Deep
In the below investigation as API, I use http://example.com instead of http://myApiUrl/login from your question, because this first one working. I assume that your page is on http://my-site.local:8088.
NOTE: The API and your page have different domains!
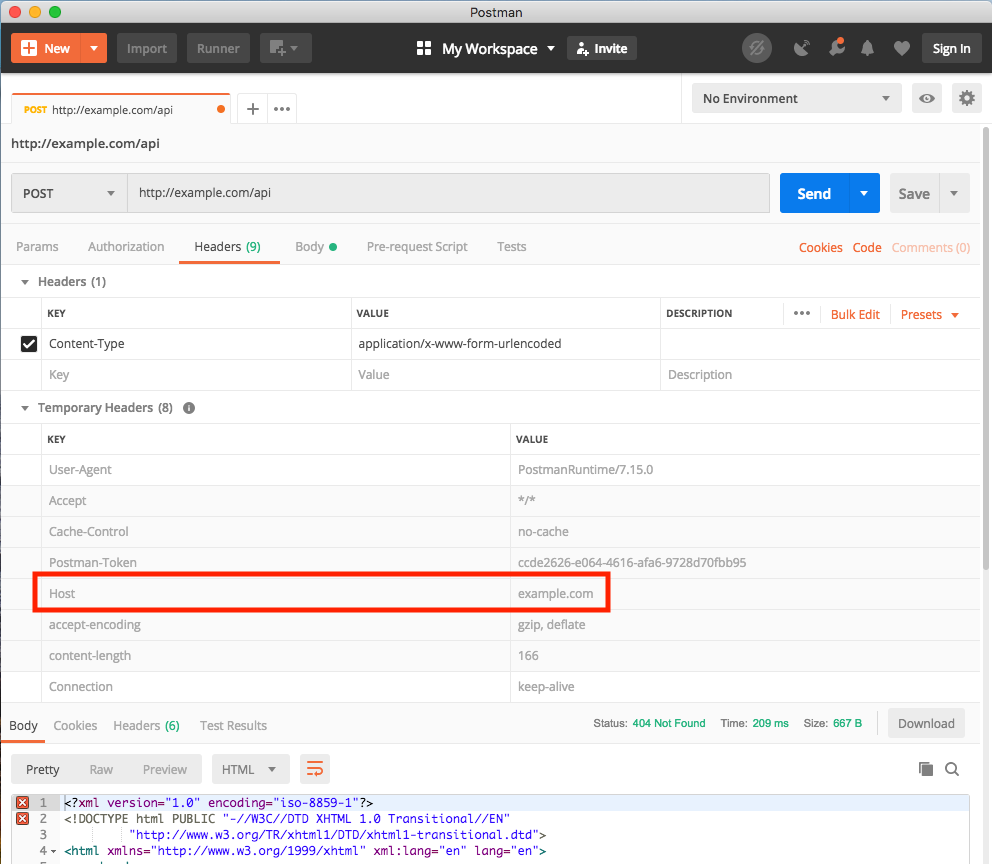
The reason why you see different results is that Postman:
- set header
Host=example.com (your API)
- NOT set header
Origin
- Postman actually not use your website url at all (you only type your API address into Postman) - he only send request to API, so he assume that website has same address as API (browser not assume this)
This is similar to browsers' way of sending requests when the site and API has the same domain (browsers also set the header item Referer=http://my-site.local:8088, however I don't see it in Postman). When Origin header is not set, usually servers allow such requests by default.
![Enter image description here]()
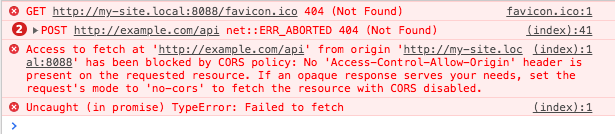
This is the standard way how Postman sends requests. But a browser sends requests differently when your site and API have different domains, and then CORS occurs and the browser automatically:
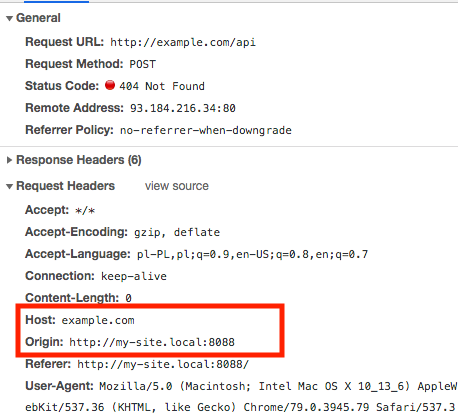
- sets header
Host=example.com (yours as API)
- sets header
Origin=http://my-site.local:8088 (your site)
(The header Referer has the same value as Origin). And now in Chrome's Console & Networks tab you will see:
![Enter image description here]()
![Enter image description here]()
When you have Host != Origin this is CORS, and when the server detects such a request, it usually blocks it by default.
Origin=null is set when you open HTML content from a local directory, and it sends a request. The same situation is when you send a request inside an <iframe>, like in the below snippet (but here the Host header is not set at all) - in general, everywhere the HTML specification says opaque origin, you can translate that to Origin=null. More information about this you can find here.
fetch('http://example.com/api', {method: 'POST'});
Look on chrome-console > network tab
If you do not use a simple CORS request, usually the browser automatically also sends an OPTIONS request before sending the main request - more information is here. The snippet below shows it:
fetch('http://example.com/api', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
});
Look in chrome-console -> network tab to 'api' request.
This is the OPTIONS request (the server does not allow sending a POST request)
You can change the configuration of your server to allow CORS requests.
Here is an example configuration which turns on CORS on nginx (nginx.conf file) - be very careful with setting always/"$http_origin" for nginx and "*" for Apache - this will unblock CORS from any domain (in production instead of stars use your concrete page adres which consume your api)
location ~ ^/index\.php(/|$) {
...
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' "$http_origin" always;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true' always;
if ($request_method = OPTIONS) {
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' "$http_origin"; # DO NOT remove THIS LINES (doubled with outside 'if' above)
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000; # cache preflight value for 20 days
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'My-First-Header,My-Second-Header,Authorization,Content-Type,Accept,Origin';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain charset=UTF-8';
return 204;
}
}
Here is an example configuration which turns on CORS on Apache (.htaccess file)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# | Cross-domain Ajax requests |
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Enable cross-origin Ajax requests.
# http://code.google.com/p/html5security/wiki/CrossOriginRequestSecurity
# http://enable-cors.org/
# <IfModule mod_headers.c>
# Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*"
# </IfModule>
# Header set Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*"
# Header always set Access-Control-Allow-Credentials "true"
Access-Control-Allow-Origin "http://your-page.com:80"
Header always set Access-Control-Allow-Methods "POST, GET, OPTIONS, DELETE, PUT"
Header always set Access-Control-Allow-Headers "My-First-Header,My-Second-Header,Authorization, content-type, csrf-token"