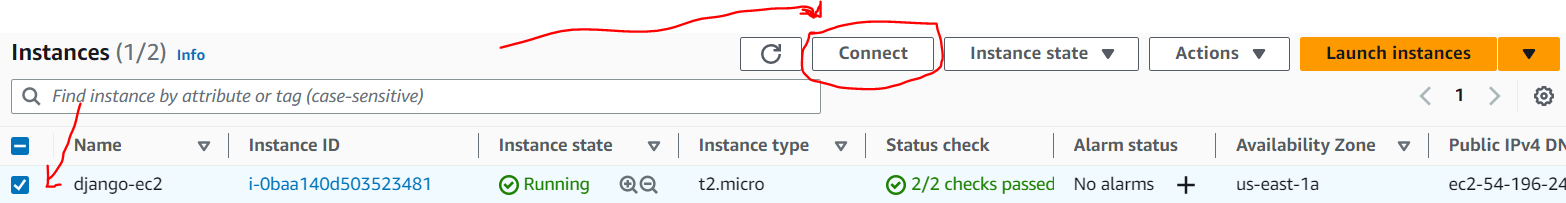
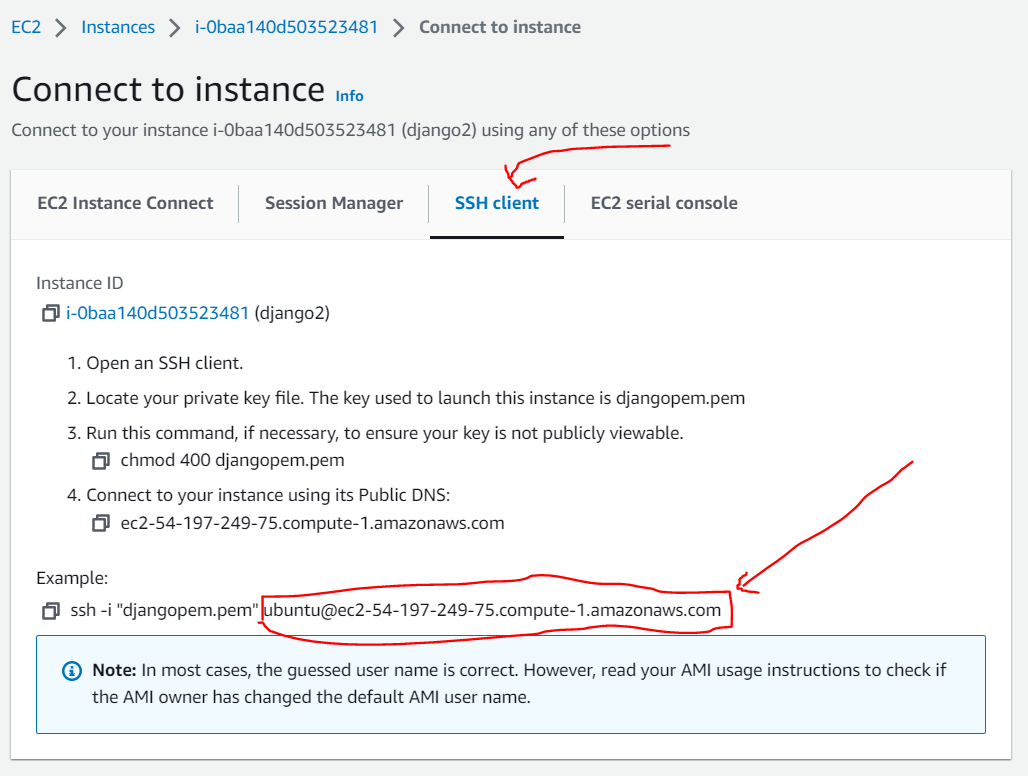
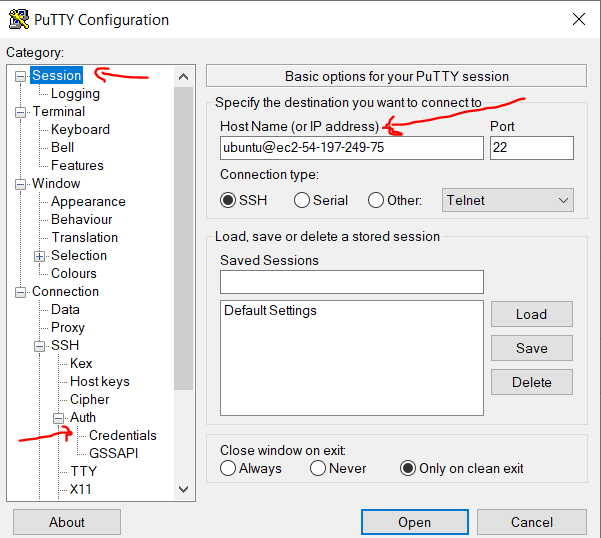
I have created my own EBS AMI, shared it with another AWS account, launched NEW instance based on this image with NEW key-pair and now when I am trying to connect to this new instance I am getting error: "Server Refused our key".
This is what I did (step by step):
- Configured new CentOS 6.3 server in my personal account (with my personal key-pair)
- Created EBS AMI image of that server
- Shared this image with my client's account
- Launched new instance in my clients account based on this shared image + new key-pair
- New launched instance doesnt want to take new key-pair. After some testing I figure that it accepts my personal key-pair instead.
How do I make new instance from my image to accept new key-pairs? I even tried removing ".ssh/authorized_keys" file in original image, launch new instance based on this image without public key and still no success.
Please advise how to create images that would not be attached to old key-pairs