It seems to be obvious, but I found myself a bit confused about when to use curly braces for importing a single module in ES6. For example, in the React-Native project I am working on, I have the following file and its content:
File initialState.js
var initialState = {
todo: {
todos: [
{id: 1, task: 'Finish Coding', completed: false},
{id: 2, task: 'Do Laundry', completed: false},
{id: 2, task: 'Shopping Groceries', completed: false},
]
}
};
export default initialState;
In the TodoReducer.js, I have to import it without curly braces:
import initialState from './todoInitialState';
If I enclose the initialState in curly braces, I get the following error for the following line of code:
Cannot read property todo of undefined
File TodoReducer.js:
export default function todos(state = initialState.todo, action) {
// ...
}
Similar errors also happen to my components with the curly braces. I was wondering when I should use curly braces for a single import, because obviously, when importing multiple component/modules, you have to enclose them in curly braces, which I know.
The Stack Overflow post at here does not answer my question, instead I am asking when I should or should not use curly braces for importing a single module, or I should never use curly braces for importing a single module in ES6 (this is apparently not the case, as I have seen single import with curly braces required).

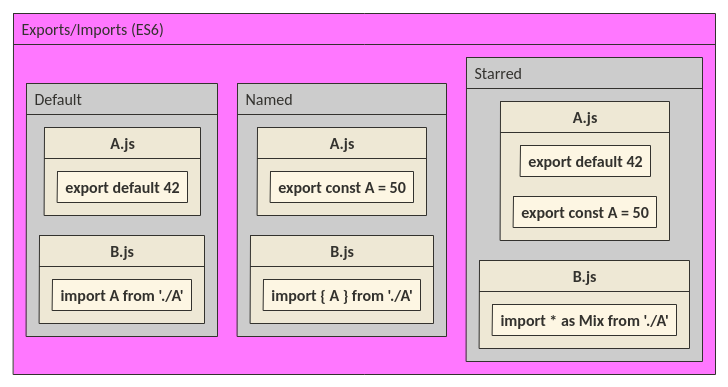

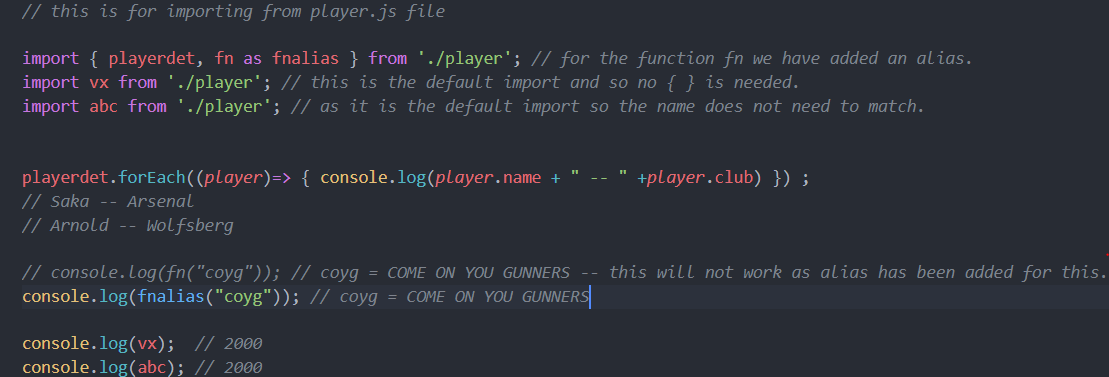
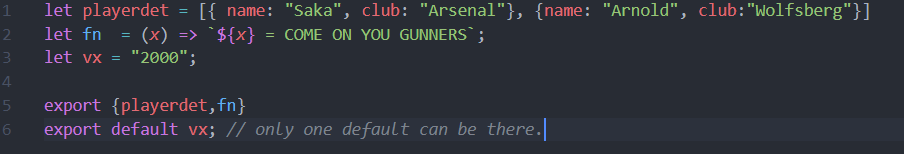
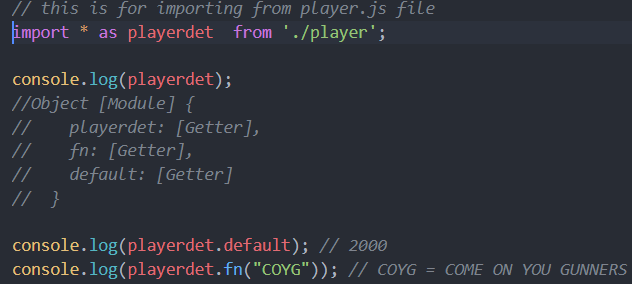
import * as whatIsIt from 'the-module'and thenconsole.log(whatIsIt)to examine the object that's imported. It may have adefaultproperty, and/or other named properties. – Lepper