I have added all of the details I could find, with all of the links, and there is no way to get plpython3u to work on Windows in PostgreSQL 13, it seems.
OLD, since the accepted answer shows that v3.7.0 solves it:
Better do not read through this long question and rather just jump to the answer: not to use Windows PostgreSQL when you need plpython3u. This question has been opened long enough, no solution in sight.
Perhaps a higher PostgreSQL version for Windows will solve this, then please answer.
Spin-off
This is a spin-off from
Can't “install” plpython3u - postgresql and all of its comments
and from
Steps of errors and solutions up to now
I have taken these steps which were totally scattered across Stack Overflow:
Step 0
If you run a sql that uses the language plpython3u without it being installed, you get
ERROR: language "plpython3u" does not exist HINT: Use CREATE EXTENSION to load the language into the database.
SQL state: 42704
Related:
Step 1
At error
ERROR: could not load library "C:/Program Files (x86)/PostgreSQL/13/lib/plpython3u.dll": The specified module could not be found.
SQL state: 58P01
look up C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\13\doc\installation-notes.html to find the needed Python version to be installed for the installed PostgreSQL version.
PostgreSQL 13
Installation Notes
Welcome to the PostgreSQL 13 Installation Wizard.
Procedural Languages
The procedural languages pl/Perl, pl/Python and pl/Tcl are included in this distribution of PostgreSQL. The server has been built using the LanguagePack community distributions of those language interpreters. To use any of the these languages from within PostgreSQL, download and install the appropriate interpreters and ensure they are included in the PATH variable under which the database server will be started. The versions used are shown below - newer minor (bugfix) releases may also work, but have not been tested:
Perl 5.26 Python 3.7 Tcl 8.6
Thus, Python 3.7 is needed.
Credits go to:
- could not load library plpython3.dll --> comment: Where to find this information ? Like for plpython3u which python version is required ?, answered Jul 17 '20
- Error during: CREATE EXTENSION plpython3u; on PostgreSQL 9.6.0, edited Oct 2 '20
Related:
Step 2
Install Python version using the webinstaller of Python Releases for Windows
The most recent sub-version 3.7.10 does not have any files in the list of stable releases and I am too lazy to install Python from source on Windows. The source code of v3.7.10 is available here Looking for a specific release?, for anyone who wants to try):
Python 3.7.10 - Feb. 15, 2021
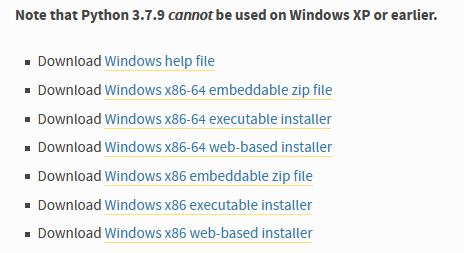
Note that Python 3.7.10 cannot be used on Windows XP or earlier.
No files for this release.
Explanation copied from How to build Python 3.4.6 from source?
The Python 3.7 branch is in security fixes only mode. This means that only security fixes will be accepted on this branch, no more non-critical bug fixes. New releases on this branch are source-only, no binaries will be provided.
See the official announcement.
If you really need a python 3.7.10 binary for windows, you will have to compile it yourself.
Cannot install plpython for postgres 12 recommends to install a specific version from source:
you want to use a specific python version > use source and compile it
Again, since I am lazy, I take the most recent stable release of 3.7, which is sub-version 3.7.9, and this should be no problem following the remark, as you seem to be free to choose the sub-version:
Try version python-3.4.0.amd64 for windows 64bit or other versions from this Python 3.4.0 downloads Link
From: could not load library plpython3.dll
As I said, I am too lazy to take the effort of compiling the binaries of v3.7.10 on Windows when v3.7.9 is available, thus:
Python 3.7.9 - Aug. 17, 2020
Note that Python 3.7.9 cannot be used on Windows XP or earlier.
Download Windows help file Download Windows x86-64 embeddable zip file Download Windows x86-64 executable installer Download Windows x86-64 web-based installer Download Windows x86 embeddable zip file Download Windows x86 executable installer Download Windows x86 web-based installer
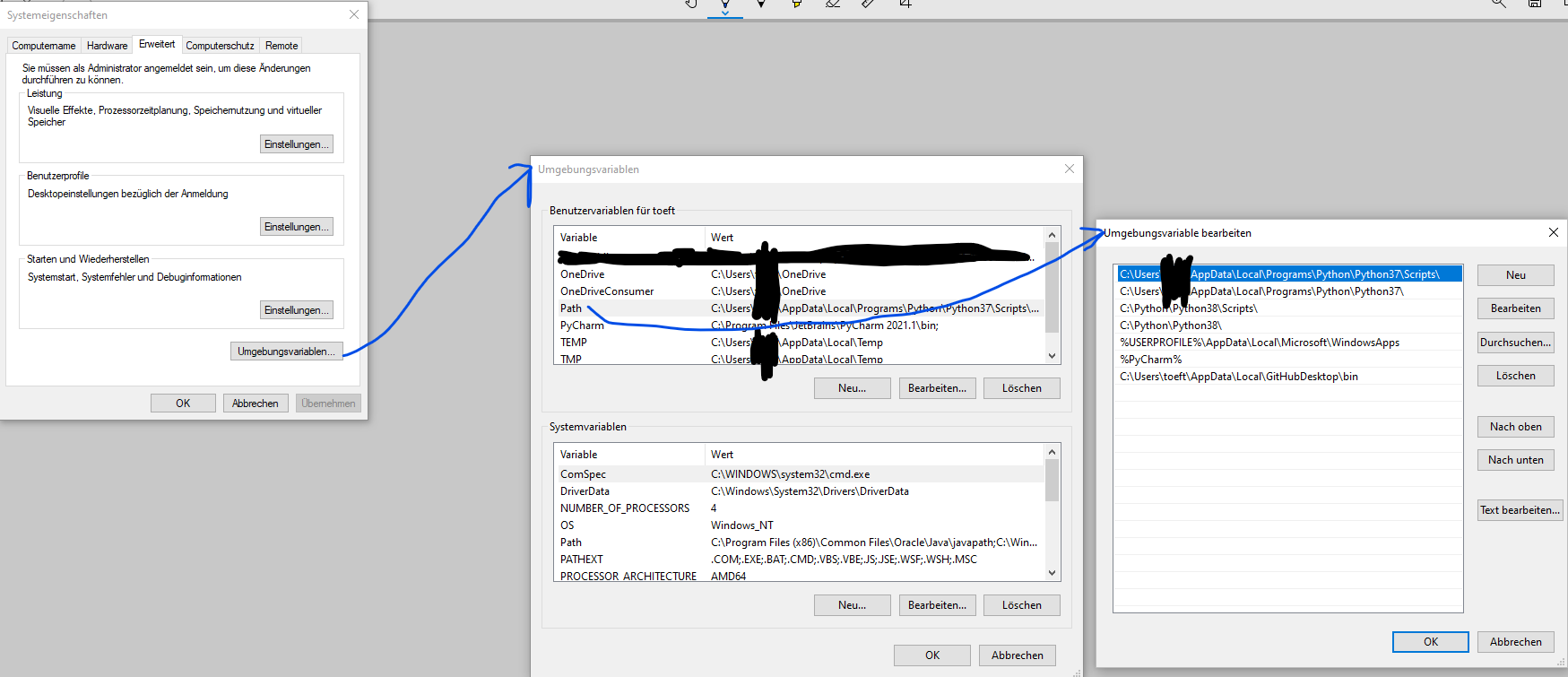
I install "Download Windows x86-64 web-based installer" (side-note: you cannot change the installation path, they seem to force you to use this; to reach it quickly, in Windows Explorer, type in the path %appdata% --> go to parent folder "appdata" --> then to "local" --> "programs" --> "python" to quickly get there) and check the box for adding the PATH variables as well.
You will have a new entry in your user environment variable "PATH" and you may check this, but you do not need to:
C:\Users\MY_USER\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\Scripts\
and
C:\Users\MY_USER\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\
Credits go to:
- could not load library plpython3.dll, answered Jan 31 '18
Step 3
When executing
CREATE EXTENSION plpython3u;
in the query tool of PostgreSQL pgAdmin4, I get the error:
could not load library "C:/Program Files/PostgreSQL/13/lib/plpython3u.dll": The specified module could not be found
Go to your Python 3.7 installation folder, in my case
C:\Users\MY_USER\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37
and copy "python37.dll" from there to
C:\Windows\System32
by confirming that you have admin rights.
Now execute again and it will work:
CREATE EXTENSION plpython3u;
Credits go to:
- Error during: CREATE EXTENSION plpython3u; on PostgreSQL 9.6.0, answered Sep 18 '17
- Is there any recipe to successfully install PLPython in Postgresql 9.3 64bit or 32bit on Windows 64 bits?, answered Feb 8 '14
- Cannot install plpython for postgres 12, answered Oct 2 '20
Related questions:
- PostgreSQL unable to create plpythonu extension
- How to install PL/Python on PostgreSQL 9.3 x64 Windows 7?
- i'm facing issues to create a postgresql plpython3u extension
Step 4 (optional)
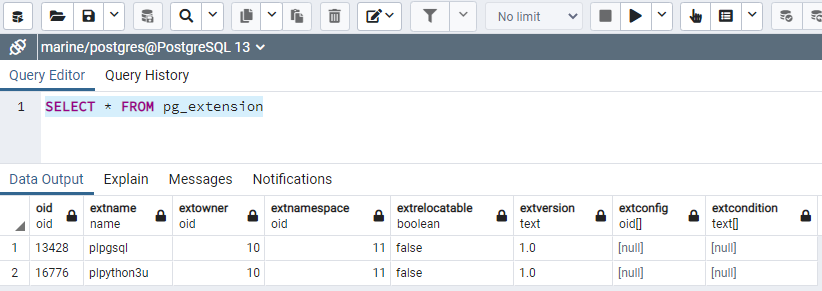
SELECT * FROM pg_extension;
Output:
old | extname | extowner | extrelocatable | extversion | extversion | extconfig | extcondition
"13428"| "plpgsql" | "10" | "11" | false | "1.0" | [null] | [null]
"16776"| "plpython3u" | "10" | "11" | false | "1.0" | [null] | [null]
And another check with:
SELECT * FROM pg_language;
Output:
lanname | lanowner | lanispl | lanpltrusted | lanplcallfoid | laninline | lanvalidator | lanacl
------------+----------+---------+--------------+---------------+-----------+--------------+--------
internal | 10 | f | f | 0 | 0 | 2246 |
c | 10 | f | f | 0 | 0 | 2247 |
sql | 10 | f | t | 0 | 0 | 2248 |
plpgsql | 10 | t | t | 12279 | 12280 | 12281 |
plpython3u | 10 | t | f | 40963 | 40964 | 40965 |
(5 rows)
Now the available extensions (that is, all possible extensions that can be installed) also show installed_version = 1.0 for the plpython3u extension:
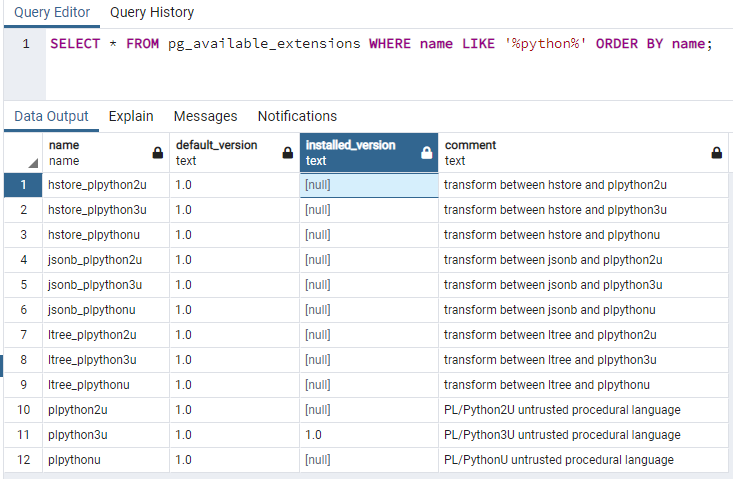
SELECT * FROM pg_available_extensions WHERE name LIKE '%python%' ORDER BY name;
Output:
or the output when running the same in psql:
name | default_version | installed_version | comment
------------+-----------------+-------------------+-------------------------------------------
plpython3u | 1.0 | 1.0 | PL/Python3U untrusted procedural language
(1 Zeile)
We see here probably one of the main reasons why there is no recent image that offers plpython extensions: PL/Python3U untrusted procedural language.
And another query which shows the same:
SELECT * FROM pg_pltemplate;
Output:
tmplname | tmpltrusted | tmpldbacreate | tmplhandler | tmplinline | tmplvalidator | tmpllibrary | tmplacl
------------+-------------+---------------+------------------------+--------------------------+---------------------+-------------------+---------
plpgsql | t | t | plpgsql_call_handler | plpgsql_inline_handler | plpgsql_validator | $libdir/plpgsql |
pltcl | t | t | pltcl_call_handler | | | $libdir/pltcl |
pltclu | f | f | pltclu_call_handler | | | $libdir/pltcl |
plperl | t | t | plperl_call_handler | plperl_inline_handler | plperl_validator | $libdir/plperl |
plperlu | f | f | plperlu_call_handler | plperlu_inline_handler | plperlu_validator | $libdir/plperl |
plpythonu | f | f | plpython_call_handler | plpython_inline_handler | plpython_validator | $libdir/plpython2 |
plpython2u | f | f | plpython2_call_handler | plpython2_inline_handler | plpython2_validator | $libdir/plpython2 |
plpython3u | f | f | plpython3_call_handler | plpython3_inline_handler | plpython3_validator | $libdir/plpython3 |
(8 rows)
For the plpython extensions, we see False in the tmpltrusted column and False in the tmpdbacreate column, while the three trusted extensions "plpgsql", "pltcl" and "plperl" are True in the same columns.
Credits go to:
- Using psql how do I list extensions installed in a database?
- PostgreSQL: how to install plpythonu extension
- Run python script from PostgreSQL function
- Can't “install” plpython3u - postgresql, commented Jun 9 '20
Step 5
Now run a general test query like this:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION return_version()
RETURNS VARCHAR
AS $$
import sys
return sys.version
$$ LANGUAGE plpython3u;
If this worked, you would be able to run the SQL query SELECT return_version() and get
Output:
CREATE FUNCTION
Test:
postgres=# SELECT return_version();
return_version
------------------------------------------
3.8.10 (default, Jun 2 2021, 10:49:15) +
[GCC 9.4.0]
(1 row)
Of course, we cannot see this, elsewise the question would be solved. It would be 3.7.9 in this case, I used the Linux installation where plpython3u works, see the Linux hint in the answer.
Side note: a more complicated test with loaded modules
Normally, you can ignore this second test and stop at the return_version() function test.
Of course, if the creating the function return_version() fails, the following will also fail. This second test is just to check whether you can also load modules as soon as plpython3u can be used. You will need to install the needed Python packages which must be compatible with Python 3.7, in this case. It seems that one has to use pip and not conda since Python was meant to be downloaded from the official website. To avoid dependency conflicts, it might be good to use Poetry as a package manager (similar to conda, just for pip).
When executing this PostgreSQL query of Machine Learning in PostgreSQL Part 1: Kmeans clustering, using the language plpython3u (the needed packages "pandas" and "sklearn" are installed in the base environment of Python3.7, that is, no virtual environment is used to avoid the unsolved Can python venv be used with plpython3u for postgresql?, which is absolutely not what I expected from a standard setter like PostgreSQL):
CREATE OR replace FUNCTION kmeans(input_table text, columns text[], clus_num int) RETURNS bytea AS
$$
from pandas import DataFrame
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from pickle import dumps
all_columns = ",".join(columns)
if all_columns == "":
all_columns = "*"
rv = plpy.execute('SELECT %s FROM %s;' % (all_columns, plpy.quote_ident(input_table)))
frame = []
for i in rv:
frame.append(i)
df = DataFrame(frame).astype('float')
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=clus_num, random_state=0).fit(df._get_numeric_data())
return dumps(kmeans)
$$ LANGUAGE plpython3u;
End of the sidenote
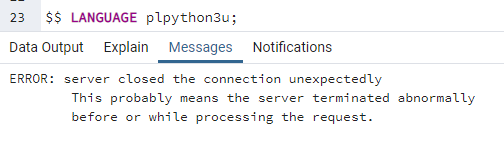
Any test query using LANGUAGE plpython3u will cause the error:
ERROR: server closed the connection unexpectedly
This probably means the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request.
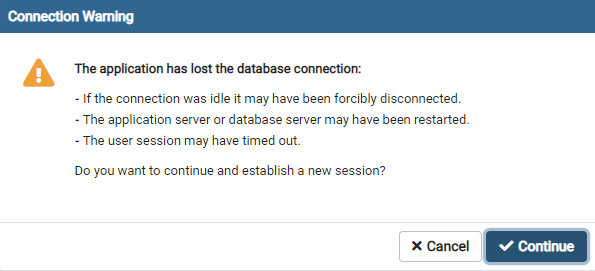
and when I run another query after this, it runs, but before clicking "Continue", I get:
The application has lost the database connection.
- If the connection was idle, it may have been forcibly disconnected.
- The application server or database server may have been restarted.
- The user session may have timed out.
Do you want to continue and establish a new session?
This might be solved by the thread PosgreSQL 11 lost connection when i'm trying to create function with plpython3u [WIN10, pgAdmin4 3.5]. Such an answer shows that the sub-version of v3.7.9 or v3.7.10 or another could indeed matter! Do I need to install version 3.7.10 from source just to have the most recent version?
I do not want to take the effort of installing Python 3.7.10 from source just to check this out. Who says that changing from v3.6.5 to v3.6.7 has really solved it in the link above, and that it was not rather something happening just because of a new install?
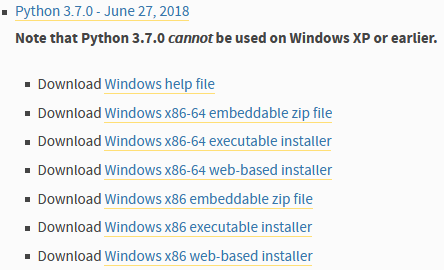
I could also try out v3.7.0.
Python 3.7.0 - June 27, 2018
Note that Python 3.7.0 cannot be used on Windows XP or earlier.
Download Windows help file Download Windows x86-64 embeddable zip file Download Windows x86-64 executable installer Download Windows x86-64 web-based installer Download Windows x86 embeddable zip file Download Windows x86 executable installer Download Windows x86 web-based installer
But since version v3.6.7 once seems to have worked, I do not see a reason why I should invest into this.
Credits go to:
- PosgreSQL 11 lost connection when i'm trying to create function with plpython3u [WIN10, pgAdmin4 3.5], answered Nov 25 '18
- Can't “install” plpython3u - postgresql --> comments, commented Jun 9 '20
Related:
Windows installation with EDB and Stack Builder
EDB and Stack Builder is the installation method that is recommended by the PostgreSQL website. I found this at Cannot install plpython for postgres 12 (a thread which just deals with not being able to create the extension at all and therefore cannot help out). I installed PostgreSQL 10 since plpython3u works with that in the timescaleDB Linux container (see "Docker" below) and my hope was that this lower PostgreSQL version would solve it. But with this official installation method, using EDB and then the Stack Builder for the additional "pl/python language pack", I still get the same error.
Question
Which sub-version of Python 3.7 (v3.7.10, v3.7.0, or another; perhaps my v3.7.9 is also already right since plpython extension could be created with that) is surely working together with PostgreSQL13, and how would this have to be found out if not just by testing around? And if choosing the right Python sub-version is not the issue here (which is more likely), how else can I fix the Step 5 errors that pop up from using the LANGUAGE plpython3u:
ERROR: server closed the connection unexpectedly
This probably means the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request.
(which is a question at psql: server closed the connection unexepectedly but is not focused on this Python extension problem)
and
The application has lost the database connection.
(which is a question at PosgreSQL 11 lost connection when i'm trying to create function with plpython3u [WIN10, pgAdmin4 3.5] but would mean installing v3.7.10 from source only to have the most recent sub-version, and I try to find out the right sub-version or another trick to get it run before doing so)