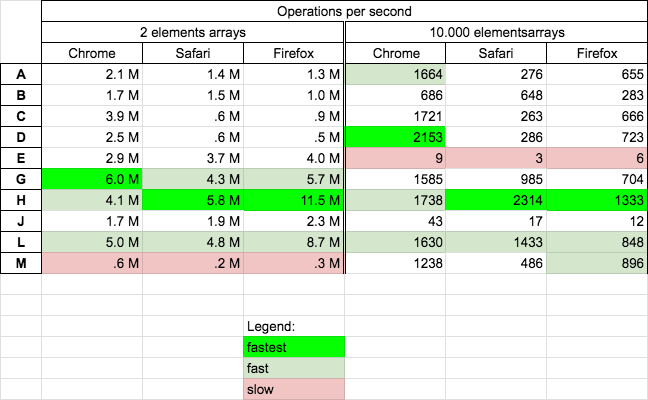
To just merge the arrays (without removing duplicates)
ES5 version use Array.concat:
var array1 = ["Vijendra", "Singh"];
var array2 = ["Singh", "Shakya"];
array1 = array1.concat(array2);
console.log(array1);
2023 update
The original answer was from years ago. ES6 is fully supported and IE is finally dead. Here's the simplest way to merge primitive and object arrays:
const merge = (a, b, predicate = (a, b) => a === b) => {
const c = [...a]; // copy to avoid side effects
// add all items from B to copy C if they're not already present
b.forEach((bItem) => (c.some((cItem) => predicate(bItem, cItem)) ? null : c.push(bItem)))
return c;
}
merge(['a', 'b', 'c'], ['c', 'x', 'd']);
// => ['a', 'b', 'c', 'x', 'd']
merge([{id: 1}, {id: 2}], [{id: 2}, {id: 3}], (a, b) => a.id === b.id);
// [{id: 1}, {id: 2}, {id: 3}]
Original answer
const array1 = ["Vijendra","Singh"];
const array2 = ["Singh", "Shakya"];
const array3 = [...array1, ...array2];
Since there is no 'built in' way to remove duplicates (ECMA-262 actually has Array.forEach which would be great for this), we have to do it manually. Note that this pollutes the Array prototype, use with caution.
Array.prototype.unique = function() {
var a = this.concat();
for(var i=0; i<a.length; ++i) {
for(var j=i+1; j<a.length; ++j) {
if(a[i] === a[j])
a.splice(j--, 1);
}
}
return a;
};
Then, to use it:
var array1 = ["Vijendra","Singh"];
var array2 = ["Singh", "Shakya"];
// Merges both arrays and gets unique items
var array3 = array1.concat(array2).unique();
This will also preserve the order of the arrays (i.e, no sorting needed).
Since many people are annoyed about prototype augmentation of Array.prototype and for in loops, here is a less invasive way to use it:
function arrayUnique(array) {
var a = array.concat();
for(var i=0; i<a.length; ++i) {
for(var j=i+1; j<a.length; ++j) {
if(a[i] === a[j])
a.splice(j--, 1);
}
}
return a;
}
var array1 = ["Vijendra","Singh"];
var array2 = ["Singh", "Shakya"];
// Merges both arrays and gets unique items
var array3 = arrayUnique(array1.concat(array2));
For those who are fortunate enough to work with browsers where ES5 is available, you can use Object.defineProperty like this:
Object.defineProperty(Array.prototype, 'unique', {
enumerable: false,
configurable: false,
writable: false,
value: function() {
var a = this.concat();
for(var i=0; i<a.length; ++i) {
for(var j=i+1; j<a.length; ++j) {
if(a[i] === a[j])
a.splice(j--, 1);
}
}
return a;
}
});