Building on the answer by @unutbu, I have compared the iteration performance of two identical lists when using Python 3.6's zip() functions, Python's enumerate() function, using a manual counter (see count() function), using an index-list, and during a special scenario where the elements of one of the two lists (either foo or bar) may be used to index the other list. Their performances for printing and creating a new list, respectively, were investigated using the timeit() function where the number of repetitions used was 1000 times. One of the Python scripts that I had created to perform these investigations is given below. The sizes of the foo and bar lists had ranged from 10 to 1,000,000 elements.
Results:
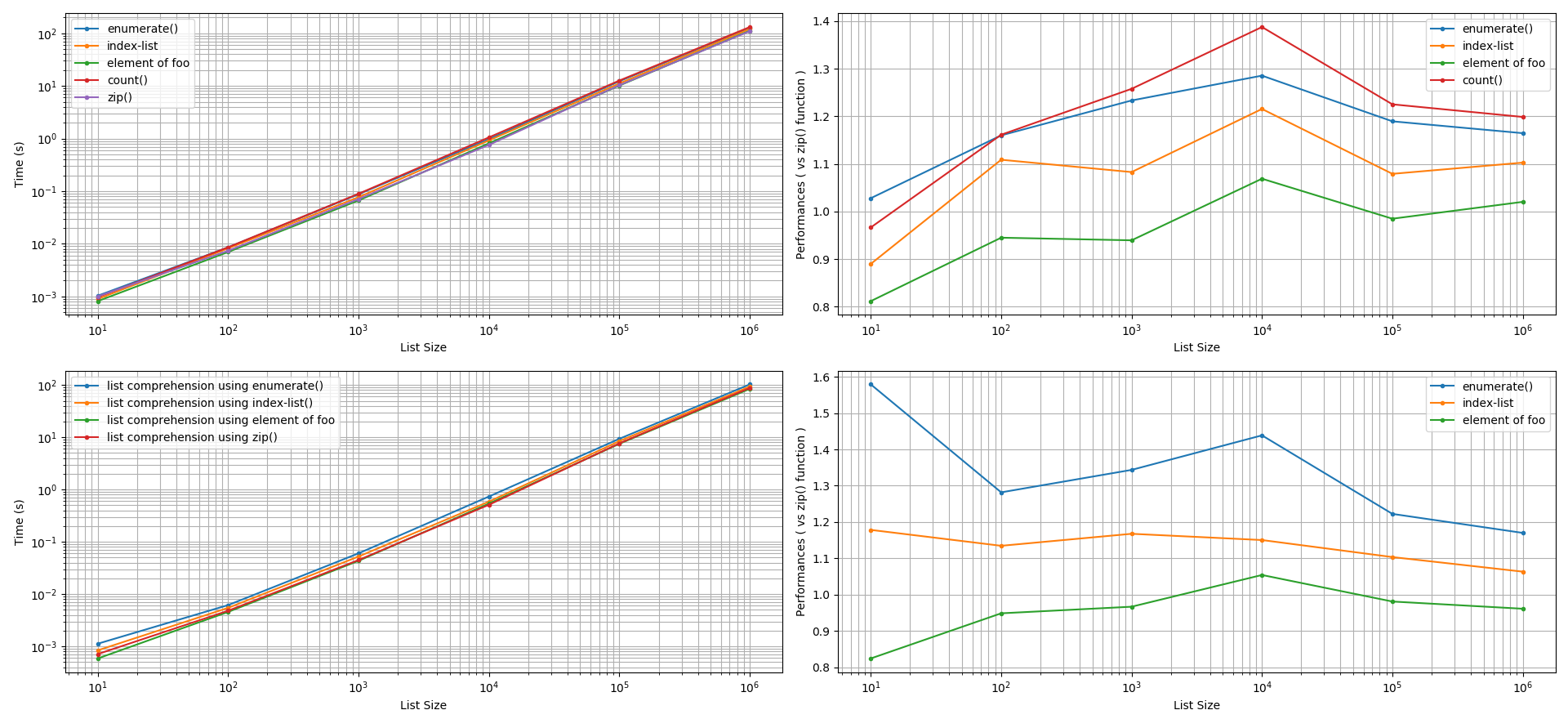
For printing purposes: The performances of all the considered approaches were observed to be approximately similar to the zip() function, after factoring an accuracy tolerance of +/-5%. An exception occurred when the list size was smaller than 100 elements. In such a scenario, the index-list method was slightly slower than the zip() function while the enumerate() function was ~9% faster. The other methods yielded similar performance to the zip() function.
![Print loop 1000 reps]()
For creating lists: Two types of list creation approaches were explored: using the (a) list.append() method and (b) list comprehension. After factoring an accuracy tolerance of +/-5%, for both of these approaches, the zip() function was found to perform faster than the enumerate() function, than using a list-index, than using a manual counter. The performance gain by the zip() function in these comparisons can be 5% to 60% faster. Interestingly, using the element of foo to index bar can yield equivalent or faster performances (5% to 20%) than the zip() function.
![Creating List - 1000reps]()
Making sense of these results:
A programmer has to determine the amount of compute-time per operation that is meaningful or that is of significance.
For example, for printing purposes, if this time criterion is 1 second, i.e. 10**0 sec, then looking at the y-axis of the graph that is on the left at 1 sec and projecting it horizontally until it reaches the monomials curves, we see that lists sizes that are more than 144 elements will incur significant compute cost and significance to the programmer. That is, any performance gained by the approaches mentioned in this investigation for smaller list sizes will be insignificant to the programmer. The programmer will conclude that the performance of the zip() function to iterate print statements is similar to the other approaches.
Conclusion
Notable performance can be gained from using the zip() function to iterate through two lists in parallel during list creation. When iterating through two lists in parallel to print out the elements of the two lists, the zip() function will yield similar performance as the enumerate() function, as to using a manual counter variable, as to using an index-list, and as to during the special scenario where the elements of one of the two lists (either foo or bar) may be used to index the other list.
The Python 3.6 script that was used to investigate list creation.
import timeit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def test_zip( foo, bar ):
store = []
for f, b in zip(foo, bar):
#print(f, b)
store.append( (f, b) )
def test_enumerate( foo, bar ):
store = []
for n, f in enumerate( foo ):
#print(f, bar[n])
store.append( (f, bar[n]) )
def test_count( foo, bar ):
store = []
count = 0
for f in foo:
#print(f, bar[count])
store.append( (f, bar[count]) )
count += 1
def test_indices( foo, bar, indices ):
store = []
for i in indices:
#print(foo[i], bar[i])
store.append( (foo[i], bar[i]) )
def test_existing_list_indices( foo, bar ):
store = []
for f in foo:
#print(f, bar[f])
store.append( (f, bar[f]) )
list_sizes = [ 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000 ]
tz = []
te = []
tc = []
ti = []
tii= []
tcz = []
tce = []
tci = []
tcii= []
for a in list_sizes:
foo = [ i for i in range(a) ]
bar = [ i for i in range(a) ]
indices = [ i for i in range(a) ]
reps = 1000
tz.append( timeit.timeit( 'test_zip( foo, bar )',
'from __main__ import test_zip, foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
te.append( timeit.timeit( 'test_enumerate( foo, bar )',
'from __main__ import test_enumerate, foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
tc.append( timeit.timeit( 'test_count( foo, bar )',
'from __main__ import test_count, foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
ti.append( timeit.timeit( 'test_indices( foo, bar, indices )',
'from __main__ import test_indices, foo, bar, indices',
number=reps
)
)
tii.append( timeit.timeit( 'test_existing_list_indices( foo, bar )',
'from __main__ import test_existing_list_indices, foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
tcz.append( timeit.timeit( '[(f, b) for f, b in zip(foo, bar)]',
'from __main__ import foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
tce.append( timeit.timeit( '[(f, bar[n]) for n, f in enumerate( foo )]',
'from __main__ import foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
tci.append( timeit.timeit( '[(foo[i], bar[i]) for i in indices ]',
'from __main__ import foo, bar, indices',
number=reps
)
)
tcii.append( timeit.timeit( '[(f, bar[f]) for f in foo ]',
'from __main__ import foo, bar',
number=reps
)
)
print( f'te = {te}' )
print( f'ti = {ti}' )
print( f'tii = {tii}' )
print( f'tc = {tc}' )
print( f'tz = {tz}' )
print( f'tce = {te}' )
print( f'tci = {ti}' )
print( f'tcii = {tii}' )
print( f'tcz = {tz}' )
fig, ax = plt.subplots( 2, 2 )
ax[0,0].plot( list_sizes, te, label='enumerate()', marker='.' )
ax[0,0].plot( list_sizes, ti, label='index-list', marker='.' )
ax[0,0].plot( list_sizes, tii, label='element of foo', marker='.' )
ax[0,0].plot( list_sizes, tc, label='count()', marker='.' )
ax[0,0].plot( list_sizes, tz, label='zip()', marker='.')
ax[0,0].set_xscale('log')
ax[0,0].set_yscale('log')
ax[0,0].set_xlabel('List Size')
ax[0,0].set_ylabel('Time (s)')
ax[0,0].legend()
ax[0,0].grid( b=True, which='major', axis='both')
ax[0,0].grid( b=True, which='minor', axis='both')
ax[0,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(te)/np.array(tz), label='enumerate()', marker='.' )
ax[0,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(ti)/np.array(tz), label='index-list', marker='.' )
ax[0,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(tii)/np.array(tz), label='element of foo', marker='.' )
ax[0,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(tc)/np.array(tz), label='count()', marker='.' )
ax[0,1].set_xscale('log')
ax[0,1].set_xlabel('List Size')
ax[0,1].set_ylabel('Performances ( vs zip() function )')
ax[0,1].legend()
ax[0,1].grid( b=True, which='major', axis='both')
ax[0,1].grid( b=True, which='minor', axis='both')
ax[1,0].plot( list_sizes, tce, label='list comprehension using enumerate()', marker='.')
ax[1,0].plot( list_sizes, tci, label='list comprehension using index-list()', marker='.')
ax[1,0].plot( list_sizes, tcii, label='list comprehension using element of foo', marker='.')
ax[1,0].plot( list_sizes, tcz, label='list comprehension using zip()', marker='.')
ax[1,0].set_xscale('log')
ax[1,0].set_yscale('log')
ax[1,0].set_xlabel('List Size')
ax[1,0].set_ylabel('Time (s)')
ax[1,0].legend()
ax[1,0].grid( b=True, which='major', axis='both')
ax[1,0].grid( b=True, which='minor', axis='both')
ax[1,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(tce)/np.array(tcz), label='enumerate()', marker='.' )
ax[1,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(tci)/np.array(tcz), label='index-list', marker='.' )
ax[1,1].plot( list_sizes, np.array(tcii)/np.array(tcz), label='element of foo', marker='.' )
ax[1,1].set_xscale('log')
ax[1,1].set_xlabel('List Size')
ax[1,1].set_ylabel('Performances ( vs zip() function )')
ax[1,1].legend()
ax[1,1].grid( b=True, which='major', axis='both')
ax[1,1].grid( b=True, which='minor', axis='both')
plt.show()


zip's for-loop and item-getting is implemented in C. In contrast,[(x[i], y[i]) for i in range(...)]uses a Python-level for-loop and eachx[i]ory[i]requires a Python-level call to__getitem__. Generally, C-loops beat Python loops and fewer function calls is faster than more function calls. So intuition points tozipbeing faster than indexing. – Lewes