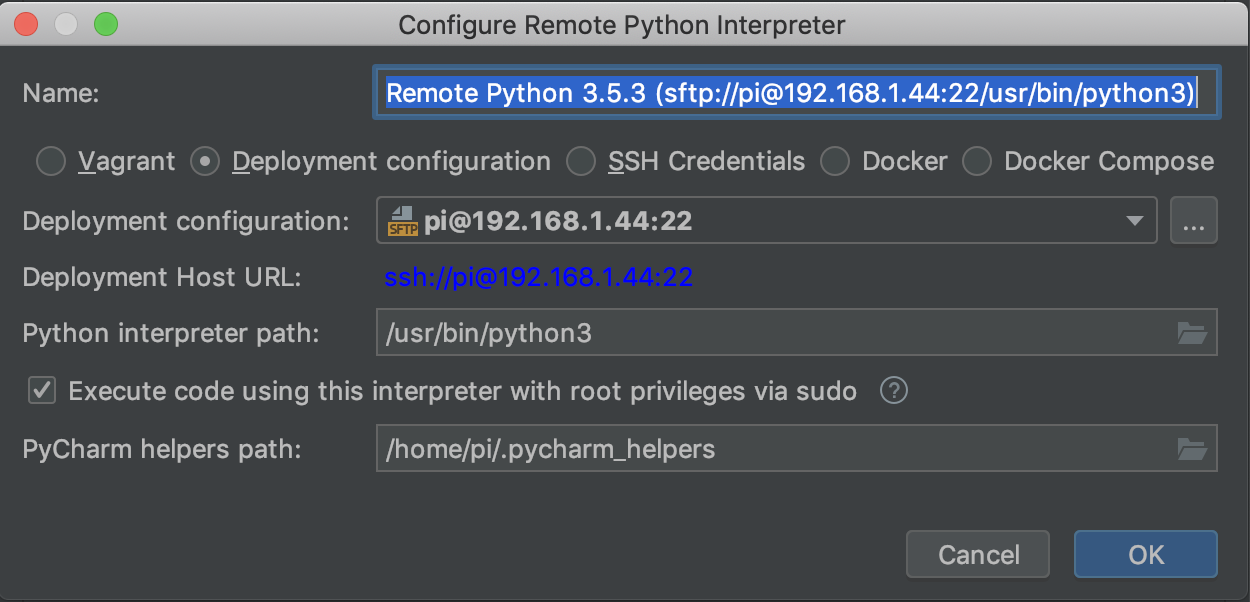
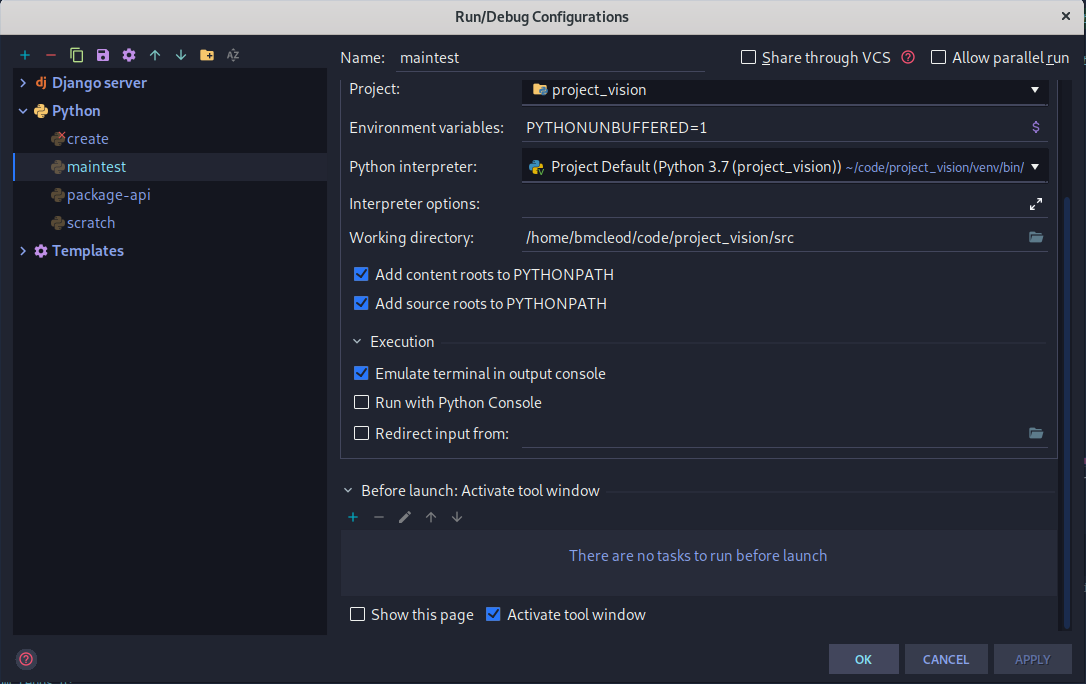
I have encounter another way to solve this issue so I thought to share it (this answer is more like an alternative for the other answers).
It is worth to mention here that this solution "attacks" the problem by running only a certain Python script (within the pPyCharm IDE) in root mode , and not the entire PyCharm application.
1) Disable requiring password for running Python:
This will be achieved by editing the /etc/sudoers.d/python file. What we need to do is to add an entry in that file as follows:
user host = (root) NOPASSWD: full_path_to_python, for example:
guya ubuntu = (root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/python
NOTES:
user can be detected by the command: whoami
host can be detected by the command: hostname
2) Create a "sudo script": The purpose of this script is to give Python privilege to run as root user.
Create a script called python-sudo.sh , and add the following into it:
#!/bin/bash
sudo /usr/bin/python "$@"
Note again that the path is the path to your Python as the previous phase.
Also, this path is the path to Python2 on the system.
Don't forget to give execution permissions to this script using the command: chmod
chmod +x python-sudo.sh
3) Use the python-sudo.sh script as your PyCharm interpreter:
Within PyCharm go to: File --> Settings --> Project interpreter
At the right top hand side click the "setting" icon, and click "Add local".
In the browser option choose the python-sudo.sh script we have created previously. This will give PyCharm the privilege to run a Python script as root.
4) Debug the test: All there is left to do is actually debug the specific Python script in the PyCharm IDE. This can be done easily via Right-click on the script to debug --> hit Debug sample_script_to_debug.py