How can I get the current time and date in an Android app?
You could use:
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
Date currentTime = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();
There are plenty of constants in Calendar for everything you need.
Check the Calendar class documentation.
Calendar.getInstance().getTime() or Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis() will work. –
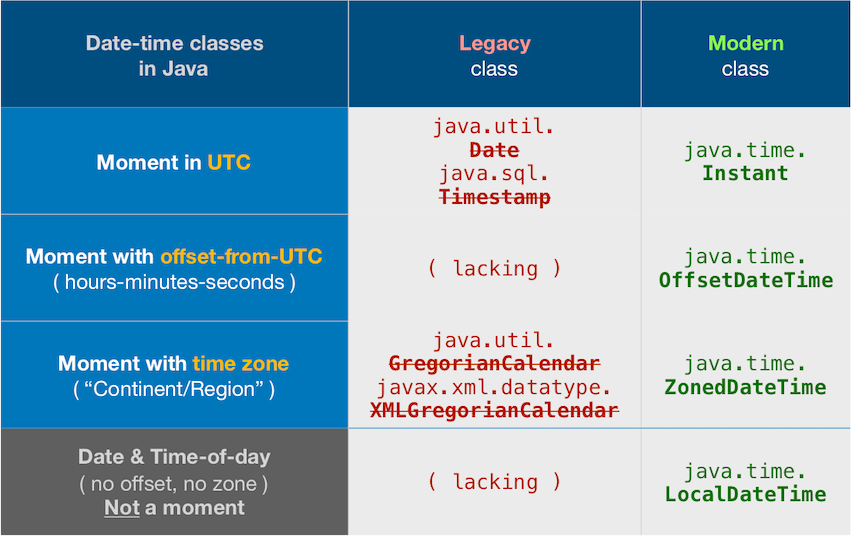
Chapland java.util.Date, java.util.Calendar, and java.text.SimpleDateFormat are now legacy, supplanted by the java.time classes. Much of the java.time functionality is back-ported to Java 6 & Java 7 in the ThreeTen-Backport project. Further adapted for earlier Android in the ThreeTenABP project. See How to use ThreeTenABP…. –
Omophagia new Date()? –
Greenbrier String bugun = new SimpleDateFormat("dd.MM.yyyy", Locale.getDefault()).format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime()); –
Inflammatory You can (but no longer should - see below!) use android.text.format.Time:
Time now = new Time();
now.setToNow();
From the reference linked above:
The Time class is a faster replacement for the java.util.Calendar and java.util.GregorianCalendar classes. An instance of the Time class represents a moment in time, specified with second precision.
NOTE 1: It's been several years since I wrote this answer, and it is about an old, Android-specific and now deprecated class. Google now says that "[t]his class has a number of issues and it is recommended that GregorianCalendar is used instead".
NOTE 2: Even though the Time class has a toMillis(ignoreDaylightSavings) method, this is merely a convenience to pass to methods that expect time in milliseconds. The time value is only precise to one second; the milliseconds portion is always 000. If in a loop you do
Time time = new Time(); time.setToNow();
Log.d("TIME TEST", Long.toString(time.toMillis(false)));
... do something that takes more than one millisecond, but less than one second ...
The resulting sequence will repeat the same value, such as 1410543204000, until the next second has started, at which time 1410543205000 will begin to repeat.
SystemClock.uptimeMillis() for interval timing. Since that is what most built-in functions use, there is strong motivation for it to be well-implemented on all devices. See discussion in SystemClock... If you want to correlate that with time of day, in app's onResume, read both this, and Time/setToNow/toMillis. Remember the difference between those. –
Hakim GregorianCalendar was supplanted years ago in Java and in later Android by the java.time classes, specifically ZonedDateTime. For earlier Android, see the ThreeTen-Backport and ThreeTenABP projects. –
Omophagia If you want to get the date and time in a specific pattern you can use the following:
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd_HHmmss", Locale.getDefault());
String currentDateandTime = sdf.format(new Date());
Or,
Date:
String currentDate = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy", Locale.getDefault()).format(new Date());
Time:
String currentTime = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss", Locale.getDefault()).format(new Date());
SimpleDateFormat inside onDraw() ?? –
Synsepalous String currentDateandTime = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()); –
Dudleyduds sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getDefault()) in the middle –
Shala For those who might rather prefer a customized format, you can use:
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("EEE, d MMM yyyy, HH:mm");
String date = df.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
Whereas you can have DateFormat patterns such as:
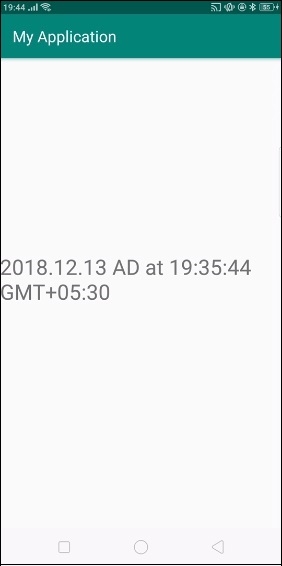
"yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' HH:mm:ss z" ---- 2001.07.04 AD at 12:08:56 PDT
"hh 'o''clock' a, zzzz" ----------- 12 o'clock PM, Pacific Daylight Time
"EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Z"------- Wed, 4 Jul 2001 12:08:56 -0700
"yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ"------- 2001-07-04T12:08:56.235-0700
"yyMMddHHmmssZ"-------------------- 010704120856-0700
"K:mm a, z" ----------------------- 0:08 PM, PDT
"h:mm a" -------------------------- 12:08 PM
"EEE, MMM d, ''yy" ---------------- Wed, Jul 4, '01
Actually, it's safer to set the current timezone set on the device with Time.getCurrentTimezone(), or else you will get the current time in UTC.
Time today = new Time(Time.getCurrentTimezone());
today.setToNow();
Then, you can get all the date fields you want, like, for example:
textViewDay.setText(today.monthDay + ""); // Day of the month (1-31)
textViewMonth.setText(today.month + ""); // Month (0-11)
textViewYear.setText(today.year + ""); // Year
textViewTime.setText(today.format("%k:%M:%S")); // Current time
See android.text.format.Time class for all the details.
UPDATE
As many people are pointing out, Google says this class has a number of issues and is not supposed to be used anymore:
This class has a number of issues and it is recommended that GregorianCalendar is used instead.
Known issues:
For historical reasons when performing time calculations all arithmetic currently takes place using 32-bit integers. This limits the reliable time range representable from 1902 until 2037.See the wikipedia article on the Year 2038 problem for details. Do not rely on this behavior; it may change in the future. Calling switchTimezone(String) on a date that cannot exist, such as a wall time that was skipped due to a DST transition, will result in a date in 1969 (i.e. -1, or 1 second before 1st Jan 1970 UTC). Much of the formatting / parsing assumes ASCII text and is therefore not suitable for use with non-ASCII scripts.
tl;dr
Instant.now() // Current moment in UTC.
…or…
ZonedDateTime.now( ZoneId.of( "America/Montreal" ) ) // In a particular time zone
Details
The other answers, while correct, are outdated. The old date-time classes have proven to be poorly designed, confusing, and troublesome.
java.time
Those old classes have been supplanted by the java.time framework.
- Java 8 and later: The java.time framework is built-in.
- Java 7 & 6: Use the backport of java.time.
- Android: Use this wrapped version of that backport.
These new classes are inspired by the highly successful Joda-Time project, defined by JSR 310, and extended by the ThreeTen-Extra project.
See the Oracle Tutorial.
Instant
An Instant is a moment on the timeline in UTC with resolution up to nanoseconds.
Instant instant = Instant.now(); // Current moment in UTC.
Time Zone
Apply a time zone (ZoneId) to get a ZonedDateTime. If you omit the time zone your JVM’s current default time zone is implicitly applied. Better to specify explicitly the desired/expected time zone.
Use proper time zone names in the format of continent/region such as America/Montreal, Europe/Brussels, or Asia/Kolkata. Never use the 3-4 letter abbreviations such as EST or IST as they are neither standardized nor unique.
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of( "America/Montreal" ); // Or "Asia/Kolkata", "Europe/Paris", and so on.
ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant( instant , zoneId );
Generating Strings
You can easily generate a String as a textual representation of the date-time value. You can go with a standard format, your own custom format, or an automatically localized format.
ISO 8601
You can call the toString methods to get text formatted using the common and sensible ISO 8601 standard.
String output = instant.toString();
2016-03-23T03:09:01.613Z
Note that for ZonedDateTime, the toString method extends the ISO 8601 standard by appending the name of the time zone in square brackets. Extremely useful and important information, but not standard.
2016-03-22T20:09:01.613-08:00[America/Los_Angeles]
Custom format
Or specify your own particular formatting pattern with the DateTimeFormatter class.
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern( "dd/MM/yyyy hh:mm a" );
Specify a Locale for a human language (English, French, etc.) to use in translating the name of day/month and also in defining cultural norms such as the order of year and month and date. Note that Locale has nothing to do with time zone.
formatter = formatter.withLocale( Locale.US ); // Or Locale.CANADA_FRENCH or such.
String output = zdt.format( formatter );
Localizing
Better yet, let java.time do the work of localizing automatically.
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime( FormatStyle.MEDIUM );
String output = zdt.format( formatter.withLocale( Locale.US ) ); // Or Locale.CANADA_FRENCH and so on.
About java.time
The java.time framework is built into Java 8 and later. These classes supplant the troublesome old legacy date-time classes such as java.util.Date, Calendar, & SimpleDateFormat.
To learn more, see the Oracle Tutorial. And search Stack Overflow for many examples and explanations. Specification is JSR 310.
The Joda-Time project, now in maintenance mode, advises migration to the java.time classes.
You may exchange java.time objects directly with your database. Use a JDBC driver compliant with JDBC 4.2 or later. No need for strings, no need for java.sql.* classes. Hibernate 5 & JPA 2.2 support java.time.
Where can the java.time classes be obtained?
- Java SE 8, Java SE 9, Java SE 10, Java SE 11, and later - Part of the standard Java API with a bundled implementation.
- Java 9 brought some minor features and fixes.
- Java SE 6 and Java SE 7
- Most of the java.time functionality is back-ported to Java 6 & 7 in ThreeTen-Backport.
- Android
- Later versions of Android (26+) bundle implementations of the java.time classes.
- For earlier Android (<26), the process of API desugaring brings a subset of the java.time functionality not originally built into Android.
- If the desugaring does not offer what you need, the ThreeTenABP project adapts ThreeTen-Backport (mentioned above) to Android. See How to use ThreeTenABP….
Instant.now() and ZonedDateTime.now() is required API 26 –
Celesta For the current date and time, use:
String mydate = java.text.DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
Which outputs:
Feb 27, 2012 5:41:23 PM
Try with the following way. All formats are given below to get the date and time formats.
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat dateformat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MMM-yyyy hh:mm:ss aa");
String datetime = dateformat.format(c.getTime());
System.out.println(datetime);
To ge the current time you can use System.currentTimeMillis() which is standard in Java. Then you can use it to create a date
Date currentDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
And as mentioned by others to create a time
Time currentTime = new Time();
currentTime.setToNow();
System.currentTimeMillis(); simply new Date() does the same thing. –
Lipo Cannot resolve constructor Date() in android, the Android SDK uses a mixture of Java 6 and 7. –
Domiciliate new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()) in not right: (a) it is redundant, as that is the exact same as new Date(). (b) The troublesome java.util.Date class is now supplanted by java.time.Instant as of Java 8 and later. Back-ported to Java 6 & 7 in the ThreeTen-Backport project, and to earlier Android (<26) in ThreeTenABP. –
Omophagia You can use the code:
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String strDate = sdf.format(c.getTime());
Output:
2014-11-11 00:47:55
You also get some more formatting options for SimpleDateFormat from here.
java.util.Date, java.util.Calendar, and java.text.SimpleDateFormat are now legacy, supplanted by the java.time classes built into Java 8 and later. See Tutorial by Oracle. –
Omophagia Easy. You can dissect the time to get separate values for current time, as follows:
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
int millisecond = cal.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND);
int second = cal.get(Calendar.SECOND);
int minute = cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
// 12-hour format
int hour = cal.get(Calendar.HOUR);
// 24-hour format
int hourofday = cal.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
Same goes for the date, as follows:
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
int dayofyear = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
int year = cal.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int dayofweek = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
int dayofmonth = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
SimpleDateFormat databaseDateTimeFormate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
SimpleDateFormat databaseDateFormate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("dd.MM.yy");
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' hh:mm:ss z");
SimpleDateFormat sdf3 = new SimpleDateFormat("EEE, MMM d, ''yy");
SimpleDateFormat sdf4 = new SimpleDateFormat("h:mm a");
SimpleDateFormat sdf5 = new SimpleDateFormat("h:mm");
SimpleDateFormat sdf6 = new SimpleDateFormat("H:mm:ss:SSS");
SimpleDateFormat sdf7 = new SimpleDateFormat("K:mm a,z");
SimpleDateFormat sdf8 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MMMMM.dd GGG hh:mm aaa");
String currentDateandTime = databaseDateTimeFormate.format(new Date()); //2009-06-30 08:29:36
String currentDateandTime = databaseDateFormate.format(new Date()); //2009-06-30
String currentDateandTime = sdf1.format(new Date()); //30.06.09
String currentDateandTime = sdf2.format(new Date()); //2009.06.30 AD at 08:29:36 PDT
String currentDateandTime = sdf3.format(new Date()); //Tue, Jun 30, '09
String currentDateandTime = sdf4.format(new Date()); //8:29 PM
String currentDateandTime = sdf5.format(new Date()); //8:29
String currentDateandTime = sdf6.format(new Date()); //8:28:36:249
String currentDateandTime = sdf7.format(new Date()); //8:29 AM,PDT
String currentDateandTime = sdf8.format(new Date()); //2009.June.30 AD 08:29 AM
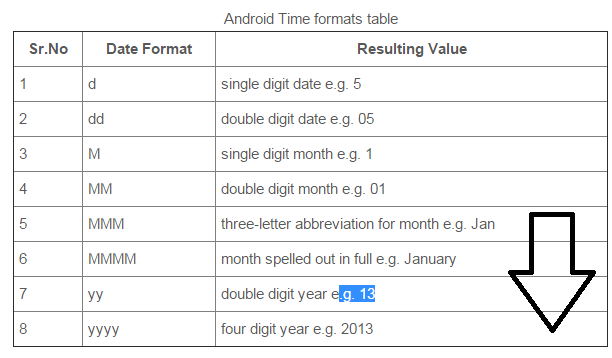
Date format Patterns
G Era designator (before christ, after christ)
y Year (e.g. 12 or 2012). Use either yy or yyyy.
M Month in year. Number of M's determine length of format (e.g. MM, MMM or MMMMM)
d Day in month. Number of d's determine length of format (e.g. d or dd)
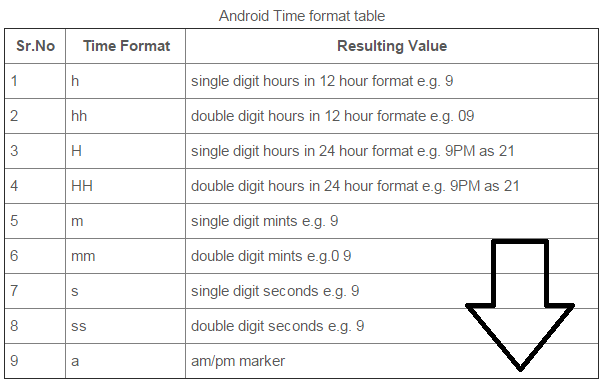
h Hour of day, 1-12 (AM / PM) (normally hh)
H Hour of day, 0-23 (normally HH)
m Minute in hour, 0-59 (normally mm)
s Second in minute, 0-59 (normally ss)
S Millisecond in second, 0-999 (normally SSS)
E Day in week (e.g Monday, Tuesday etc.)
D Day in year (1-366)
F Day of week in month (e.g. 1st Thursday of December)
w Week in year (1-53)
W Week in month (0-5)
a AM / PM marker
k Hour in day (1-24, unlike HH's 0-23)
K Hour in day, AM / PM (0-11)
z Time Zone
For the current date and time with format, use:
In Java
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String strDate = sdf.format(c.getTime());
Log.d("Date", "DATE: " + strDate)
In Kotlin
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
val current = LocalDateTime.now()
val formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd.MM.yyyy. HH:mm:ss")
var myDate: String = current.format(formatter)
Log.d("Date", "DATE: " + myDate)
} else {
var date = Date()
val formatter = SimpleDateFormat("MMM dd yyyy HH:mma")
val myDate: String = formatter.format(date)
Log.d("Date", "DATE: " + myDate)
}
Date formatter patterns
"yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' HH:mm:ss z" ---- 2001.07.04 AD at 12:08:56 PDT
"hh 'o''clock' a, zzzz" ----------- 12 o'clock PM, Pacific Daylight Time
"EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Z"------- Wed, 4 Jul 2001 12:08:56 -0700
"yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ"------- 2001-07-04T12:08:56.235-0700
"yyMMddHHmmssZ"-------------------- 010704120856-0700
"K:mm a, z" ----------------------- 0:08 PM, PDT
"h:mm a" -------------------------- 12:08 PM
"EEE, MMM d, ''yy" ---------------- Wed, Jul 4, '01
SimpleDateFormat class. Even before Oreo you don’t need to, you may instead use ThreeTenABP, the backport of java.time, the modern Java date and time API. –
Aton final Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
int mYear = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int mMonth = c.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int mDay = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
textView.setText("" + mDay + "-" + mMonth + "-" + mYear);
This is a method that will be useful to get date and time:
private String getDate(){
DateFormat dfDate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
String date=dfDate.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
DateFormat dfTime = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm");
String time = dfTime.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
return date + " " + time;
}
You can call this method and get the current date and time values:
2017/01//09 19:23
SimpleDateFormats & 2 Dates... can't you just use "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm" as the format & call calendar once? –
Pinnace If you need the current date:
Calendar cc = Calendar.getInstance();
int year = cc.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = cc.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int mDay = cc.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println("Date", year + ":" + month + ":" + mDay);
If you need the current time:
int mHour = cc.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int mMinute = cc.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
System.out.println("time_format" + String.format("%02d:%02d", mHour , mMinute));
You can also use android.os.SystemClock. For example SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() will give you more accurate time readings when the phone is asleep.
Use:
Time time = new Time();
time.setToNow();
System.out.println("time: " + time.hour + ":" + time.minute);
This will give you, for example, "12:32".
Remember to import android.text.format.Time;.
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("time => " + dateFormat.format(cal.getTime()));
String time_str = dateFormat.format(cal.getTime());
String[] s = time_str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println("date => " + s[i]);
}
int year_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[0].split("/")[0]);
int month_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[0].split("/")[1]);
int day_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[0].split("/")[2]);
int hour_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[1].split(":")[0]);
int min_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[1].split(":")[1]);
System.out.println("year_sys => " + year_sys);
System.out.println("month_sys => " + month_sys);
System.out.println("day_sys => " + day_sys);
System.out.println("hour_sys => " + hour_sys);
System.out.println("min_sys => " + min_sys);
You can simply use the following code:
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm"); // Format time
String time = df.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
DateFormat df1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd"); // Format date
String date = df1.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
Current time and date in Android with the format
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current dateTime => " + c.getTime());
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss a");
String formattedDate = df.format(c.getTime());
System.out.println("Format dateTime => " + formattedDate);
Output
I/System.out: Current dateTime => Wed Feb 26 02:58:17 GMT+05:30 2020
I/System.out: Format dateTime => 26-02-2020 02:58:17 AM
For a customized time and date format:
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssZZZZZ",Locale.ENGLISH);
String cDateTime = dateFormat.format(new Date());
The output is in this format:
2015-06-18T10:15:56-05:00
Time now = new Time();
now.setToNow();
Try this works for me as well.
You can obtain the date by using:
Time t = new Time(Time.getCurrentTimezone());
t.setToNow();
String date = t.format("%Y/%m/%d");
This will give you a result in a nice form, as in this example: "2014/02/09".
Time t = new Time(); will use the default timezone. In my experience, default == current. –
Conspicuous Well, I had problems with some answers by the API, so I fused this code:
Time t = new Time(Time.getCurrentTimezone());
t.setToNow();
String date1 = t.format("%Y/%m/%d");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("hh:mm aa", Locale.ENGLISH);
String var = dateFormat.format(date);
String horafecha = var+ " - " + date1;
tvTime.setText(horafecha);
Output:
03:25 PM - 2017/10/03
Java
Long date=System.currentTimeMillis();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat =new SimpleDateFormat("dd / MMMM / yyyy - HH:mm", Locale.getDefault());
String dateStr = dateFormat.format(date);
Kotlin
date if milliseconds and 13 digits(hex to date)
val date=System.currentTimeMillis() //here the date comes in 13 digits
val dtlong = Date(date)
val sdfdate = SimpleDateFormat(pattern, Locale.getDefault()).format(dtlong)
Date Formatter
"dd / MMMM / yyyy - HH:mm" -> 29 / April / 2022 - 12:03
"dd / MM / yyyy" -> 29 / 03 / 2022
"dd / MMM / yyyy" -> 29 / Mar / 2022 (shortens the month)
"EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss" -> Wed, 4 Jul 2022 12:08:56
SimpleDateFormat and friends. Use desugaring in order to use java.time, the modern Java date and time API. It is so much nicer to work with. –
Aton Date todayDate = new Date();
todayDate.getDay();
todayDate.getHours();
todayDate.getMinutes();
todayDate.getMonth();
todayDate.getTime();
You should use the Calender class according to the new API. The Date class is deprecated now.
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
String date = "" + cal.get(Calendar.DATE) + "-" + (cal.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1) + "-" + cal.get(Calendar.YEAR);
String time = "" + cal.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) + ":" + cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
Try This
String mytime = (DateFormat.format("dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss", new java.util.Date()).toString());
The below method will return the current date and time in a String, Use a different time zone according to your actual time zone. I've used GMT.
public static String GetToday(){
Date presentTime_Date = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
dateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT"));
return dateFormat.format(presentTime_Date);
}
Try this to get the current date and time in an easy way:
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
String currentDateandTime = sdf.format(new Date());
Try to use the below code:
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormatWithZone = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'",Locale.getDefault());
String currentDate = dateFormatWithZone.format(date);
For a 12-hour clock with suffix "AM" or "PM":
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("KK:mm:ss a, dd/MM/yyyy", Locale.getDefault());
String currentDateAndTime = df.format(new Date());
For a 24-hour clock with suffix "AM" or "PM":
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss a, dd/MM/yyyy", Locale.getDefault());
String currentDateAndTime = df.format(new Date());
To remove the suffix, just remove "a" written with the time format.
Try this code. It displays the current date and time.
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("hh:mm aa",
Locale.ENGLISH);
String var = dateFormat.format(date));
//currentTimeMillis is System.currentTimeMillis()
long totalSeconds = currentTimeMillis / 1000;
int currentSecond = (int)totalSeconds % 60;
long totalMinutes = totalSeconds / 60;
int currentMinute = (int)totalMinutes % 60;
long totalHours = totalMinutes / 60;
int currentHour = (int)totalHours % 12;
TextView tvTime = findViewById(R.id.tvTime);
tvTime.setText((currentHour + OR - TIME YOU ARE FROM GMT) + ":" + currentMinute + ":" + currentSecond);
String DataString = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.SHORT).format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
To get the short date formatted String in the localised format of the unit.
I can't understand why so many answers use hardcoded date and time formats when the OS/Java supplies correct localisation of date and time. Isn't it better always to use the formats of the device than of the programmer?
It also supplies the reading of dates in localised formats:
DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.SHORT);
Date date = null;
try {
date = format.parse(DateString);
}
catch(ParseException e) {
}
Then it is up to the user setting the format to show the dates and time and not you. Regardless of languages, etc., there are different formats in different countries with the same language.
Here are a few ways to get time and date:
public static void getCurrentTimeUsingDate() {
Date date = new Date();
String strDateFormat = "hh:mm:ss a";
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(strDateFormat);
String formattedDate= dateFormat.format(date);
Toast.makeText(this, formattedDate, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
Time using Calender
public static void getCurrentTimeUsingCalendar() {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
Date date=cal.getTime();
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDate=dateFormat.format(date);
Toast.makeText(this, formattedDate, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
Local time and date
public static void getCurrentTime(){
System.out.println("-----Current time of your time zone-----");
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
Toast.makeText(this, time, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
Zone wise Time
public static void getCurrentTimeWithTimeZone(){
Toast.makeText(this, "Current time of a different time zone using LocalTime", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("America/Los_Angeles");
LocalTime localTime=LocalTime.now(zoneId);
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss");
String formattedTime=localTime.format(formatter);
Toast.makeText(this,formattedTime , Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
Easy way to get the current time and date
import java.util.Calendar
Date currentTime = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();
Kotlin
Here are various ways in to get the current date time in Kotlin.
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println(System.currentTimeMillis()) // Current milliseconds
val date = Calendar.getInstance().time // Current date object
val date1 = Date(System.currentTimeMillis())
println(date.toString())
println(date1.toString())
val now = Time(System.currentTimeMillis()) // Current time object
println(now.toString())
val sdf = SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM:dd h:mm a", Locale.getDefault())
println(sdf.format(Date())) // Format current date
println(DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(System.currentTimeMillis())) // using getDateTimeInstance()
println(LocalDateTime.now().toString()) // Java 8
println(ZonedDateTime.now().toString()) // Java 8
}
You can get the time & date separately from Calendar.
// You can pass time zone and Local to getInstance() as parameter
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
int currentHour = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int currentMinute = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int second = calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND);
int date = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
There is a ISO8601Utils utilities class in the com.google.gson.internal.bind.util package, so if you Gson in your app you can use this.
It supports milliseconds and time zones, so it's a pretty good option right out of the box.
You can get your local time with GMT time from this function
public String getCurrentDate() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy MMM dd hh:mm a zzz");
Date date = new Date();
sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT+6:00"));
return sdf.format(date);
}
You can get the current date and time using this code:
val current_data_time= SimpleDateFormat("MMMMddyyyyHHmm", Locale.getDefault())
val currentDateandTime: String = current_data_time.format(Date())
If you use MMMM: Then month name shows e.g. "March"
If you use MM: Then number shows e.g. "3"
dd for day and yyyy for year
If you want only the last two digits then yy.
If you change month and year first and last then need to change MMMM and dd and yyyy left and right, e.g., 12/3/2021 12:12 dd/MM/YYYY HH:mm
In Kotlin, you can get current time data using Calendar.
val calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
This will give this output, Thu Apr 06 17:38:57 GMT+05:30 2023
Get current time hour, minute and second value like this.
val hour = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)
val minute = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE)
val second = calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND)
val currentTime = "$hour:$minute:$second"
Output of currentTime will be this 17:38:57.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.