A one-command simple solution to solve it
If your computer has no SSH key added to the GitHub account, I add information for you to do it at the end of the answer. You should do it first.
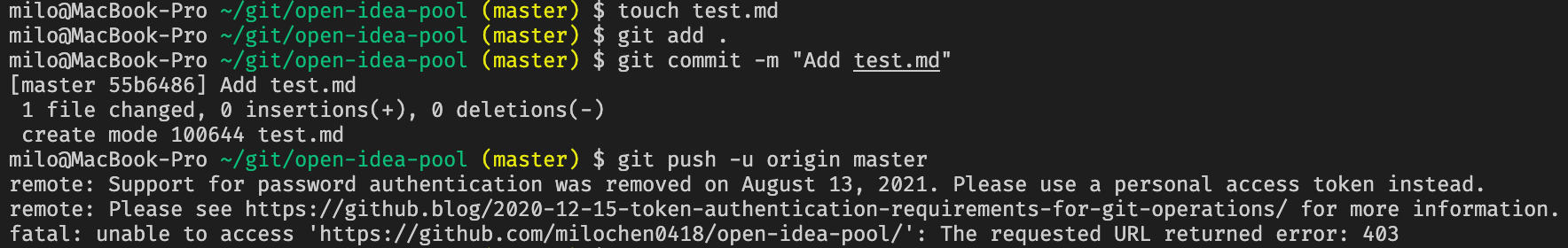
After push failed, then do this:
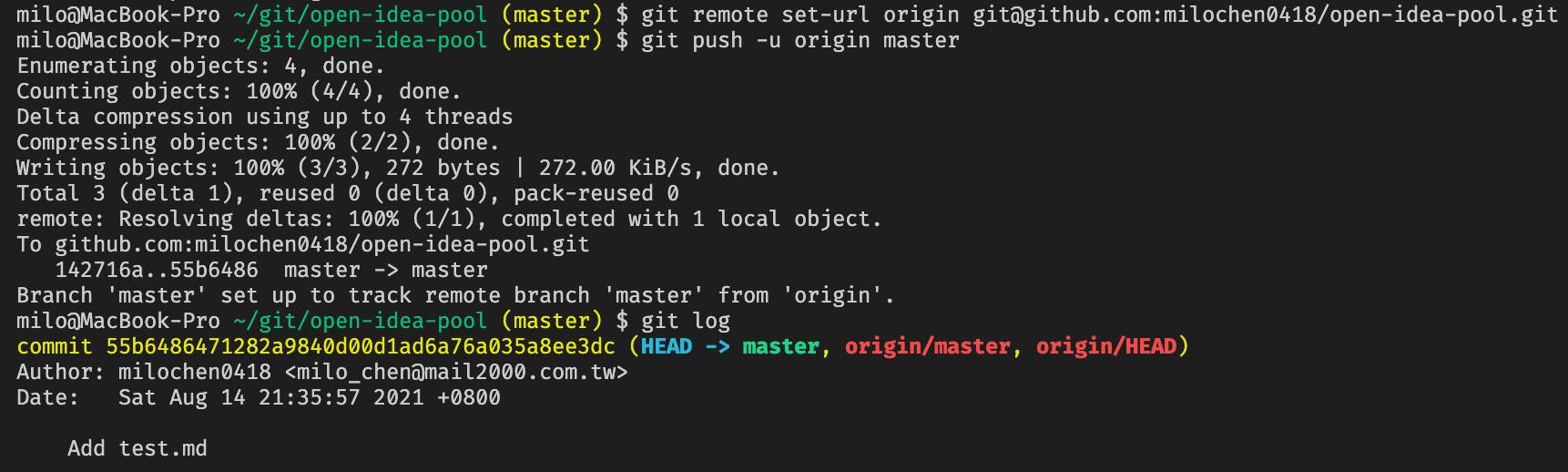
git remote set-url origin [email protected]:{user_id}/{project_name}.git
And push again. Then it works.
Let me show my case in the following.
(And I will guide you on how to do your case.)
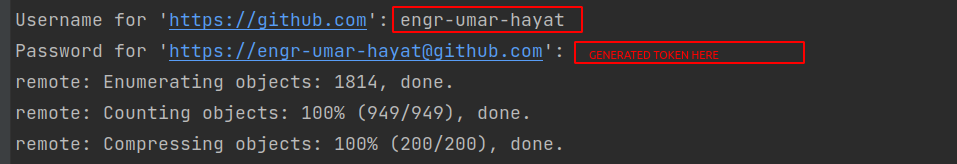
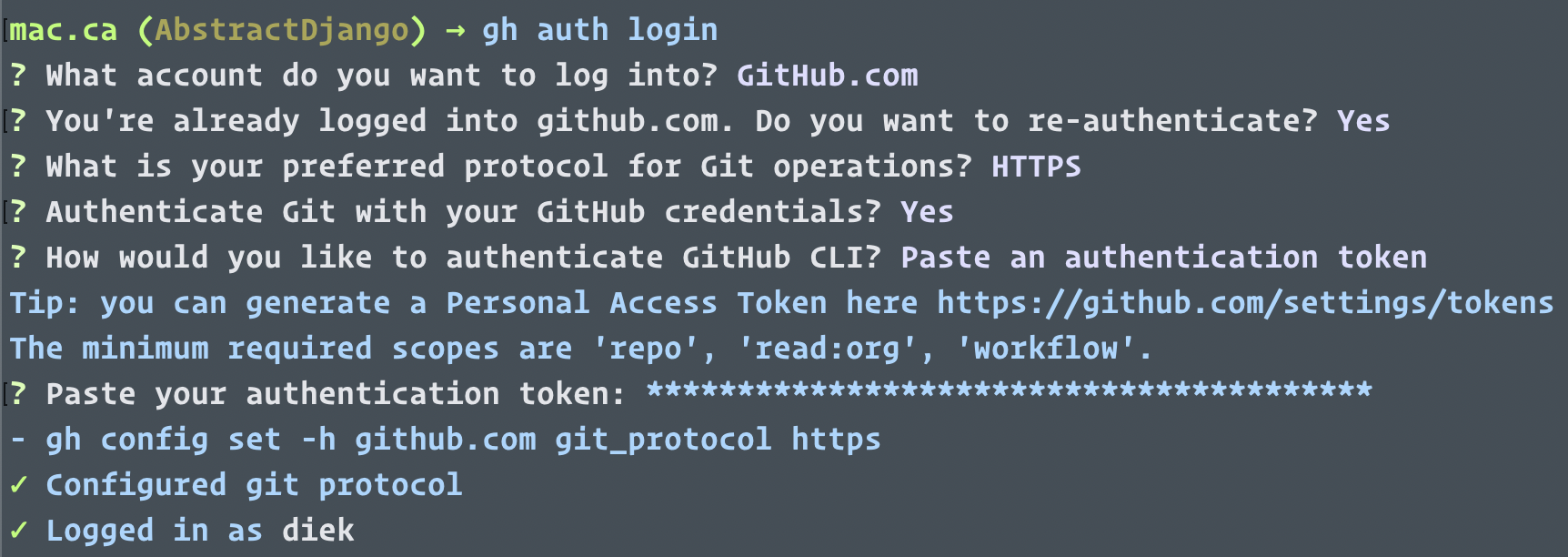
At the first, when I add, commit, and push, then I meet this issue:
![Enter image description here]()
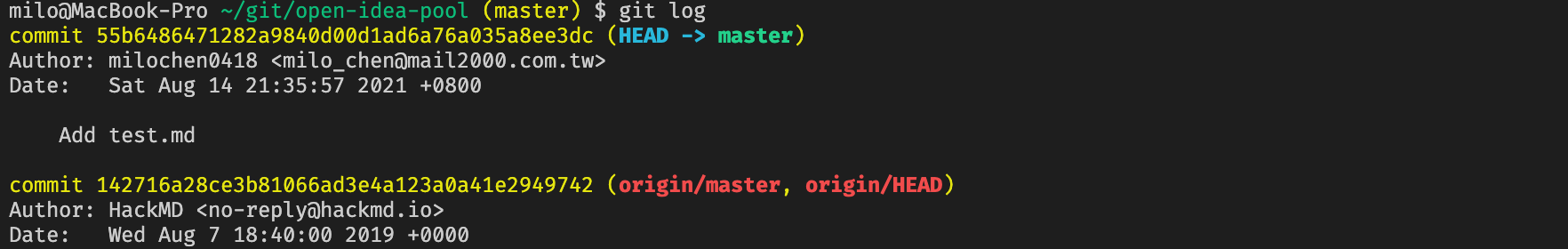
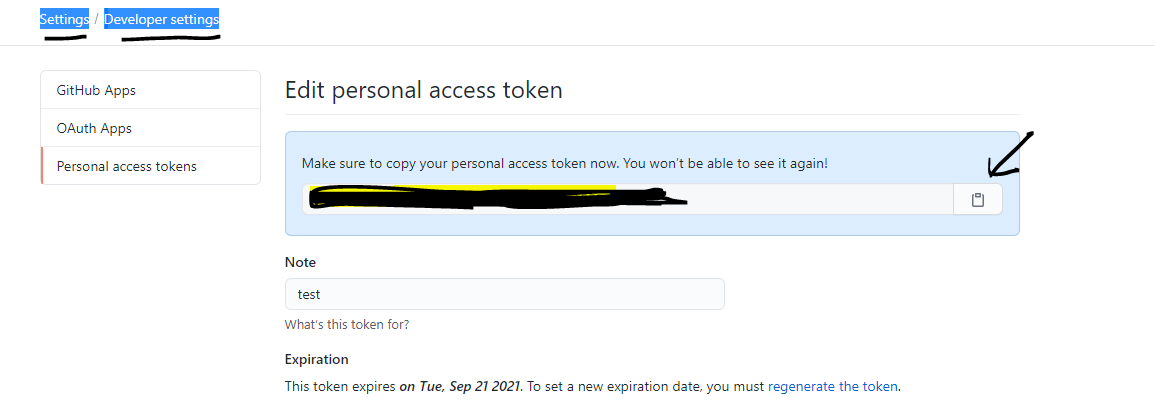
And then, my current Git log is the following.
![Enter image description here]()
In the final, this is my way to solve the issue.
![Enter image description here]()
In my case,
{project_name} <-> open-idea-pool
{user_id} <-> milochen0418 is the
{branch_name} <-> master
(your branch_name maybe is main, but not master)
When I push failed, the only thing I need is this one command:
git remote set-url origin [email protected]:{user_id}/{project_name}.git
Then I push it again by:
git push -u origin {branch_name}
For the example of my case,
git remote set-url origin [email protected]:milochen0418/open-idea-pool.git
git push -u origin master
It works.
--
By the way, this is the process of creating an SSH key to GitHub account.
You can refer to these two links to do it. The information here supports Mac, Windows, and Linux.
- Issue on adding SSH key to GitHub
- Adding a new SSH key to your GitHub account
Furthermore, if you want to clone a new project, you can do the following command:
git clone [email protected]:{user_id}/{project_name}.git


unset SSH_ASKPASS– Haase