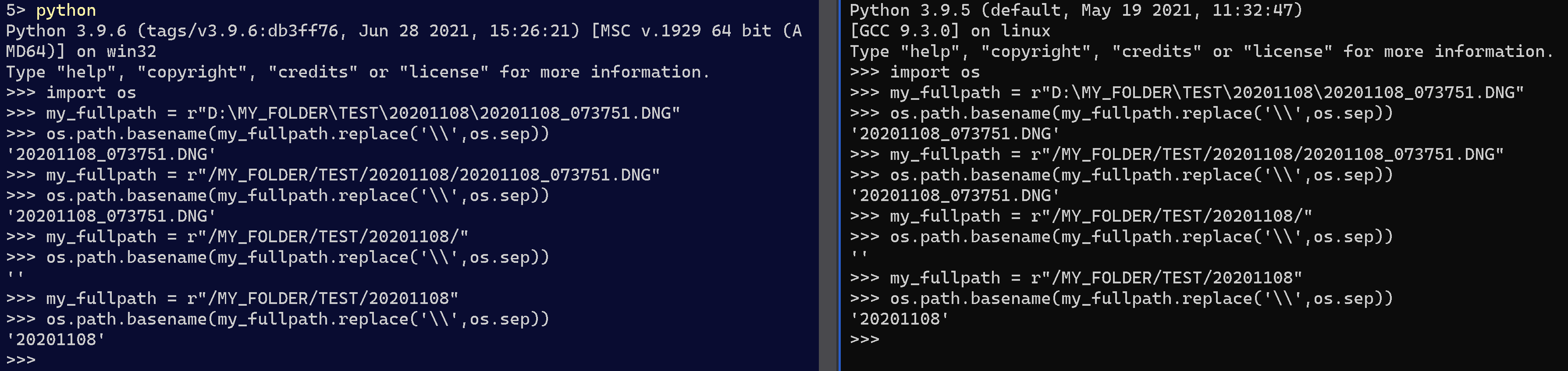
Here's a regex-only solution, which seems to work with any OS path on any OS.
No other module is needed, and no preprocessing is needed either :
import re
def extract_basename(path):
"""Extracts basename of a given path. Should Work with any OS Path on any OS"""
basename = re.search(r'[^\\/]+(?=[\\/]?$)', path)
if basename:
return basename.group(0)
paths = ['a/b/c/', 'a/b/c', '\\a\\b\\c', '\\a\\b\\c\\', 'a\\b\\c',
'a/b/../../a/b/c/', 'a/b/../../a/b/c']
print([extract_basename(path) for path in paths])
# ['c', 'c', 'c', 'c', 'c', 'c', 'c']
extra_paths = ['C:\\', 'alone', '/a/space in filename', 'C:\\multi\nline']
print([extract_basename(path) for path in extra_paths])
# ['C:', 'alone', 'space in filename', 'multi\nline']
Update:
If you only want a potential filename, if present (i.e., /a/b/ is a dir and so is c:\windows\), change the regex to: r'[^\\/]+(?![\\/])$' . For the "regex challenged," this changes the positive forward lookahead for some sort of slash to a negative forward lookahead, causing pathnames that end with said slash to return nothing instead of the last sub-directory in the pathname. Of course there is no guarantee that the potential filename actually refers to a file and for that os.path.is_dir() or os.path.is_file() would need to be employed.
This will match as follows:
/a/b/c/ # nothing, pathname ends with the dir 'c'
c:\windows\ # nothing, pathname ends with the dir 'windows'
c:hello.txt # matches potential filename 'hello.txt'
~it_s_me/.bashrc # matches potential filename '.bashrc'
c:\windows\system32 # matches potential filename 'system32', except
# that is obviously a dir. os.path.is_dir()
# should be used to tell us for sure
The regex can be tested here.

reliableway to parse a path with forward and backward slashes on all operating systems. On Unix you CAN have a backslash in a folder name. You can only implement something that will work "most of the time", aka bug. Better find a way to avoid such crazy paths. Use system libraries for parsing paths, but also for building paths to begin with. The best solution to this problem is to eliminate such ambiguous paths. Good Luck! – Cyclo\a\b\cis a valid filename on Linux. Returning justcinstead may be invalid and dangerous. – L