profile: This can be done by using the following commands
open ~/.bash_profile
This opens up the bash_profile in an editor.
Locate the platform_tools, usually they are present at the following location: Users/"user_folder"/Library/Android/sdk/platform_tools
Paste the following command in the bash_profile file which opens up:
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/A374375/Library/Android/sdk/platform-toolsSave the file using the command:
source ~/.bash_profile
Check if the path is saved by typing:
echo $PATH: You should be able to find the entire path displayed in the output.Type
adbto see if the configuration worked. If you have any devices connected to the machine or any emulators running on your system they would be displayed when you typeadb devices
For Mac users : Step 1: Install the Android Studio
Step2 : Open the terminal and type
cd
Step 3: Type below mentioned command changing the userName:
export PATH=“/Users/{user_name}/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools”:$PATH
On MacOS Big Sur do the following:
Open config file:
nano ~/.zshrc
Add paths to PATH variable:
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/tools:$PATH
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools:$PATH
close file and save changes. Then in terminal write:
source ~/.zshrc
And then you'll be able to run:
adb devices
adb kill-server
cd sdk/platform-tools/ and then use ./adb devices instead
/Users/ashokr/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools and then it works. –
Speck This solution is for Mac:
Considering you have already downloaded SDK platform tools & trying to set adb path:
If you want to check the SDK is available or not, just check it by following this path:
User > Library (Hidden folder) > Android > sdk > platform-tools > adb

To set the PATH for the adb command on a macOS system, firstly need to edit your shell configuration file. The default shell on macOS is Bash or Zash.
If you're using Bash, so you will need to edit the ~/.bash_profile file otherwise edit ~/.zprofile in your home directory.
Here's how to do it:
By Terminal:
- Open a terminal window and enter the following command:
nano ~/.bash_profile
or
nano ~/.zprofile
This will open the ~/.bash_profile or ~/.zprofile file in the Nano text editor.
- Add the following line to the file:
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/tools:$PATH
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools:$PATH
Press Ctrl+X to exit the Nano editor, then press Y to save the changes and Enter to confirm the filename.
- Run the following command to reload your shell configuration:
source ~/.bash_profile
or
source ~/.zprofile
After you have set the PATH for adb, you should be able to run the adb command from any terminal window.
By Manual:
- Go to the
Homedirectory & tapcommand+shift+.(To show the hidden files)
![View IMAGE]()
- Search file ~/.bash_profile or ~/.zprofile & open it.
![View IMAGE]()
- Add required path & save it.
![View IMAGE]()
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/tools:$PATH
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools:$PATH
- Run the following command to reload your shell configuration:
source ~/.bash_profile
or
source ~/.zprofile
After you have set the PATH for adb, you should be able to run the adb command from any terminal window.
If you using zsh then you need do the add the following to your .zshrc
Steps: Step 1: Open your .zshrc profile
open -e .zshrc
Step 2: Add the following to the file
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/${YourUser}/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools
export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/${YourUser}/Library/Android/sdk
Step 3: Save the file and close. Step 4: Reload the .zshrc
source .zshrc
Step 5: Check the devices connected
adb devices
if you are using Android Studio in MAC OS X , you could exec the following command in your terminal app:
echo 'alias adb="/Applications/Android\ Studio.app/sdk/platform-tools/adb"' >> .bashrc
exec $SHELL
and next:
adb devices
and you should be showing a list with your android devices connected via USB cable in your MAC, for example something like this:
* daemon not running. starting it now on port 5037 *
* daemon started successfully *
List of devices attached
deb7bed5 device
MAC Solution.
cd /Users/<user>/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools
./adb devices
For macOS Users Updated to MacOs Catalina,
~/.bash_profile changed to ~/.zshrc
So ,to run adb command and all other commands already exported to ~/.bash_profile easy walkaround is to export bash_profile to zshrc
To do that,
1) Navigate to the home directory in finder
2) I used Cmd + Shift + . to show the hidden files in Finder
3) Create .zshrc file if already not exist
4) Add line "source ~/.bash_profile" without quotes
5) Save
6) Quit and open terminal
start using adb devices
Here's a detailed manual:
http://codexpi.com/add-android-adb-path-mac-os-x-mavericks/
To sum this up:
Create and open the bash_profile file
touch .bash_profile
open -e .bash_profileAdd the path of the platform-tools folder (within the Android SDK)
export PATH="$PATH:/Users/USERNAME/PATH TO ANDROID SDK/platform-tools/Run the command
. .bash_profileto update (no need to restart the terminal)
If you are using ZSH and have Android Studio 1.3:
1. Open .zshrc file (Located in your home directory, file is hidden so make sure you can see hidden files)
2. Add this line at the end: alias adb="/Users/kamil/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/adb"
3. Quit terminal
4. Open terminal and type in adb devices
5. If it worked it will give you list of all connected devices
Mac OS Open Terminal
touch ~/.bash_profile; open ~/.bash_profile
Copy and paste:
export ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Library/Android/sdk
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools
command + S for save.
zsh: command not found: adb after opening a new terminal window. EDIT: I just had to follow these steps afterwards: [ https://mcmap.net/q/53567/-set-up-adb-on-mac-os-x ] –
Tull If you are setting the path in Catalina use below command one after another in the terminal. It's working fine for me.
export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk
export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools
source ~/.bash_profile
Download Android Platform Tools for macOS from:
https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/platform-tools
Extract to your somewhere e.g ~/installs/platform-tools
Add that folder to path by running:
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:~/installs/platform-tools' >> ~/.zshrc
Either restart terminal or run:
source ~/.zshrc
Assuming that you are using zsh.
Commenting with some updated information from 2018.
Executable Binaries for Platform tools are made available for mac by Android here: https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/platform-tools.html
Download these to your mac. Place them in a directory e.g. I placed in ~/Software/platform-tools
If you have root access, the easiest way I have found on a mac is to add your directories to the list in /etc/paths. I like this way because after a few additions the $PATH starts to look too messy and hard to read, the /etc/pathshas everything in separate line, clean and organized. The downside is that you require root access.
$ cat /etc/paths # check contents of the file
$ sudo nano /etc/paths
Paste the full path of your platform-tools directory (something like /Users/GodZilla/Software/platform-tools/adb) at the end of this list and save. Quit and Open terminal again and check if it sees your platform-tools directory.
$ which adb
/Users/GodZilla/Software/platform-tools/adb
$ which fastboot
/Users/GodZilla/Software/platform-tools/fastboot
If you don't have root access, just add the platform-tools directory to $PATH in your .bash_profile (or .zshenv if you use zsh) as other users have suggested.
This totally worked for me, after dickering around for a while after installing Android Studio:
Make sure you have the .bash_profile file. This should be in your [username] directory.
From whatever directory you are on, type this:
echo "export PATH=\$PATH:/Users/${USER}/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/" >> ~/.bash_profile
Now, usually you will have this exact path, but if not, then use whatever path you have the platform-tools folder
From the directory where your .bash_profile resides, type this:
. .bash_profileNow type
adb devices. You should see a "List of devices attached" response. Now you do not have to go to the platform-tools directory each and every time to type in the more cryptic command like,./adb devices!!!
In my case, I installed Android studio, and have some apps (rust lang) that changes the ~/.profile, and adding adb to ~/.bash_profile made the rust un-executable, so I made the changes to the ~/.profile only, as:
$ echo 'PATH=$PATH:$HOME/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/' >> ~/.profile
$ source ~/.profile
$ adb --version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 29.0.4-5871666
Installed as /Users/hasan/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/adb
In my case : I did the following (on a mac) :
- backed up the ".bash_profile" and ".profile"
- cleared all the android related paths.
- created the new paths but this time around, I dragged the respective folders : { /.../sdk, /.../tools, /.../platform-tools } into the terminal. I did this for both ".bash_profile" and ".profile".
- Then after successfully saving the files each. I restarted the terminal just to be sure about the modifications I made.
- I then went on to test if adb was responding now ... by typing : (in terminal) adb devices
- I still had no luck (my devices) where not showing, then I restarted the adb, still.
- I went on to do "android update adb" . This just killed and restarted the adb
- I tried again still the devices wasnt showing.
- I totally backed up my android device and resetted the whole phone back to factory default, went over to activate the device for development and allow for usb debugging in its settings > applications.
******** WORKED LIKE A CHARM ********
I tried again with the command "adb devices" and everything was back to normal the device was visible.
All the best. Just dont give up. It took me a lot of troubleshooting. All the best of luck.
Considering you have already downloaded SDK platform tools.
This command will set ADB locally. So if you close the terminal and open it again, ADB commands won't work until you run this command again.
export PATH=~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools:$PATH
These commands will set ADB globally. So once you run these commands no need to set them again next time.
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:~/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile
If you are using zsh terminal do the following:
1) Open .zprofile file with the editor of your choice like "open -a xcode ~/.zprofile"
2) Add new PATH or Env Variable in .zprofile Save the file and quit the editor.
3) Execute your .zprofile to update your PATH: source ~/.zprofile
Add environment variable for Android Home Targetting Platform Tools
echo 'export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools' >> ~/.bash_profile
Restart Bash
source ~/.bash_profile
Now Check adb
Simply type
adb
on terminal
After trying all the solutions, none of them where working for me.
In my case I had the Android Studio and the adb was correctly working but the Android Studio was not capable to detect the adb. These was because I installed it with homebrew in another directory, not the /Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk but Usr/Library blabla
Apparently AS needed to have it in his route /Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk (same place as in preferences SDK installation route)
So I deleted all the adb from my computer (I installed several) and executed these terminal commands:
echo 'export ANDROID_HOME=/Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools' >> ~/.bash_profile
source ~/.bash_profile
adb devices
Well, after that, still wasn't working, because for some reason the route for the adb was /Users/$USER/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/platform-tools (yes, repeated) so I just copied the last platform-tools into the first directory with all the license files and started working.
Weird but true
MacPorts
It seems like android-platform-tools was first added to MacPorts only very recently — in 2018-10-20, under java/android-platform-tools/Portfile:
- https://www.macports.org/ports.php?by=name&substr=android
- https://github.com/macports/macports-ports/blob/master/java/android-platform-tools/Portfile
- https://github.com/macports/macports-ports/commit/7fde64249deb97c97edb37699f1ee8076c98d41a#diff-f03a90b4adeb82935eb39763ecd988f2
It would appear that it relies on a compiled binary that's provided by Google; it would appear that the source code for the binary might not be available.
The adb binary
Reverse-engineering the android-platform-tools/Portfile from above reveals that the following archive is fetched from Google in order to build the port:
The abd binary is pre-compiled, available in platform-tools/adb within the above archive, which is a Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64, as per file(1). It's ready to be used and doesn't seem to have any external dependencies (e.g., doesn't look like it depends on java or anything).
Using adb
In order to use adb to restart the device, for example, in case the power button is stuck, the following steps could be used:
cd /tmp
curl https://dl.google.com/android/repository/platform-tools_r28.0.1-darwin.zip -o apt.zip
unzip apt.zip
./platform-tools/adb devices
./platform-tools/adb reboot
Upon first use since a reboot, you also have to first confirm the pairing with the phone through the Allow USB debugging? popup on the phone (phone has to have USB debugging enabled through the Developer Options, no root access required).
Step 1 : Open Terminal
Step 2 : Run command :
touch ~/.bash_profile; open ~/.bash_profile
Step 3 : This will open textEdit file when you can add following command:
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/sharan/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools
Blockquote
Note : sharan is my user name check that on y our system and replace that with sharan rest will be same. You can also find that by opening android studio
File->Project Structure..->SDK Location
Under Android SDK location there is path of sdk copy that and paste that on file and save it by pressing Command+S
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.

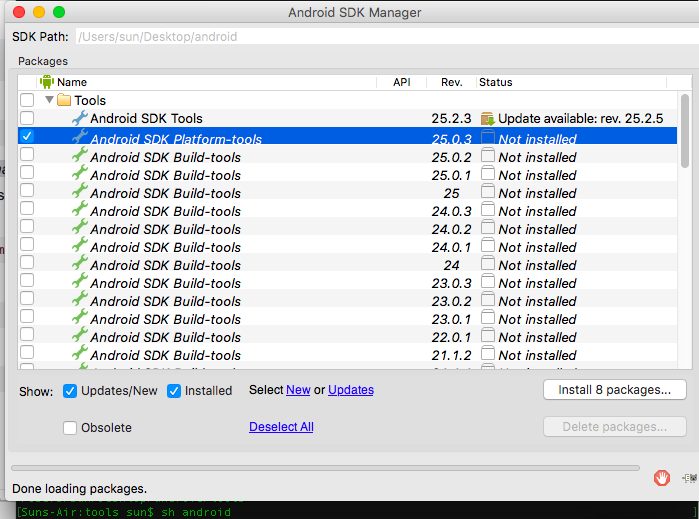
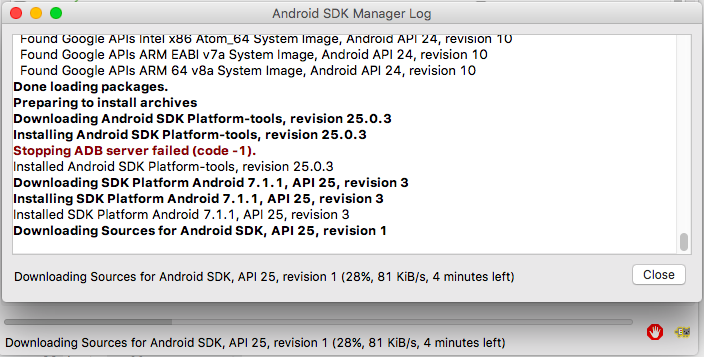



platform-toolsSDK package (which contains theadbbinary) at stackoverflow.com/tags/adb/info – Quintonquintuple