TLDR
Force pending UI changes onto the render server with CATransaction.flush() or split the work across multiple frames using CADisplayLink (example code below).
Summary
Is there perhaps a way, in UIKit, to get a callback when it has drawn-up all the views you've stacked up?
No
iOS acts like a game rendering changes (no matter how many you make) at most once per frame. The only way to guarantee a peice of code runs after your changes have been rendered on screen is to wait for the next frame.
Is there another solution?
Yes, iOS may only render changes once per frame but your app isn't what does that rendering. The window server process is.
Your app does its layout and rendering and then commit its changes to its layerTree to the render server. It will do this automatically at the end of the runloop, or you can force outstanding transactions to be sent to the render server be calling CATransaction.flush().
However, blocking the main thread is bad in general (not just because it blocks UI updates). So if you can you should avoid it.
Possible Solutions
This is the part you are interested in.
1: Do as much as possible on a background queue as you can and improve performance.
Seriously the iPhone 7 is the 3rd most powerful computer (not phone) in my house, only beaten by my gaming PC and Macbook Pro. It is faster than every other computer in my house. It shouldn't take a 3 second pause to render your apps UI.
2: Flush pending CATransactions
EDIT: As pointed out by rob mayoff you can force CoreAnimation to send the pending changes to the render server by calling CATransaction.flush()
addItems1()
CATransaction.flush()
addItems2()
CATransaction.flush()
addItems3()
This won't actually render the changes right there but sends the pending UI updates to the window server, ensuring they are included in the next screen update.
This will work, but comes with these warning in Apples documentation for it.
However, you should attempt to avoid calling flush explicitly. By allowing flush to execute during the runloop...
...and transactions and animations that work from transaction to transaction will continue to function.
However the CATransaction header file includes this quote, which seems to imply that, even if they don't like it, this is officially supported usage.
In some circumstances (i.e. no run-loop, or the run-loop is blocked) it may be necessary to use explicit transactions to get timely render tree updates.
Apple's Documentation - "Better documentation for +[CATransaction flush]".
3: dispatch_after()
Just delay the code until the next runloop. dispatch_async(main_queue) won't work, but you can use dispatch_after() with no delay.
addItems1()
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.0) {
addItems2()
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.0) {
addItems3()
}
}
You mention in your answer this doesn't work for you anymore. However, it works fine in the test Swift Playground and example iOS app I've included with this answer.
4: Use CADisplayLink
CADisplayLink gets called once per frame and allows you to ensure only one operation runs per frame, guaranteeing the screen will be able to refresh between operations.
DisplayQueue.sharedInstance.addItem {
addItems1()
}
DisplayQueue.sharedInstance.addItem {
addItems2()
}
DisplayQueue.sharedInstance.addItem {
addItems3()
}
Needs this helper class to work (or similar).
// A queue of item that you want to run one per frame (to allow the display to update in between)
class DisplayQueue {
static let sharedInstance = DisplayQueue()
init() {
displayLink = CADisplayLink(target: self, selector: #selector(displayLinkTick))
displayLink.add(to: RunLoop.current, forMode: RunLoopMode.commonModes)
}
private var displayLink:CADisplayLink!
@objc func displayLinkTick(){
if let _ = itemQueue.first {
itemQueue.remove(at: 0)() // Remove it from the queue and run it
// Stop the display link if it's not needed
displayLink.isPaused = (itemQueue.count == 0)
}
}
private var itemQueue:[()->()] = []
func addItem(block:@escaping ()->()) {
displayLink.isPaused = false // It's needed again
itemQueue.append(block) // Add the closure to the queue
}
}
5: Call the runloop directly.
I don't like it because of the possibility for an infinite loop. But, I admit that is unlikely. I'm also not sure if this is officially supported or an Apple engineer is going to read this code and look horrified.
// Runloop (seems to work ok, might lead to infitie recursion if used too frequently in the codebase)
addItems1()
RunLoop.current.run(mode: .default, before: Date())
addItems2()
RunLoop.current.run(mode: .default, before: Date())
addItems3()
This should work, unless (while responding to the runloop events) you do something else to block that runloop call from completing as the CATransaction's are sent to the window server at the end of the runloop.
Example Code
Demonstration Xcode Project & Xcode Playground (Xcode 8.2, Swift 3)
Which option should I use?
I like the solutions DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.0) and CADisplayLink the best. However, DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter doesn't guarantee it will run on the next runloop tick so you might not want to trust it?
CATransaction.flush() will force you UI changes to be pushed to the render server and this usage seems to fit Apple's comments for the class, but comes with some warnings attached.
In some circumstances (i.e. no run-loop, or the run-loop is blocked) it may be necessary to use explicit transactions to get timely render tree updates.
Detailed Explanation
The rest of this answer is is background on what's going on inside UIKit and explains why the original answers attempts to use view.setNeedsDisplay() and view.layoutIfNeeded() didn't do anything.
Overview of UIKit Layout & Rendering
CADisplayLink is totally unrelated to UIKit and the runloop.
Not quite. iOS's UI is GPU rendered like a 3D game. And tries to do as little as possible. So a lot of things, like layout and rendering don't happen when something changes but when it is needed. That is why we call ‘setNeedsLayout’ not layout subviews. Each frame the layout might change multiple times. However, iOS will try to only call layoutSubviews once per frame, instead of the 10 times setNeedsLayout might have been called.
However, quite a lot happens on the CPU (layout, -drawRect:, etc...) so how does it all fit together.
Note this is all simplified and skips lots of things like CALayer actually being the real view object that shows on screen not UIView, etc...
Each UIView can be thought of as a bitmap, an image/GPU texture. When the screen is rendered the GPU composites the view hierarchy into the resulting frame we see. It composes the views, rendering the subviews textures over the top of previous views into the finished render that we see on screen (similarly to a game).
This is what has allowed iOS to have such a smooth and easily animated interface. To animate a view across the screen it doesn't have to rerender anything. On the next frame that views texture is just composited in a slightly different place on the screen than before. Neither it, nor the view it was on top of need to have their contents rerendered.
In the past a common performance tip used to be to cut down on the number of views in the view hierarchy by rendering table view cells entirely in drawRect:. This tip was to make the GPU composting step faster on the early iOS devices. However, GPU's are so fast on modern iOS devices now this is no longer worried about very much.
LayoutSubviews and DrawRect
-setNeedsLayout invalidates the views current layout and marks it as needing layout.
-layoutIfNeeded will relayout the view if it doesn't have a valid layout
-setNeedsDisplay will mark the views as needing to be redraw. We said earlier that each view is rendered into a texture/image of the view which can be moved around and manipulated by the GPU without needing to be redrawn. This will trigger it to redraw. The drawing is done by calling -drawRect: on the CPU and so is slower than being able to rely on the GPU, which it can do most frames.
And important thing to notice is what these methods do not do. The layout methods do not do anything visual. Though if the views contentMode is set to redraw, changing the views frame might invalidate the views render (trigger -setNeedsDisplay).
You can try the following all day. It does not seem to work:
view.addItemsA()
view.setNeedsDisplay()
view.layoutIfNeeded()
view.addItemsB()
view.setNeedsDisplay()
view.layoutIfNeeded()
view.addItemsC()
view.setNeedsDisplay()
view.layoutIfNeeded()
From what we've learnt the answer should be obvious why this doesn't work now.
view.layoutIfNeeded() does nothing but recalculate the frames of its subviews.
view.setNeedsDisplay() just marks the view as needing redrawing next time UIKit sweeps through the view hierarchy updating view textures for sending to the GPU. However, is doesn't effect the subviews you tried to add.
In your example view.addItemsA() adds 100 sub views. Those are separate unrelated layers/textures on the GPU until the GPU composites them together into the next framebuffer. The only exception to this is if the CALayer has shouldRasterize set to true. In which case it creates a separate texture for the view and it's sub views and renders (in think on the GPU) the view and it's subviews into a single texture, effectively caching the compositing it would have to do each frame. This has the performance advantage of not needing to compose all its subviews every frame. However, if the view or its subviews change frequently (like during an animation) it will be a performance penalty, as it will invalidate the cached texture frequently requiring it to be redrawn (similar to frequently calling -setNeedsDisplay).
Now, any game engineer would just do this ...
view.addItemsA()
RunLoop.current.run(mode: .default, before: Date())
view.addItemsB()
RunLoop.current.run(mode: .default, before: Date())
view.addItemsC()
Now indeed, that seems to work.
But why does it work?
Now -setNeedsLayout and -setNeedsDisplay don't trigger a relayout or redraw but instead just mark the view as needing it. As UIKit comes through preparing to render the next frame it triggers views with invalid textures or layouts to redraw or relayout. After everything is ready it sends tells the GPU to composite and display the new frame.
So the main run loop in UIKit probably looks something like this.
-(void)runloop
{
//... do touch handling and other events, etc...
self.windows.recursivelyCheckLayout() // effectively call layoutIfNeeded on everything
self.windows.recursivelyDisplay() // call -drawRect: on things that need it
GPU.recompositeFrame() // render all the layers into the frame buffer for this frame and displays it on screen
}
So back to your original code.
view.addItemsA() // Takes 1 second
view.addItemsB() // Takes 1 second
view.addItemsC() // Takes 1 second
So why do all 3 changes show up at once after 3 seconds instead of one at a time 1 second apart?
Well if this bit of code is running as a result of a button press, or similar, it is executing synchronously blocking the main thread (the thread UIKit requires UI changes be made on) and so blocks the run loop on line 1, the even processing part. In effect, you are making that first line of the runloop method take 3 seconds to return.
However, we have determined that the layout won't update until line 3, the individual views won't be rendered until line 4 and no changes will actually appear on screen until the last line of the runloop method, line 5.
The reason that pumping the runloop manually works is because you are basically inserting a call to the runloop() method. Your method is running as a result of being called from within the runloop function
-runloop()
- events, touch handling, etc...
- addLotsOfViewsPressed():
-addItems1() // blocks for 1 second
-runloop()
| - events and touch handling
| - layout invalid views
| - redraw invalid views
| - tell GPU to composite and display a new frame
-addItem2() // blocks for 1 second
-runloop()
| - events // hopefully nothing massive like addLotsOfViewsPressed()
| - layout
| - drawing
| - GPU render new frame
-addItems3() // blocks for 1 second
- relayout invalid views
- redraw invalid views
- GPU render new frame
This will work, as long as it's not used very often because this is using recursion. If it's used frequently every call to the -runloop could trigger another one leading to runaway recursion.
THE END
Below this point is just clarification.
Extra information about what is going on here
CADisplayLink and NSRunLoop
If I'm not mistaken KH it appears that fundamentally you believe "the run loop" (ie: this one: RunLoop.current) is CADisplayLink.
The runloop and CADisplayLink aren't the same thing. But CADisplayLink gets attached to a runloop in order to work.
I slightly misspoke earlier (in the chat) when I said NSRunLoop calls CADisplayLink every tick, It doesn’t. To my understanding NSRunLoop is basically a while(1) loop that’s job is to keep the thread alive, process events, etc... To avoid slipping up I’m going to try to quote extensively from Apple’s own documentation for the next bits.
A run loop is very much like its name sounds. It is a loop your thread enters and uses to run event handlers in response to incoming events. Your code provides the control statements used to implement the actual loop portion of the run loop—in other words, your code provides the while or for loop that drives the run loop. Within your loop, you use a run loop object to "run” the event-processing code that receives events and calls the installed handlers.
Anatomy of a Run Loop - Threading Programming Guide - developer.apple.com
CADisplayLink uses NSRunLoop and needs to be added to one but is different. To quote the CADisplayLink header file:
“Unless paused, it will fire every vsync until removed.”
From: func add(to runloop: RunLoop, forMode mode: RunLoopMode)
And from the preferredFramesPerSecond properties documentation.
Default value is zero, which means the display link will fire at the native cadence of the display hardware.
...
For example, if the maximum refresh rate of the screen is 60 frames per second, that is also the highest frame rate the display link sets as the actual frame rate.
So if you want to do anything timed to screen refreshes CADisplayLink (with default settings) is what you want to use.
Introducing the Render Server
If you happen to block a thread, that has nothing to do with how UIKit works.
Not quite. The reason we are required to only touch UIView’s from the main thread is because UIKit is not thread safe and it runs on the main thread. If you block the main thread you have blocked the thread UIKit runs on.
Whether UIKit works "like you say" {... "send a message to stop video frames. do all our work! send another message to start video again!"}
That’s not what I’m saying.
Or whether it works "like I say" {... ie, like normal programming "do as much as you can until the frames about to end - oh no it's ending! - wait until the next frame! do more..."}
That’s not how UIKit works and I don’t see how it ever could without fundamentally changing its architecture. How is it meant to watch for the frame ending?
As discussed in the “Overview of UIKit Layout & Rendering” section of my answer UIKit tries to do no work upfront. -setNeedsLayout and -setNeedsDisplay can be called as many times per frame as you want. They only invalidate the layout and view render, if it has already been invalidated that frame then the second call does nothing. This means that if 10 changes all invalidate the layout of a view UIKit still only needs to pay the cost of recalculating the layout once (unless you used -layoutIfNeeded in between -setNeedsLayout calls).
The same is true of -setNeedsDisplay. Though as previously discussed neither of these relates to what appears on screen. layoutIfNeeded updates the views frame and displayIfNeeded updates the views render texture, but that is not related to what appears on screen. Imagine each UIView has a UIImage variable that represents it’s backing store (it’s actually in CALayer, or below, and isn’t a UIImage. But this is an illustration). Redrawing that view simply updates the UIImage. But the UIImage is still just data, not a graphic on screen until it is drawn onto the screen by something.
So how does a UIView get drawn on screen?
Earlier I wrote pseudo code UIKit’s main render runloop. So far in my answers I have been ignoring a significant part of UIKit, not all of it runs inside your process. A surprising amount of UIKit stuff related to displaying things actually happens in the render server process not your apps process. The render server/window server was SpringBoard (the home screen UI) until iOS 6 (since then then BackBoard and FrontBoard have absorbed a lot of SpringBoards more core OS related features, leaving it to focus more on being the main operating system UI. Home screen/lock screen/notification center/control center/app switcher/etc...).
The pseudo code for UIKit’s main render runloop is likely closer to this. And again, remember UIKit’s architecture is designed to do as little work as possible so it will only do this stuff once per frame (unlike network calls or whatever else the main runloop might also manage).
-(void)runloop
{
//... do touch handling and other events, etc...
UIWindow.allWindows.layoutIfNeeded() // effectively call layoutIfNeeded on everything
UIWindow.allWindows.recursivelyDisplay() // call -drawRect: on things that need to be rerendered
// Sends all the changes to the render server process to actually make these changes appear on screen
// CATransaction.flush() which means:
CoreAnimation.commit_layers_animations_to_WindowServer()
}
This makes sense, a single iOS app freezing shouldn’t be able to freeze the entire device. In fact we can demonstrate this on an iPad with 2 apps running side by side. When we cause one to freeze the other is unaffected.
![]()
These are 2 empty app templates I created and pasted the same code into both. Both should the current time in a label in the middle of the screen. When I press freeze it calls sleep(1) and freezes the app. Everything stops. But iOS as a whole is fine. The other app, control center, notification center, etc... are all unaffected by it.
Whether UIKit works "like you say" {... "send a message to stop video frames. do all our work! send another message to start video again!"}
In the app there is no UIKit stop video frames command because your app has no control over the screen at all. The screen will update at 60FPS using whatever frame the window server gives it. The window server will composite a new frame for the display at 60FPS using the last known positions, textures and layer trees your app gave it to work with.
When you freeze the main thread in your app the CoreAnimation.commitLayersAnimationsToWindowServer() line, which runs last (after your expensive add lots of views code), is blocked and doesn’t run. As a result even if there are changes, the window server hasn’t been sent them yet and so just continues to use the last state it was sent for your app.
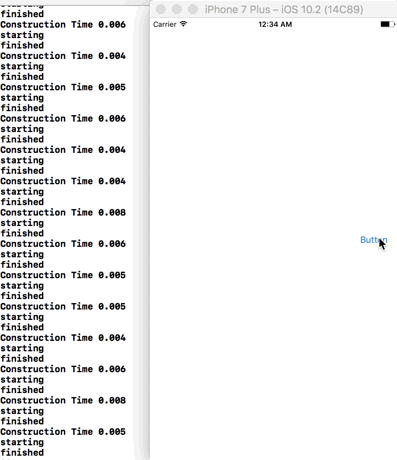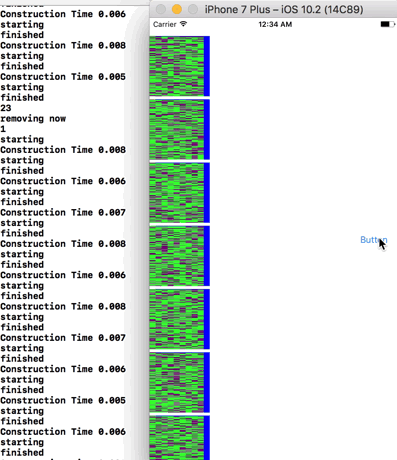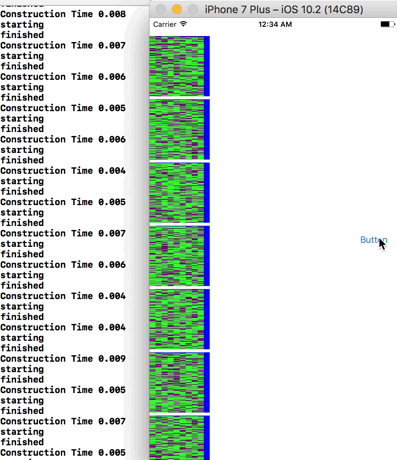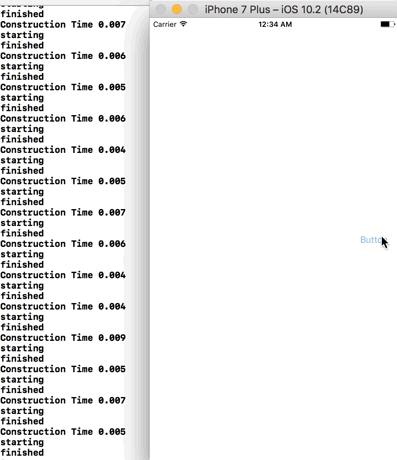
Animations is another part of UIKit that runs out of process, in the window server. If, before the sleep(1) in that example app, we start a UIView animation first we will see it start, then the label will freeze and stop updating (because sleep() has run). However, even though the apps main thread is frozen the animation will continue regardless.
func freezePressed() {
var newFrame = animationView.frame
newFrame.origin.y = 600
UIView.animate(withDuration: 3, animations: { [weak self] in
self?.animationView.frame = newFrame
})
// Wait for the animation to have a chance to start, then try to freeze it
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.1) {
NSLog("Before freeze");
sleep(2) // block the main thread for 2 seconds
NSLog("After freeze");
}
}
This is the result:
![]()
In fact we can go one better.
If we change the freezePressed() method to this.
func freezePressed() {
var newFrame = animationView.frame
newFrame.origin.y = 600
UIView.animate(withDuration: 4, animations: { [weak self] in
self?.animationView.frame = newFrame
})
// Wait for the animation to have a chance to start, then try to freeze it
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.2) { [weak self] in
// Do a lot of UI changes, these should completely change the view, cancel its animation and move it somewhere else
self?.animationView.backgroundColor = .red
self?.animationView.layer.removeAllAnimations()
newFrame.origin.y = 0
newFrame.origin.x = 200
self?.animationView.frame = newFrame
sleep(2) // block the main thread for 2 seconds, this will prevent any of the above changes from actually taking place
}
}
Now without the sleep(2) call the animation will run for 0.2 seconds then it’ll be canceled and the view will be moved to a different part of the screen a different color. However, the sleep call blocks the main thread for 2 seconds meaning none of these changes are sent to the window server until most of the way through the animation.
![]()
And just to confirm here is the result with the sleep() line commented out.
![]()
This should hopefully explain what’s going on. These changes are like the UIView’s you add in your question. They are queued up to be included in the next update, but because you are blocking the main thread by sending so many in one go you are stopping the message being sent which will get them included in the next frame. The next frame isn’t being blocked, iOS will produce a new frame showing all the updates it has received from SpringBoard, and other iOS app. But because your app is still blocking it’s main thread iOS hasn’t received any updates from your app and so won’t show any change (unless it has changes, like animations, already queued up on the window server).
So to summarise
- UIKit tries to do as little as possible so batches changes to layout and rendering up into one go.
- UIKit runs on the main thread, blocking the main thread prevents UIKit doing anything until that operation has completed.
- UIKit in process can’t touch the display, it sends layers and updates to the window server every frame
- If you block the main thread then the changes are never sent to the window server and so aren’t displayed









layout(very poorly namedlayoutIfNeededin iOS) should, in a sense, do what I ask here, but it doesn't. (the whole, entire point of this question - and the central aspect of realtime threaded UI engineering - is that, of course, "anything can be going on" and you don't know what the hell is going to happen when). there are many QA on here about the details of setNeedsLayout / setNeedsDisplay / layoutIfNeeded for anyone who needs details – Preserve