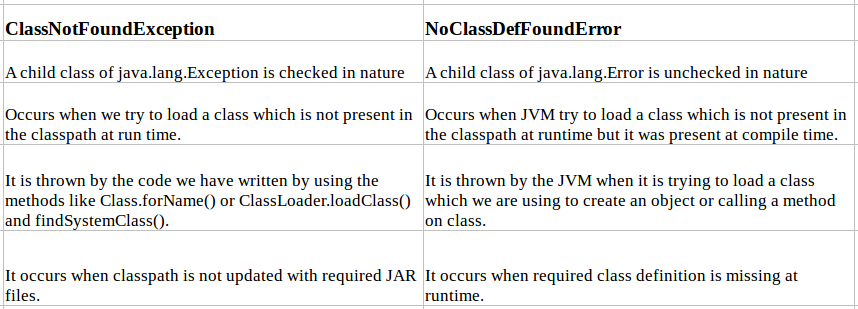
NoClassDefFoundError
Thrown if the Java Virtual Machine or a ClassLoader instance tries to
load in the definition of a class (as part of a normal method call or
as part of creating a new instance using the new expression) and no
definition of the class could be found.
The searched-for class definition existed when the currently executing
class was compiled, but the definition can no longer be found.
ClassNotFoundException
Thrown when an application tries to load in a class through its string
name using: The forName method in class Class. The findSystemClass
method in class ClassLoader . The loadClass method in class
ClassLoader.
You have to understand that the JVM can't realize the definition of the class you deleted can't be found, as the class itself can't be found which automatically throw the ClassNotFoundException.
This exception happen at runtime so it does not matter if it compiled first or not, you deleted the file, therefore it can't be found and throw the exception.
Note that NoClassDefFoundError is not actually an exception, it is an Error derived from LinkageError while ClassNotFoundException derive directly from java.lang.Exception.
To resume, the NoClassDefFoundError globally simply mean that the JVM tried to access at runtime something that according to the compiled code should exists, but does not actually exist (or is not in the classpath).
Example to reproduce ClassNotFoundException
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionExample {
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "main.java.Utils";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class loadedClass = Class.forName(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
System.out.println("Class " + loadedClass + " found successfully!");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
System.err.println("A ClassNotFoundException was caught: " + ex.getMessage());
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Example to reproduce NoClassDefFoundError
Create a simple class Test
public class Test {
public Test() {
System.out.println("A new instance of the Test class was created!");
}
}
And a class NoClassDefFoundErrorExample
public class NoClassDefFoundErrorExample {
private static Test test = new Test();
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("The definition of Test was found!");
}
}
Now create a n executable .jar which execute the main method. You can specify it in the Manifest.txt file inside the .jar
Main-Class: NoClassDefFoundErrorExample
Now run the following commands
javac Test.java
javac NoClassDefFoundErrorExample.java
jar cfm NoClassDefFoundErrorExample.jar Manifest.txt NoClassDefFoundErrorExample.class
java -jar NoClassDefFoundErrorExample.jar
Notice the NoClassDefFoundError
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: TestClass
at NoClassDefFoundErrorExample.(NoClassDefFoundErrorExample.java:2)
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: TestClass
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:372)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:361)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:360)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:424)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:357)
... 1 more

import com.random.blah.B;in class A. – Ignitron