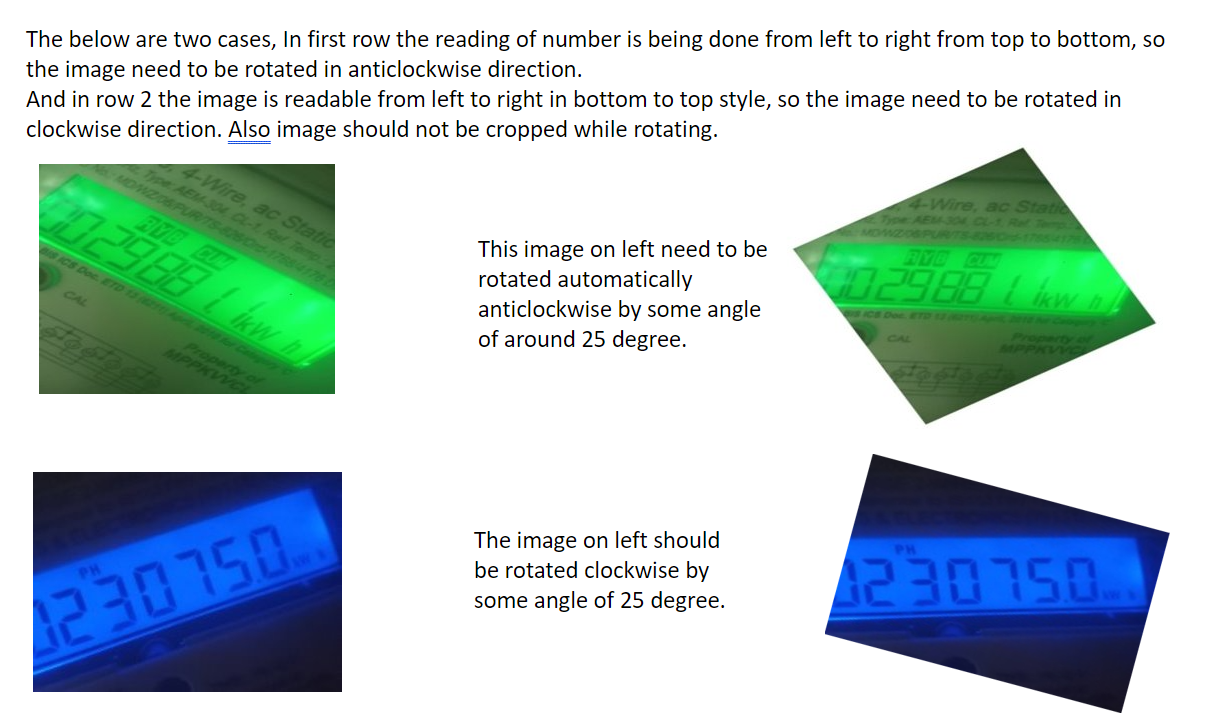
I have cropped images of electronic meter reading. Those readings are taken in random style. I need the orientation of the object(not the image) in the image to be aligned.
- The detection of contours is not working. As there are lots of contours are formed in the image and in order to calculate the angle I need to select the right contour. Some times contour is not formed.
2.I want set of rotated images as shown in figure above. I tried some code of rotating image from the OpenCV. But due to two type of use case ( as we don't know from code that the reading style may be any of the two) The images are turned out as below.

- Using the code below I am able to find the angle of rotation but for any one case. I need it to be done automatically for both type of cases. Also see the data set I have attached for other type of examples.
import cv2
import numpy as np
debug = True
# Display image
def display(img, frameName="OpenCV Image"):
if not debug:
return
h, w = img.shape[0:2]
neww = 800
newh = int(neww*(h/w))
img = cv2.resize(img, (neww, newh))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
# cv2.imshow(frameName, img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
#rotate the image with given theta value
def rotate(img, theta):
rows, cols = img.shape[0], img.shape[1]
image_center = (cols/2, rows/2)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(image_center,theta,1)
abs_cos = abs(M[0,0])
abs_sin = abs(M[0,1])
bound_w = int(rows * abs_sin + cols * abs_cos)
bound_h = int(rows * abs_cos + cols * abs_sin)
M[0, 2] += bound_w/2 - image_center[0]
M[1, 2] += bound_h/2 - image_center[1]
# rotate orignal image to show transformation
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(bound_w,bound_h),borderValue=(255,255,255))
return rotated
def slope(x1, y1, x2, y2):
if x1 == x2:
return 0
slope = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
theta = np.rad2deg(np.arctan(slope))
return theta
def main(filePath):
img = cv2.imread(filePath)
(hi, wi) = img.shape[:2]
textImg = img.copy()
small = cv2.cvtColor(textImg, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# find the gradient map
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (3, 3))
grad = cv2.morphologyEx(small, cv2.MORPH_GRADIENT, kernel)
display(grad)
# Binarize the gradient image
_, bw = cv2.threshold(grad, 0.0, 255.0, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
display(bw)
# connect horizontally oriented regions
# kernal value (9,1) can be changed to improved the text detection
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9, 1))
connected = cv2.morphologyEx(bw, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
display(connected)
# using RETR_EXTERNAL instead of RETR_CCOMP
# _ , contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(connected.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(connected.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) #opencv >= 4.0
mask = np.zeros(bw.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
display(mask)
# cumulative theta value
cummTheta = 0
# number of detected text regions
ct = 0
flag=False
for idx in range(len(contours)):
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[idx])
mask[y:y+h, x:x+w] = 0
# fill the contour
cv2.drawContours(mask, contours, idx, (255, 255, 255), -1)
display(mask)
# ratio of non-zero pixels in the filled region
r = float(cv2.countNonZero(mask[y:y+h, x:x+w])) / (w * h)
# assume at least 45% of the area is filled if it contains text
# if r > 0.39 and w > 8 and h > 8:
if (h/hi)>0.4 and (w/wi)>0.4:
flag=True
print(r,w,h)
# cv2.rectangle(textImg, (x1, y), (x+w-1, y+h-1), (0, 255, 0), 2)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[idx])
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
cv2.drawContours(textImg,[box],0,(0,0,255),2)
center = (int(rect[0][0]),int(rect[0][1]))
width = int(rect[1][0])
height = int(rect[1][1])
angle = int(rect[2])
print(angle)
print(width,height)
if width < height:
angle = 90+angle
print(angle,'final')
# we can filter theta as outlier based on other theta values
# this will help in excluding the rare text region with different orientation from ususla value
theta = slope(box[0][0], box[0][1], box[1][0], box[1][1])
cummTheta += theta
ct +=1
# print("Theta", theta)
# find the average of all cumulative theta value
# orientation = cummTheta/ct
print("Image orientation in degress: ", angle)
finalImage = rotate(img, angle)
display(textImg, "Detectd Text minimum bounding box")
display(finalImage)
out_path='cropped_corrected/rotated/'+filePath.split('\\')[-1]
print(out_path)
cv2.imwrite(out_path,finalImage)
print('image svaed here in rotated')
break
if not flag:
out_path='cropped_corrected/not_rotated/'+filePath.split('\\')[-1]
print(out_path)
cv2.imwrite(out_path,img)
print('image svaed here without rotated')
if __name__ == "__main__":
filePath = 'cropped/N3963001963.jpg'
main(filePath)
I am attaching some sample images that need to be rotated and the object inside the image needs to be aligned:






