We need to integrate Karma test runner into TeamCity and for that I'd like to give sys-engineers small script (powershell or whatever) that would:
pick up desired version number from some config file (I guess I can put it as a comment right in the
karma.conf.js)check if the defined version of karma runner installed in npm's global repo
if it's not, or the installed version is older than desired: pick up and install right version
run it:
karma start .\Scripts-Tests\karma.conf.js --reporters teamcity --single-run
So my real question is: "how can one check in a script, if desired version of package installed?". Should you do the check, or it's safe to just call npm -g install everytime?
I don't want to always check and install the latest available version, because other config values may become incompatible




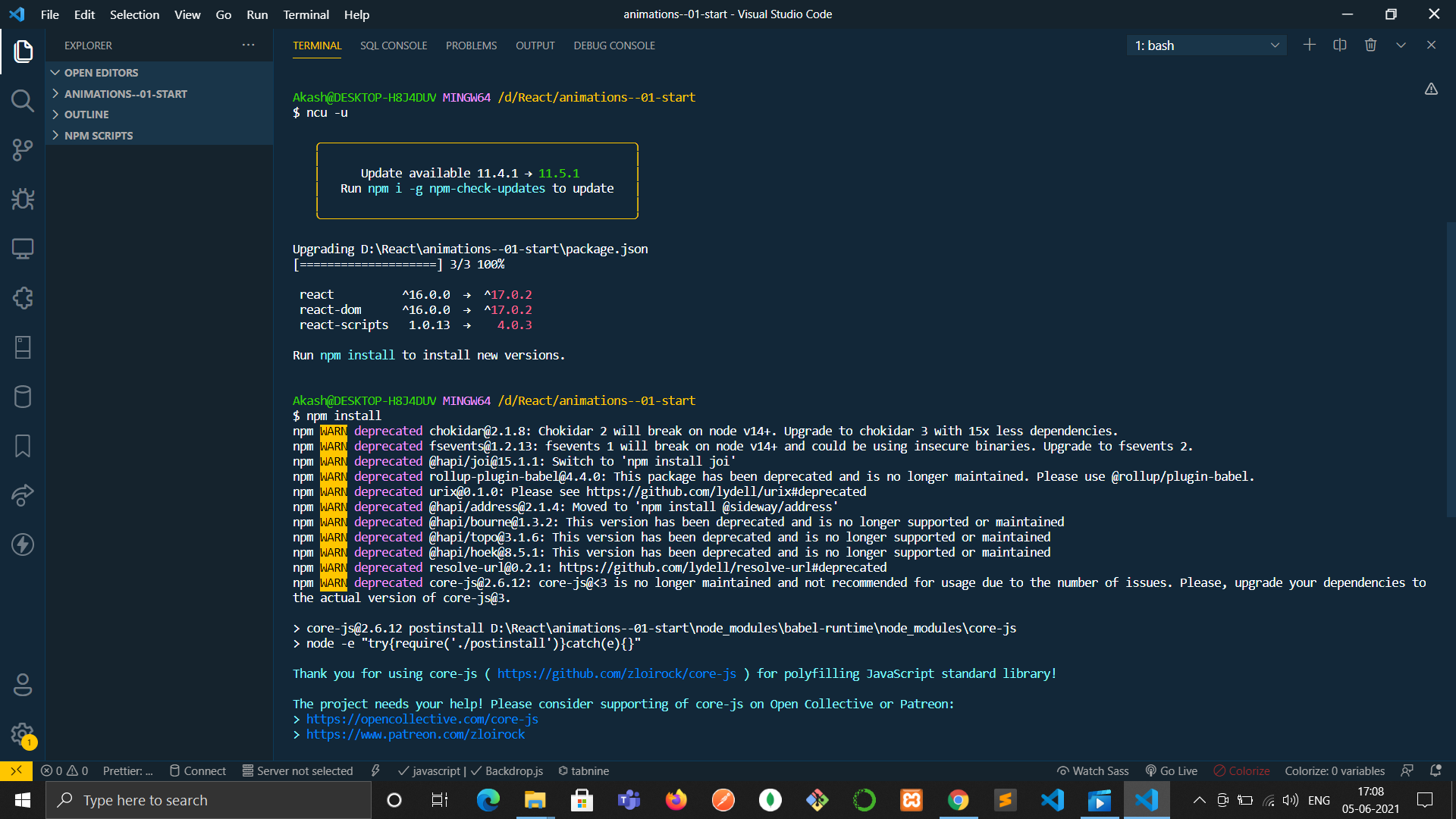
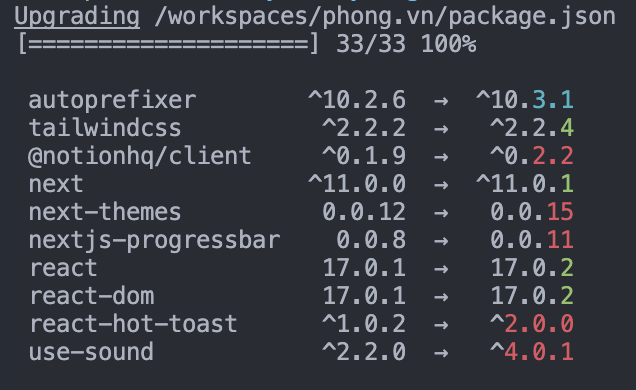
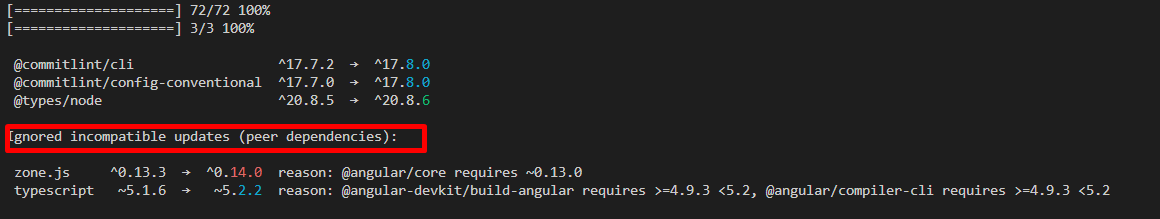
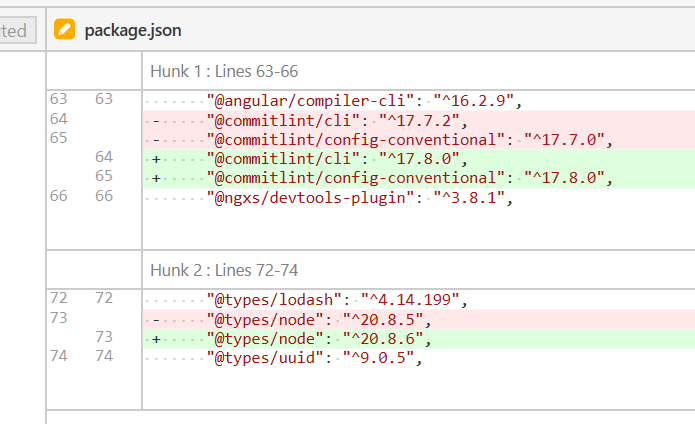
npm upgrade... I don't know what "Team City" is, but for anyone else just using Node.js, you can runnpm upgrade. – Barthol