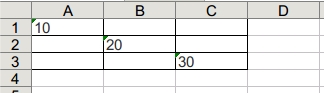
One way of doing that - using one wrapper method to write cell, and helper method to overwrite cell's value and style
import xlsxwriter
class XLSGenerator:
def __init__(self):
self.workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('file.xls')
sheet1 = self.workbook.add_worksheet('sheet1')
sheet2 = self.workbook.add_worksheet('sheet2')
self.sheets = {'sheet1': sheet1, 'sheet2': sheet2}
# dictionary with all written cells
self.written_cells = {sheet: {} for sheet in self.sheets}
def write_cell(self, sheet_name, cell, value, cell_format_dict=None):
"""Writes value and style, and saves it in self.written_cells"""
sheet = self.sheets[sheet_name]
if cell_format_dict:
cell_format = self.workbook.add_format(cell_format_dict)
sheet.write(cell, value, cell_format)
else:
cell_format_dict = None
sheet.write(cell, value)
# save sheet_name, cell and cell_value, and cell_format (dict)
# example ['sheet1']['C12'] = ('some_text', {'font_size': 14, 'bold': True}
self.written_cells[sheet_name][cell] = (value, cell_format_dict)
def apply_style(self, sheet_name, cell, cell_format_dict):
"""Apply style for any cell, with value or not. Overwrites cell with joined
cell_format_dict and existing format and with existing or blank value"""
written_cell_data = self.written_cells[sheet_name].get(cell)
if written_cell_data:
existing_value, existing_cell_format_dict = self.written_cells[sheet_name][cell]
updated_format = dict(existing_cell_format_dict or {}, **cell_format_dict)
else:
existing_value = None
updated_format = cell_format_dict
self.write_cell(sheet_name, cell, existing_value, updated_format)
Usage like this
generator = XLSGenerator()
generator.write_cell('sheet1', 'A1', '10')
generator.write_cell('sheet1', 'B2', '20')
generator.write_cell('sheet1', 'C3', '30')
table_borders = {"left": 1, 'right': 1, 'top': 1, 'bottom': 1}
for cell in ('A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'):
generator.apply_style('sheet1', cell, table_borders)
generator.workbook.close()
![enter image description here]()