Understanding this error
Pushing the Limits of Windows: USER and GDI Objects – Part 1 by Mark Russinovich:
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/markrussinovich/2010/02/24/pushing-the-limits-of-windows-user-and-gdi-objects-part-1/
Troubleshooting this error
You need to be able to reproduce the problem. Here is one way of recording the steps to do that https://mcmap.net/q/276526/-user-activity-logging-telemetry-and-variables-in-global-exception-handlers.
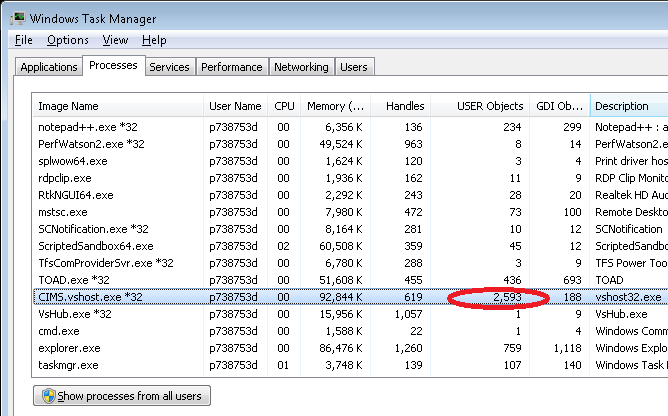
The easiest way to work out what is creating so many handles is to have TaskMgr.exe open. In TaskMgr.exe you need to have the USER Object, GDI Object and Handles columns visible as shown, to do this choose View Menu > Select Columns:
![enter image description here]()
Go through the steps to cause the problem and watch the USER Object count increase to around 10,000 or GDI Objects or Handles reach their limits.
When you see the Object or Handles increase (typically dramatically) you can halt the code execution in Visual Studio by clicking the Pause button.
Then just hold down F10 or F11 to cruise through the code watching when the Object/Handle counts increases dramatically.
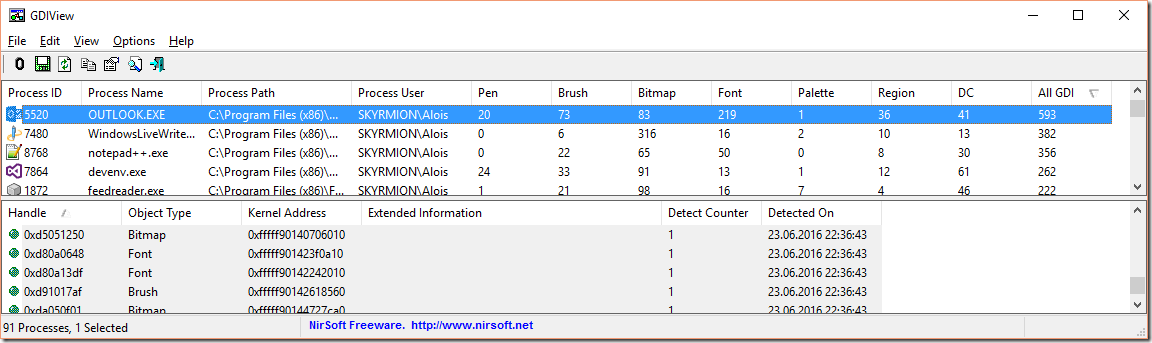
The best tool I have found so far is GDIView from NirSoft, it breaks up the GDI Handle fields:
![enter image description here]()
I tracked it down to this code used when setting DataGridViews "Filter Combobox" Columns Location and Width:
If Me.Controls.ContainsKey(comboName) Then
cbo = CType(Me.Controls(comboName), ComboBox)
With cbo
.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(cumulativeWidth, 0)
.Width = Me.Columns(i).Width
End With
'Explicitly cleaning up fixed the issue of releasing USER objects.
cbo.Dispose()
cbo = Nothing
End If
In my case (above) the solution was explicitly disposing and cleaning up that fixed the issue of releasing USER objects.
This is the stack trace:
at System.Windows.Forms.Control.CreateHandle() at
System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox.CreateHandle() at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.get_Handle() at
System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox.InvalidateEverything() at
System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox.OnResize(EventArgs e) at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.OnSizeChanged(EventArgs e) at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.UpdateBounds(Int32 x, Int32 y, Int32
width, Int32 height, Int32 clientWidth, Int32 clientHeight) at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.UpdateBounds(Int32 x, Int32 y, Int32
width, Int32 height) at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.SetBoundsCore(Int32 x, Int32 y, Int32
width, Int32 height, BoundsSpecified specified) at
System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox.SetBoundsCore(Int32 x, Int32 y, Int32
width, Int32 height, BoundsSpecified specified) at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.SetBounds(Int32 x, Int32 y, Int32 width,
Int32 height, BoundsSpecified specified) at
System.Windows.Forms.Control.set_Width(Int32 value)
Here is the crux of a helpful article by Fabrice that helped me work out the limits:
"Error creating window handle"
When a big Windows Forms application I'm working on for a client is used actively, users often get "Error creating window handle" exceptions.
Aside from the fact that the application consumes too much resources, which is a separate issue altogether that we are already addressing, we had difficulties with determining what resources were getting exhausted as well as what the limits are for these resources.
We first thought about keeping an eye on the Handles counter in the Windows Task Manager. That was because we noticed that some processes tended to consume more of these resources than they normally should. However, this counter is not the good one because it keeps track of resources such as files, sockets, processes and threads. These resources are named Kernel Objects.
The other kinds of resources that we should keep an eye on are the GDI Objects and the User Objects. You can get an overview of the three categories of resources on MSDN.
User Objects
Window creation issues are directly related to User Objects.
We tried to determine what the limit is in terms of User Objects an application can use.
There is a quota of 10,000 user handles per process. This value can be changed in the registry, however this limit was not the real show-stopper in our case.
The other limit is 66,536 user handles per Windows session. This limit is theoretical. In practice, you'll notice that it can't be reached. In our case, we were getting the dreaded "Error creating window handle" exception before the total number of User Objects in the current session reached 11,000.
Desktop Heap
We then discovered which limit was the real culprit: it was the "Desktop Heap".
By default, all the graphical applications of an interactive user session execute in what is named a "desktop". The resources allocated to such a desktop are limited (but configurable).
Note: User Objects are what consumes most of the Desktop Heap's memory space. This includes windows.
For more information about the Desktop Heap, you can refer to the very good articles published on the NTDebugging MSDN blog:
What's the real solution? Be green!
Increasing the Desktop Heap is an effective solution, but that's not the ultimate one. The real solution is to consume less resources (less window handles in our case). I can guess how disappointed you can be with this solution. Is this really all what I can come up with??
Well, there is no big secret here. The only way out is to be lean. Having less complicated UIs is a good start. It's good for resources, it's good for usability too. The next step is to avoid waste, to preserve resources, and to recycle them!
Here is how we're doing this in my client's application:
We use TabControls and we create the content of each tab on the fly, when it becomes visible;
We use expandable/collapsible regions, and again fill them with controls and data only when needed;
We release resources as soon as possible (using the Dispose method). When a region is collapsed, it's possible to clear it's child controls. The same for a tab when it becomes hidden;
We use the MVP design pattern, which helps in making the above possible because it separates data from views;
We use layout engines, the standard FlowLayoutPanel and TableLayoutPanel ones, or custom ones, instead of creating deep hierarchies of nested panels, GroupBoxes and Splitters (an empty splitter itself consumes three window handles...).
The above are just hints at what you can do if you need to build rich Windows Forms screens. There's not doubt that you can find other approaches.
The first thing you should do in my opinion is building your applications around use cases and scenarios. This helps in displaying only what's needed at a given time, and for a given user.
Of course, another solution would be to use a system that doesn't rely on handles... WPF anyone?