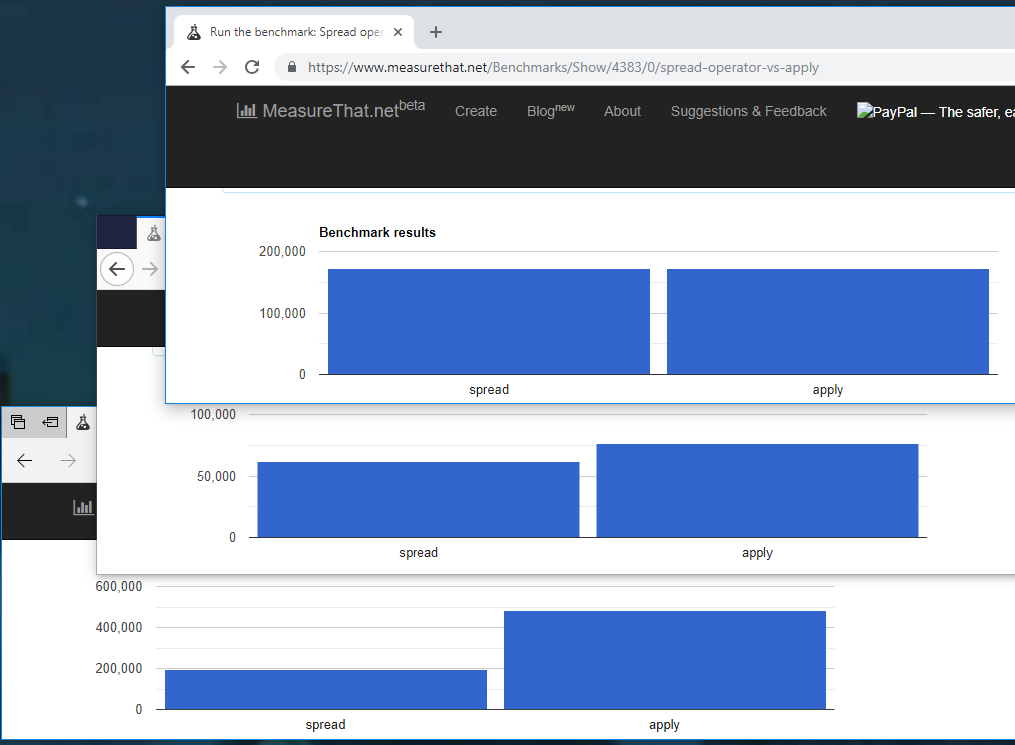
Interpreting the question as which is more performant in general, using .push() as an example it looks like apply is [only slightly] faster (except for MS Edge, see below).
Here's a performance test on just the overhead on calling a function dynamically for the two methods.
function test() { console.log(arguments[arguments.length - 1]); }
var using = (new Array(200)).fill(null).map((e, i) => (i));
test(...using);
test.apply(null, using)
I tested in Chrome 71.0.3578.80 (Official Build) (64-bit), FF 63.0.3 (64-bit), & Edge 42.17134.1.0, and these were my resulsts after running them a few times on their own The initial results were always skewed one way or the other
![benchmark results for the three browsers]()
As you can see Edge seems to have a better implementation for apply than it does for ... (but don't try to compare the results across browsers, we cant tell whether Edge has a better apply than the others, a worse ..., or a bit of both from this data).
Given this, unless you're targeting Edge specifically, I'd say go with ... just as it reads cleaner, especially if you need to pass an object back in to apply for this.
It's possible that it's dependent on the size of the array, too, so like @Jaromanda X said, do your own testing and change 200 if you need to really make sure.
The other answers interpreted the question as which would be better for .push() specifically, and get caught up on the 'problem' being solved, simply recommending to just use .concat(), which is basically the standard why are you doing it that way? which can irk some people coming from google that aren't looking for solutions to do with .push() (say, Math.max, or your own custom function).

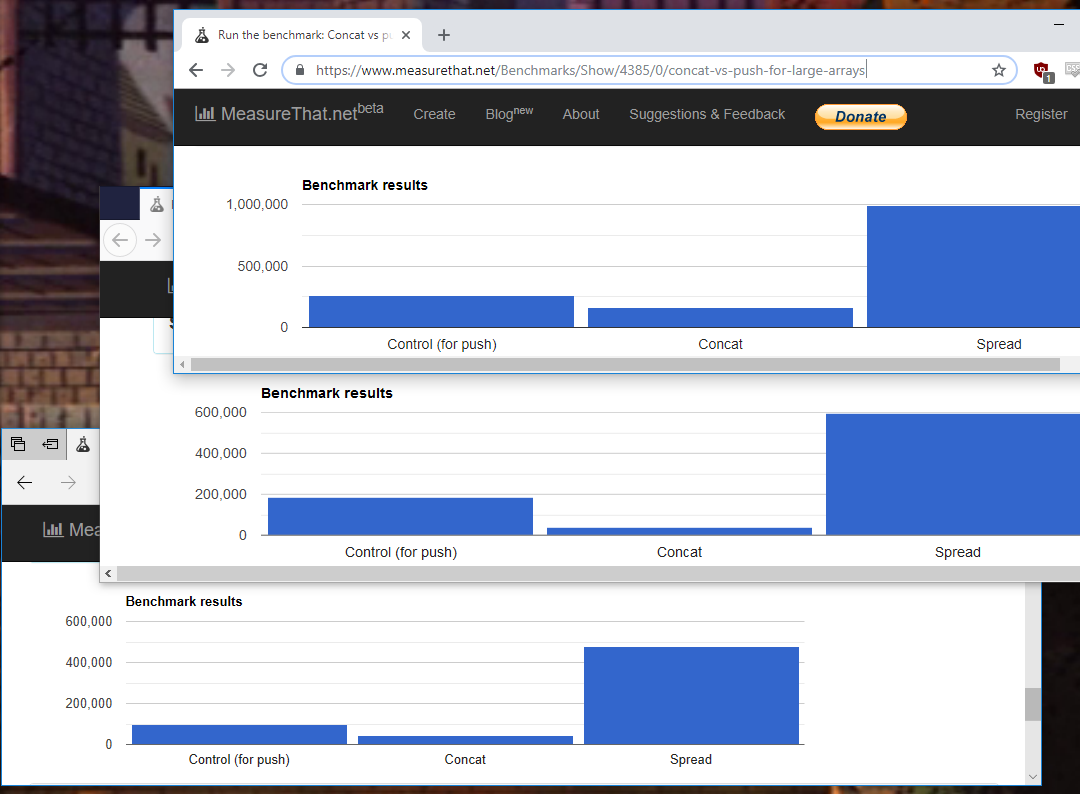
pets.push.apply. In any case, the chance that there is any performance difference that would affect the speed of your app is miniscule. Why did you wonder? – Gait.concat()would be more appropriate. – Filler